Semi-supervised Meta-learning with Disentanglement for Domain-generalised Medical Image Segmentation
This repository contains the official Pytorch implementation of Semi-supervised Meta-learning with Disentanglement for Domain-generalised Medical Image Segmentation(accepted by MICCAI 2021 as Oral).
The repository is created by Xiao Liu, Spyridon Thermos, Alison O'Neil, and Sotirios A. Tsaftaris, as a result of the collaboration between The University of Edinburgh and Canon Medical Systems Europe. You are welcome to visit our group website: vios.s
System Requirements
- Pytorch 1.5.1 or higher with GPU support
- Python 3.7.2 or higher
- SciPy 1.5.2 or higher
- CUDA toolkit 10 or newer
- Nibabel
- Pillow
- Scikit-image
- TensorBoard
- Tqdm
Abstract
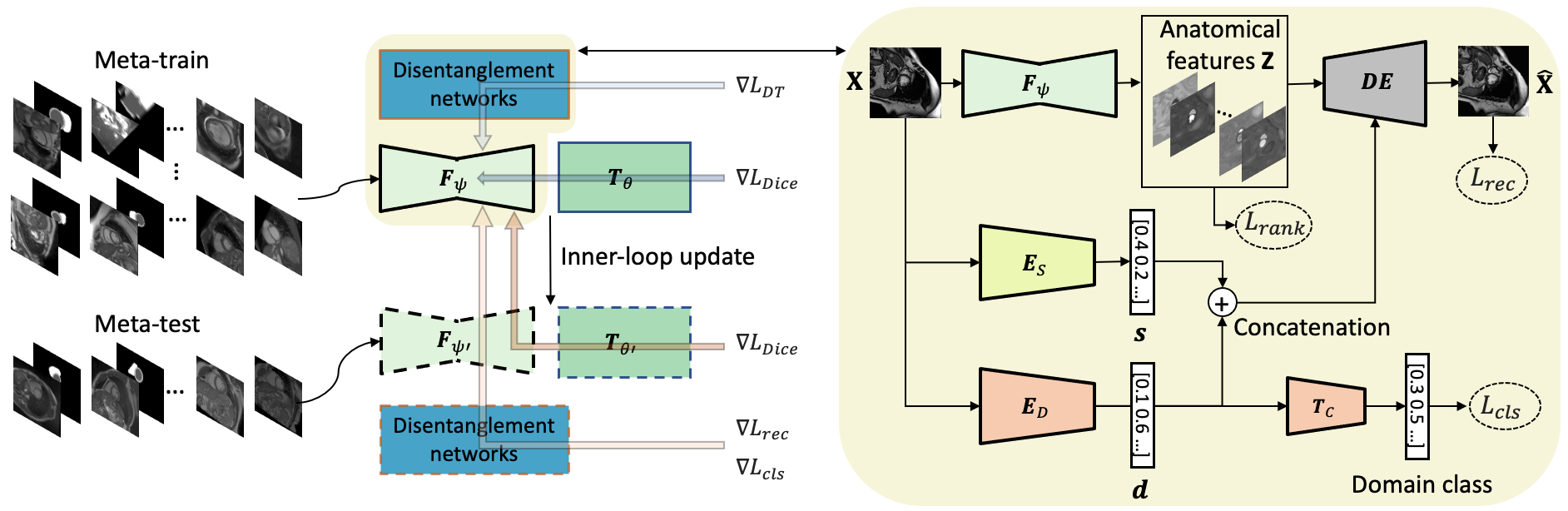
Generalising deep models to new data from new centres (termed here domains) remains a challenge. This is largely attributed to shifts in data statistics (domain shifts) between source and unseen domains. Recently, gradient-based meta-learning approaches where the training data are split into meta-train and meta-test sets to simulate and handle the domain shifts during training have shown improved generalisation performance. However, the current fully supervised meta-learning approaches are not scalable for medical image segmentation, where large effort is required to create pixel-wise annotations. Meanwhile, in a low data regime, the simulated domain shifts may not approximate the true domain shifts well across source and unseen domains. To address this problem, we propose a novel semi-supervised meta-learning framework with disentanglement. We explicitly model the representations related to domain shifts. Disentangling the representations and combining them to reconstruct the input image allows unlabeled data to be used to better approximate the true domain shifts for meta-learning. Hence, the model can achieve better generalisation performance, especially when there is a limited amount of labeled data. Experiments show that the proposed method is robust on different segmentation tasks and achieves state-of-the-art generalisation performance on two public benchmarks.
Training
Note that the hyperparameters in the current version are not tuned. We will release the tuned parameters soon.
