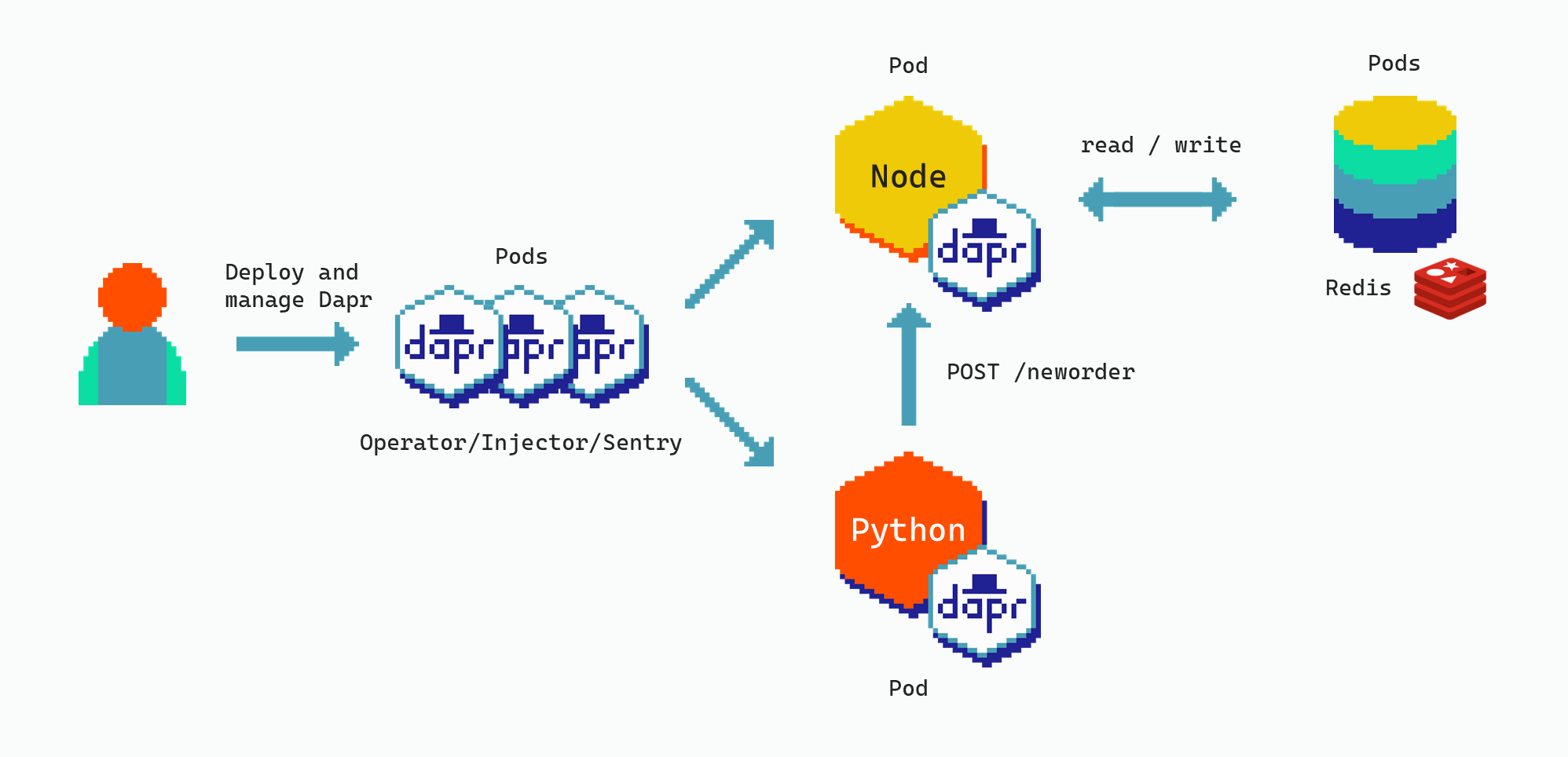
This how-to guide combines two Dapr docs articles and explains how to run Dapr apps on Scaleway Kubernetes. You don't need to follow the three original articles, as this guide contains all the steps necessary.
