This runtime application self-protection (RASP) solution is designed for AWS Lambda functions. Lambda-rasp is added to existing functions as a layer/extension and runs within the targeted function. When the function is initialized, the lambda-rasp layer modifies the container's memory replacing AWS's native runtime API with a new socket value pointing to a local web server. Events passed to the function then go directly to lambda-rasp before reaching the function's application handler. This positions lambda-rasp as an inspection point where many OWASP ModSecurity regex rules have been hardcoded to check incoming events for malicious strings. If a malicious string is detected lambda-rasp will describe the rules violated as standard output and kill further processing before the event would be passed to the function's application.
Consider the Performance section for config setting guidance The following constants are set in
src/main.rsand are used to tune and troubleshoot lambda-rasp deployments based on your needs:
VERBOSE: display debug messagesFAIL_OPEN: run lambda if layer failsBLOCKING_MODE: Kill lambda if rule violatedRULE_MODE: Performance vs security tuning: 0=performance, rule run durations 0-10ms; 1=balanced, rule run duration 11-99ms; 2=paranoid, rule run durations 100+msRULE_CLASS: Set the classes of rules to apply. Limited by RULE_MODE. For example, if RFI RULE_CLASS is selected with RULE_MODE 0, only the RFI rules in mode 0 will be used.
Class counts by mode
| Class | Mode 0 | Mode 1 | Mode 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LFI | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| RFI | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| RCE | 14 | 13 | 5 |
| DESERIAL | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| PP | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| DOS | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| SSRF | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| XSS | 10 | 4 | 1 |
| TEMPLATE | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| SQLI | 22 | 23 | 1 |
| NOSQLI | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| FIXATION | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| UPLOAD | 1 | 0 | 0 |
The following table offers example time costs of running lambda-rasp using various settings.
| Mode | Classes | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | null | ~8ms |
| 0 | RCE | ~148ms |
| 0 | RCE, SQLI | ~310ms |
| 1 | RCE, SQLI | ~1100ms |
| 1 | all | ~1579ms |
| 2 | all | ~2419ms |
- Create function that you want to protect
- Create a layer with x86_64 arch (no arm supported)
- Update deploy-test.sh function variable with the name of the function from step 1.
- Update deploy-test.sh layer variable with the arn of the layer created in step 2.
- Update deploy-test.sh runtimes variable as needed
- Configure AWS credentials (eg profile, environment variables, etc)
- Run deploy-test.sh
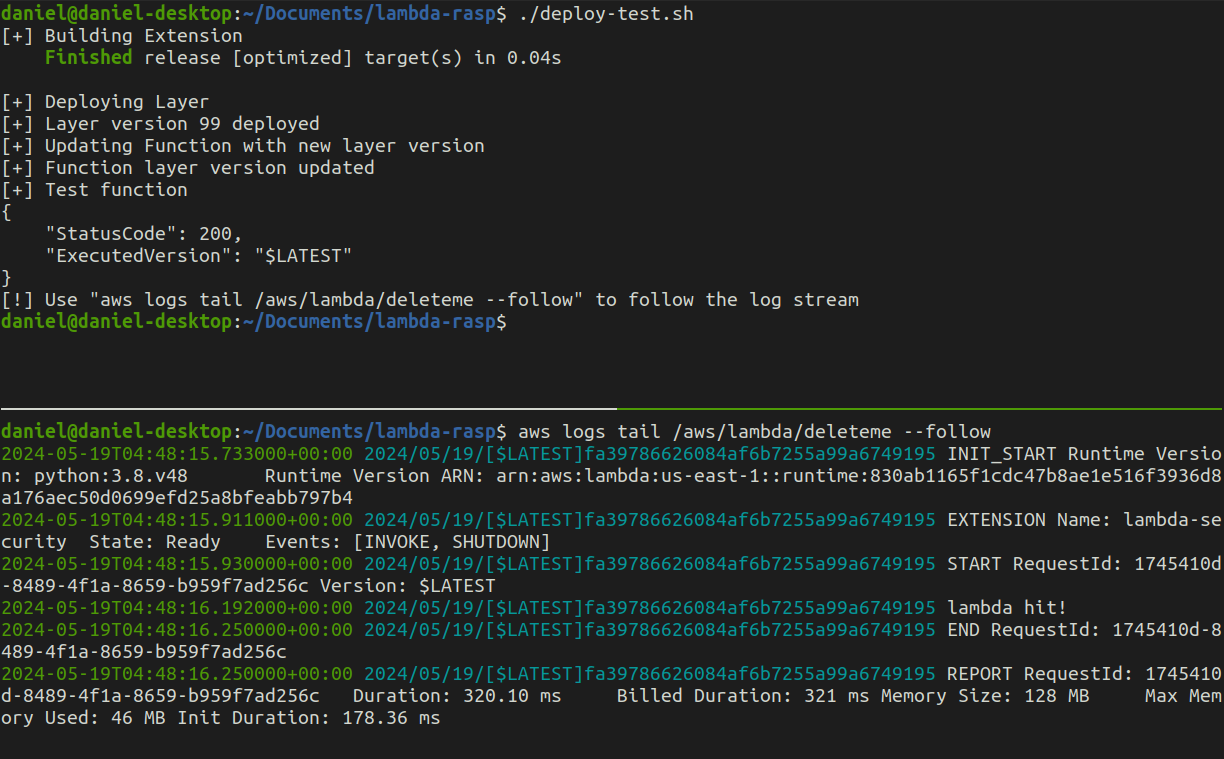
Running benign payload scenario. Deployed function (top pane), function events (bottom pane) displays "lambda hit!" which is from a Python print statement as a placeholder for the function's app.