Datasets
We used two datasets in the paper: Multi-Centre, Multi-Vendor & Multi-Disease Cardiac Image Segmentation Challenge (M&Ms) datast and Spinal cord grey matter segmentation challenge dataset. The dataloader in this repo is only for M&Ms dataset.
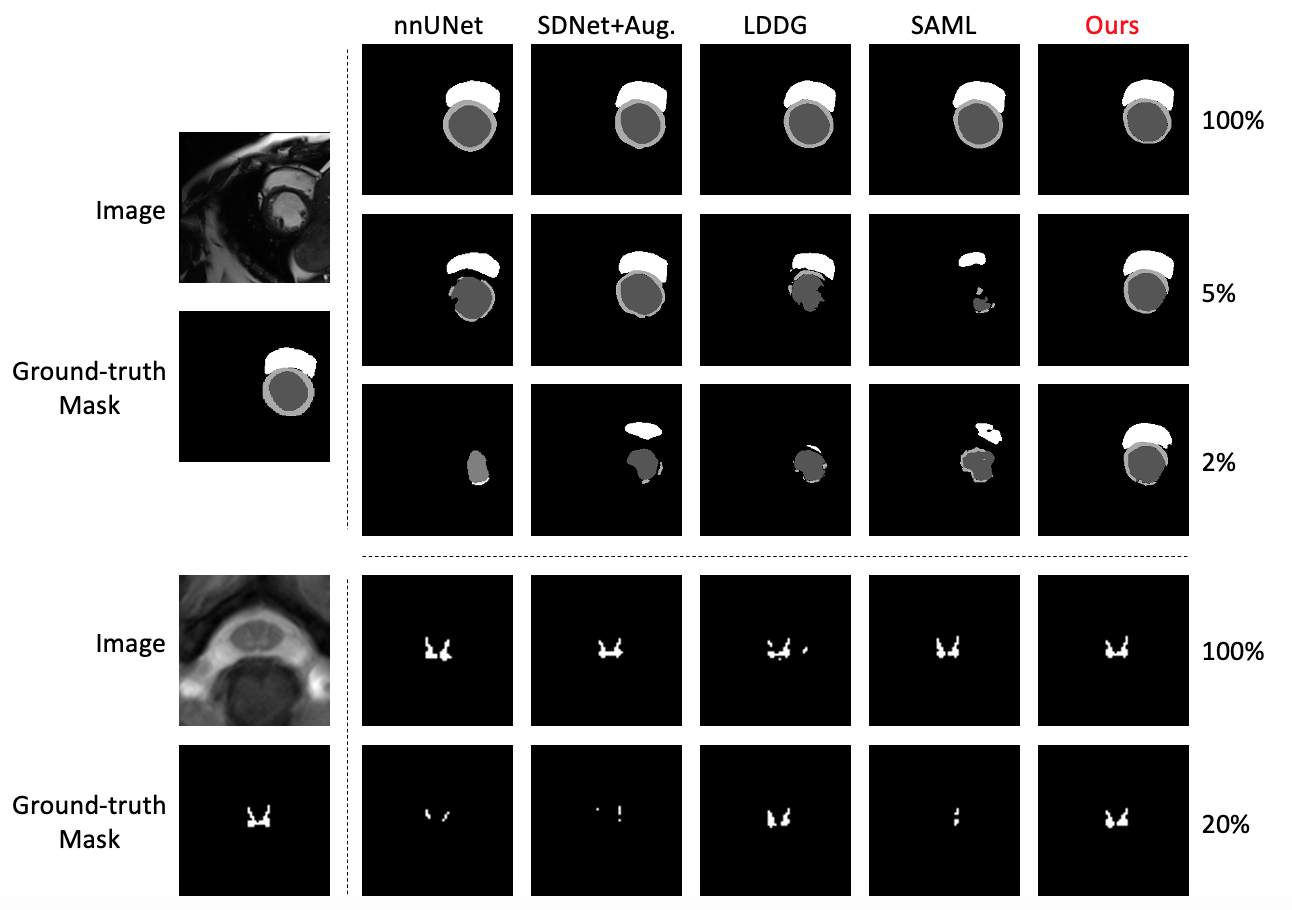
Qualitative results
Citation
@inproceedings{liu2021semi,
title={Semi-supervised Meta-learning with Disentanglement for Domain-generalised Medical Image Segmentation},
author={Liu, Xiao and Thermos, Spyridon and O’Neil, Alison and Tsaftaris, Sotirios A},
booktitle={International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention},
pages={307--317},
year={2021},
organization={Springer}
}
Acknowlegement
Part of the code is based on SDNet, MLDG, medical-mldg-seg and Pytorch-UNet.
License
All scripts are released under the MIT License.