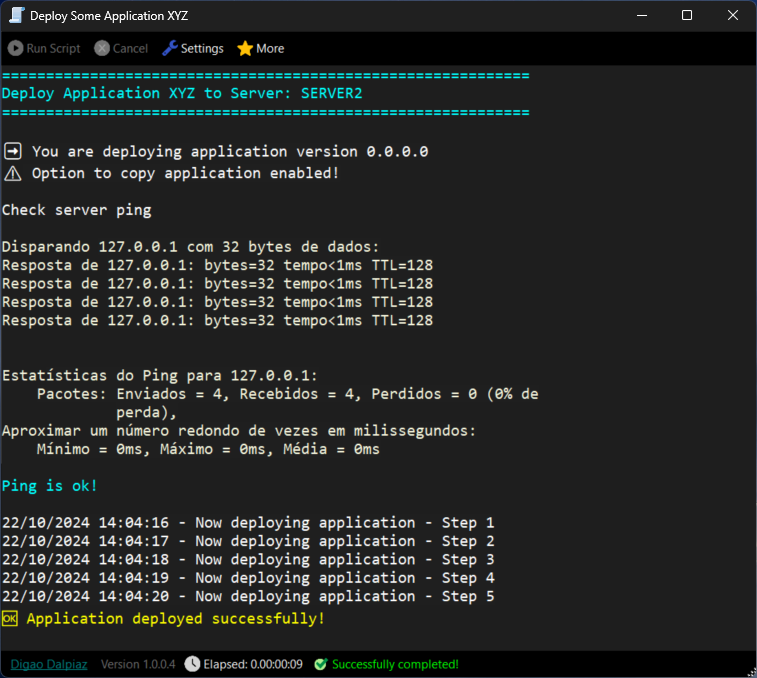
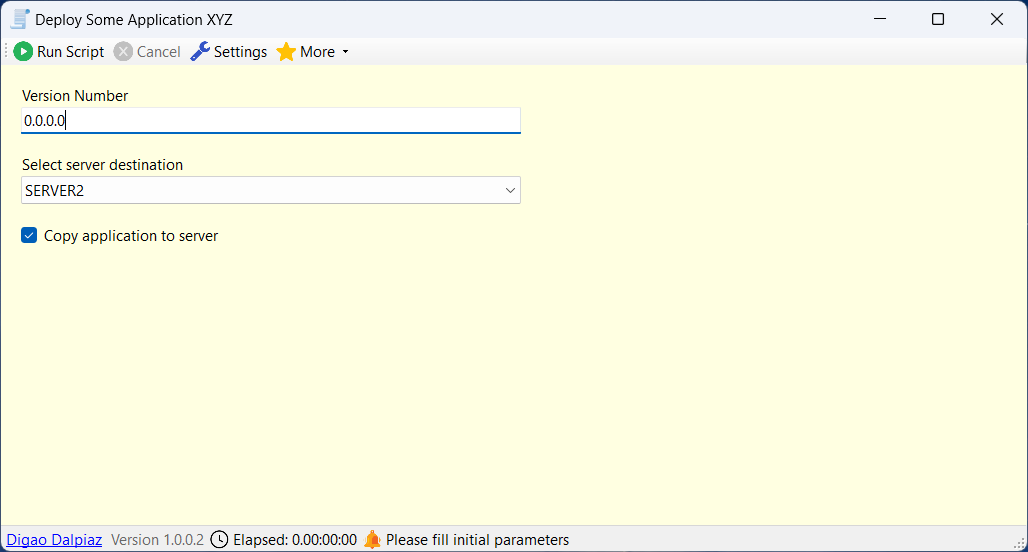
In my work environment, I frequently need to create scripts to automate processes. Whether it's to copy files from one place to another for deploying an application or even for more complex tasks involving multiple steps, such as installing services, configuring Windows settings, reading files and extracting information, or any other activity that can be automated.
These are typically tasks where it's not worth writing a specific program. In such cases, we usually resort to a Batch script (.BAT or .CMD) or the more modern PowerShell.
But let's be honest, for any of these scripts, the language is not very practical, and the script ends up being hard to read and understand, and it's not efficient. For example, error handling in these scripts is cumbersome, and typically, the processes continue even if an error occurs in the middle of the script.
With all this in mind, I developed Digao Runner, which is essentially a debugger for scripts with the .ds (Digao Script) extension, where you can write the script using C# code in a very practical and easy way. The code is very clean, has exception handling, and you can also configure input fields for the user to fill in at runtime, like parameters or variables of the script.