In this guide:
- A Scaleway Kubernetes cluster will be created.
- Dapr will be installed on the cluster.
- Redis will be installed as the state store.
- Two Dapr applications will be deployed to the cluster.
The NodeJS application has a neworder POST endpoint that persists order IDs, and an order GET endpoint to retrieve the latest order ID.
The Python application creates the order IDs and calls the neworder endpoint of the NodeJS service in a continuous loop.
- Scaleway account
- Scaleway CLI
- Initialize the CLI by running
scw init
- Initialize the CLI by running
- Docker
- kubectl
- helm
- Dapr CLI
- Optional: VSCode with REST client
-
Using the Scaleway CLI create a cluster with two nodes with the smallest node type:
scw k8s cluster create name=dapr-scw-k8s pools.0.size=2 pools.0.node-type=PLAY2-NANO pools.0.name=dapr-scw-k8s-pool
Expected response:
ID <CLUSTER_ID> Type kapsule Name dapr-scaleway Status creating Version 1.26.2 ...
-
Check that the cluster is in ready state before continuing:
scw k8s cluster list
Expected response:
ID NAME STATUS VERSION REGION <CLUSTER_ID> dapr-scw-k8s ready 1.26.2 nl-ams
-
Install the KubeConfig using the Scaleway CLI:
scw k8s kubeconfig install <CLUSTER_ID>
Expected response:
Kubeconfig for cluster <CLUSTER_ID> successfully written at / Users/<YOURUSERNAME>/.kube/config
-
Verify the connection to the cluster:
kubectl cluster-info
Expected response:
Kubernetes control plane is running at <CONTROL_PLANE_URL> CoreDNS is running at <CONTROL_PLANE_URL>/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/coredns:dns/proxy
-
Verify the two nodes are created:
scw k8s node list cluster-id=<CLUSTER-ID>
Expected response:
ID NAME STATUS PUBLIC IPV4 PUBLIC IPV6 <NODE_ID1> <NODE_NAME1> ready <IP1> - <NODE_ID2> <NODE_NAME1> ready <IP2> -
-
Initialize Dapr on the provisioned Scaleway Kubernetes cluster:
dapr init --kubernetes --wait
Expected response:
Making the jump to hyperspace... Note: To install Dapr using Helm, see here: https://docs.dapr.io/getting-started/install-dapr-kubernetes/#install-with-helm-advanced Container images will be pulled from Docker Hub Deploying the Dapr control plane to your cluster... Success! Dapr has been installed to namespace dapr-system. To verify, run `dapr status -k' in your terminal.
-
Verify the Dapr services are running:
dapr status -k
Expected response:
NAME NAMESPACE HEALTHY STATUS REPLICAS VERSION AGE CREATED dapr-dashboard dapr-system True Running 1 0.12.0 1m 2023-03-21 11:04.03 dapr-operator dapr-system True Running 1 1.10.4 1m 2023-03-21 11:04.03 dapr-sidecar-injector dapr-system True Running 1 1.10.4 1m 2023-03-21 11:04.03 dapr-placement-server dapr-system True Running 1 1.10.4 1m 2023-03-21 11:04.03 dapr-sentry dapr-system True Running 1 1.10.4 1m 2023-03-21 11:04.03
Ensure that all services are healthy and running before continuing.
-
Add a reference to the bitnami Redis Helm chart:
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
Expected response:
"bitnami" has been added to your repositories -
Update Helm:
helm repo update
Expected response:
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories... ...Successfully got an update from the "bitnami" chart repository Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈
-
Install Redis:
helm install redis bitnami/redis --set image.tag=6.2
Expected response:
NAME: redis LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Mar 21 11:40:28 2023 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: None NOTES: CHART NAME: redis CHART VERSION: 17.8.7 APP VERSION: 7.0.10 ** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed ** Redis can be accessed on the following DNS names from within your cluster: redis-master.default.svc.cluster.local for read/write operations (port 6379) redis-replicas.default.svc.cluster.local for read-only operations (port 6379) ...