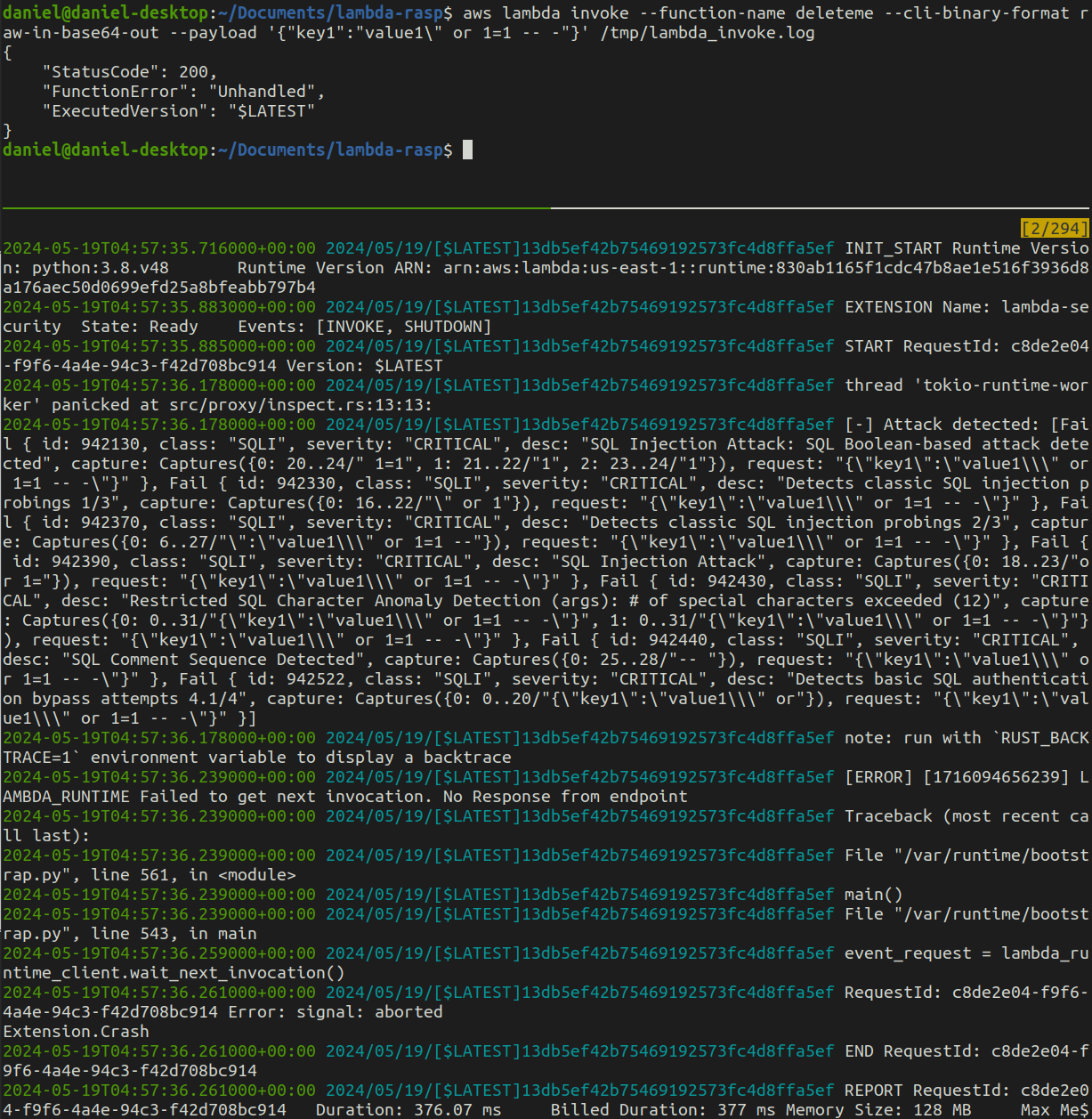
Running malicious payload scenario. Same deployment as above but this invoking the function with a SQL Injection payload.
Using Cargo Lambda to build a lambda extension.
Install Cargo Lambda:
brew tap cargo-lambda/cargo-lambda
brew install cargo-lambda
Setup Test Function:
cargo lambda new --no-interactive test-function
cargo lambda watch -v
Attach Extension:
#from within extension directory
export AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_API=http://[::]:9000/.rt
cargo run
#observe running test function log
Test Running Function+Extension:
cargo lambda invoke --data-ascii '{"command": "hi"}'
Deploy Extension
cargo lambda build --extension --release
cargo lambda deploy --extension --compatible-runtimes python3.8 --layer-arn arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:134672723840:function:deleteme
Run tests as root :(
Run tests with RULE_MODE=2 (paranoid)
cargo check
cargo test -- --nocapture
cargo test rule_xss --
- Update memory.rs proc 1 heap (dec) memory address
printf "%d\n" 0x$(sudo cat /proc/1/maps | grep heap | awk -F"-" '{print $1}') - start python web server on port 9001
Requires lambda function in account Requires aws cli + default profile
- Build extension:
cargo lambda build --extension --release - Run
aws logs tail /aws/lambda/deleteme --follow - Run ./deploy-test.sh
Manual remote test:
aws lambda invoke --function-name deleteme --cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out --payload '{"key1":"value1"}' /tmp/lambda_invoke.log