Here is an example of a Digao Runner script, used specifically to create the package for the program itself:
@DIGAOSCRIPT
VERSION=1
TITLE=Create Digao Runner Package
@CODE
Echo("========================================================", Color.Cyan);
Echo("Generate Digao Runner zip package", Color.Cyan);
Echo("========================================================", Color.Cyan);
int ret;
string vsWhere = @"C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\Installer\vswhere.exe";
string sevenZip = @"C:\Program Files\7-zip\7z.exe";
string pathProject = @".\DigaoRunnerApp\DigaoRunnerApp.csproj";
string tmpBuildDir = @".\Temp_Build";
string packageFile = @".\DigaoRunner.zip";
string vsPath;
ret = RunProcessReadOutput(vsWhere, "/latest /property installationPath", ref vsPath);
if (ret != 0) Abort("Error getting Visual Studio installation path");
vsPath = vsPath.Split(Environment.NewLine).FirstOrDefault();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(vsPath)) Abort("Visual Studio path empty");
string msBuildExe = Path.Combine(vsPath, @"MSBuild\Current\bin\msbuild.exe");
if (Directory.Exists(tmpBuildDir)) Directory.Delete(tmpBuildDir, true);
if (File.Exists(packageFile)) File.Delete(packageFile);
Echo("Compile project");
ret = RunProcess(msBuildExe,
$"\"{pathProject}\" /clp:ErrorsOnly /t:Rebuild /p:PlatformTarget=x64 /p:Configuration=Release /p:OutputPath=\"{Path.GetFullPath(tmpBuildDir)}\"");
//using GetFullPath because MSBUILD internally uses current path as project folder path
if (ret != 0) Abort("Error compiling project");
Echo("Create zip file");
//RunProcess(sevenZip, $"a -sfx DigaoRunnerSetup.exe \"{tmpBuildDir}\"");
ZipFile.CreateFromDirectory(tmpBuildDir, packageFile);
Directory.Delete(tmpBuildDir, true);
Echo("Package successfully created!", Color.Yellow);-
Download and install .NET 8 Desktop Runtime x64
-
Download last Digao Runner release (.zip) from here
-
Extract zip to a folder in your computer (Example: C:\DigaoRunner)
-
You may open DigaoRunnerApp.exe and go to menu "More" > "Register .ds files", so the scripts will automatically run with this program.
You are set. Enjoy!
To create scripts, use the following structure in the file with the .ds extension:
@DIGAOSCRIPT
VAR1=value
VAR2=value
VAR3=value
$FIELD1={...}
$FIELD2={...}
$FIELD3={...}
@CODE
Your code here in C# formatThe header section is the part after @DIGAOSCRIPT identifier, and before @CODE section. In this part, you can specify variable and fields.
VERSION=1(required)TITLE=Your script title(optional) it will appear in the window titleADMIN=true(optional) if specified, it will request Administrator elevation when running the script$MY_FIELD={...}(optional) it will show the field input when running script, before executing code section
If any field is specified (using prefix $), then when the script is run, the user will first be prompted to fill in the fields.
Comments are allowed in header section using // prefix
The fields have the following structure in JSON format:
$MY_FIELD={"Label": "Field Description", "Type": "...", "Default": ..., "Items": [], Editable: true}
Type property values:
- "text" (TextBox)
- "check" (CheckBox)
- "combo" (ComboBox)
Default property is optional and must be according to the Type. Example: When Type = text, default value must be string ("default value"). When Type = check, default value must be boolean (true or false).
Items property is a string array and should be specified when Type = combo. Example: ["VALUE1", "VALUE2", "VALUE3"].
Editable property is optional and allows configure an editable Combo Box.
The following imports are internally specified:
- System
- System.Text
- System.Linq
- System.IO
- System.IO.Compression
- System.Diagnostics
- System.Drawing
- System.Text.RegularExpressions
- Microsoft.Win32
So, you may use classes from these imports directly. Example: StringBuilder (comes from System.Text).
Use Abort method to interrupt execution with a message.
void Abort(string message);Use GetField method to get a field value.
object GetField(string name);
T GetField<T>(string name);Use Echo method to print a message line in the console.
void Echo(string text = null, Color? color = null);Use Sleep method to wait for specified miliseconds.
void Sleep(int ms);Use CheckStop method if you want to check if cancel was requested during some code execution.
void CheckStop();Use CopyFile method if you want to copy a file with progress bar
void CopyFile(string sourceFilePath, string destinationFilePath);Use SetSystemConsoleEncoding method before run a process to ensure local system encoding.
void SetSystemConsoleEncoding();Use RunProcess method to run an external process and monitoring output lines in console.
The returning is the process Exit Code. There is a variable LastExitCode available too.
int RunProcess(string fileName, string arguments);Use RunProcessReadOutput method to run an external process and get the output lines in a string variable (the output lines will not be automatically printed in the console).
The returning is the process Exit Code. There is a variable LastExitCode available too.
int RunProcessReadOutput(string fileName, string arguments, ref string output);To run scripts remotely, you can use an SSH connection. The SSH.NET Library can be used for SSH and SFTP connection (file transfer).
SSH and SFTP connection example:
@DIGAOSCRIPT
VERSION=1
TITLE=SSH and SFTP example
@CODE
using Renci.SshNet;
using Renci.SshNet.Common;
using (var ssh = new SshClient("myhost.com", 22, "user", "password"))
{
var command = ssh.RunCommand("ping 127.0.0.1 -c 6");
Echo(command.Result);
}
using (var sftp = new SftpClient("myhost.com", 22, "user", "password"))
{
sftp.WriteAllText("/home/file1.txt", "Some file text");
}