-
Verify the Redis pods are running:
kubectl get pods
Expected response:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE redis-master-0 1/1 Running 0 13m redis-replicas-0 1/1 Running 0 13m redis-replicas-1 1/1 Running 0 12m redis-replicas-2 1/1 Running 0 11m
-
Ensure you are in the root directory of this repo and apply the configuration to add the Dapr state store component for Redis:
kubectl apply -f ./resources/redis.yaml
Expected response:
component.dapr.io/statestore created
-
Ensure you're in the root of the repository and apply the Node app configuration to deploy the Node app:
kubectl apply -f ./resources/node.yaml
Expected response:
service/nodeapp created deployment.apps/nodeapp created
-
Watch the status of the deployment:
kubectl rollout status deploy/nodeapp
This should eventually result in:
deployment "nodeapp" successfully rolled out -
Get the external IP of the service:
kubectl get svc nodeapp
Expected response:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodeapp LoadBalancer <INTERNAL_IP> <EXTERNAL_IP> 80:31198/TCP 49m
-
Verify the service is running using curl or a REST client:
curl http://<EXTERNAL_IP>/ports
Expected response:
{"DAPR_HTTP_PORT":"3500","DAPR_GRPC_PORT":"50001"} -
Submit an order to the app using curl or a REST client:
curl --request POST --data "@sample.json" --header Content-Type:application/json http://<EXTERNAL_IP>/neworder
-
Confirm that the order ID is persisted using curl or a REST client:
curl http://<EXTERNAL_IP>/order
Expected response:
{ "orderId": "42" }
-
Ensure you're in the root of the repository and apply the Node app configuration to deploy the Python app:
kubectl apply -f ./resources/python.yaml
Expected response:
deployment.apps/pythonapp created
-
Watch the status of the deployment:
kubectl rollout status deploy/pythonapp
This should eventually result in:
deployment "pythonapp" successfully rolled out -
Follow the logs of the Node.js app:
kubectl logs --selector=app=node -c node -f
Expected response:
Got a new order! Order ID: 44 Successfully persisted state for Order ID: 44 Got a new order! Order ID: 45 Successfully persisted state for Order ID: 45 Got a new order! Order ID: 46 Successfully persisted state for Order ID: 46 ...
-
Confirm that the latest order ID is persisted using curl or a REST client:
curl http://<EXTERNAL_IP>/order
Follow these steps to remove all the apps, components and cloud resources created in this how-to guide.
-
If you only want to remove the Dapr applications and state component, navigate to the
resourcesfolder and run this command to delete the resources:kubectl delete -f .Expected response:
service "nodeapp" deleted deployment.apps "nodeapp" deleted service "pythonapp" deleted deployment.apps "pythonapp" deleted component.dapr.io "statestore" deleted
-
Delete the entire Scaleway cluster:
scw k8s cluster delete <CLUSTER_ID>
Expected response:
ID <CLUSTER_ID> Type kapsule Name dapr-scw-k8s Status deleting Version 1.26.2 Region nl-ams ...
-
Use the
cluster listcommand to check the status of the cluster:scw k8s cluster list
Expected response:
ID NAME STATUS VERSION REGION <CLUSTER_ID> dapr-scw-k8s deleting 1.26.2 nl-ams
- Creating and managing a Kubernetes Kapsule with CLI
- Tutorial: Configure state store and pub/sub message broker
- Hello Kubernetes
Read more about hosting Dapr on Kubernetes on the Dapr docs site.
Any questions or comments about this sample? Join the Dapr discord and post a message the #kubernetes channel.
Have you made something with Dapr? Post a message in the #show-and-tell channel, we love to see your creations!