See: #172 for more info.
with npm:
npm install --save leaflet-geosearchor yarn:
yarn add leaflet-geosearchor bower:
bower install leaflet-geosearchIf you don’t use npm, you may grab the latest UMD build from
unpkg (either a development or a production build). The UMD build
exports a global called window.GeoSearch if you add it to your page via a
<script> tag.
We don’t recommend UMD builds for any serious application.
This library is written with the latest technologies in mind. Thereby it is required to include some polyfills when you wish to support older browsers. These polyfills are recommended for IE and Safari support:
- babel-polyfill, for
array.includessupport. - whatwg-fetch, for
fetchrequests.
This library adds support for geocoding (address lookup, a.k.a. geoseaching) to your (web) application. It comes with controls to be embedded in your Leaflet map.
Check out the demo for various possibilities.
The library uses so-called "providers" to take care of building the correct service URL and parsing the retrieved data into a uniform format. Thanks to this architecture, it is pretty easy to add your own providers, so you can use your own geocoding service(s).
The control comes with a default set of six providers:
Although this project is still named leaflet-geosearch, this library is also
usable without LeafletJS, and does not have any dependencies whatsoever.
Let's first start with an little example on how to use this control without leaflet. For example as an address lookup on a webshop order form. Perhaps to search for the closest alternative package delivery point? Or to link it to your own custom map component.
// import
import { OpenStreetMapProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
// setup
const provider = new OpenStreetMapProvider();
// search
const results = await provider.search({ query: input.value });Of course, something like this should be bound to something like a form or input:
import { OpenStreetMapProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const form = document.querySelector('form');
const input = form.querySelector('input[type="text"]');
form.addEventListener('submit', async (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
const results = await provider.search({ query: input.value });
console.log(results); // » [{}, {}, {}, ...]
});Instead of es6 async / await you can also use promises like:
provider
.search({ query: '...' })
.then(function(result) {
// do something with result;
});The search event of all providers return an array of result objects. The
base structure is uniform between the providers. It provides a object like:
const result = {
x: Number, // lon,
y: Number, // lat,
label: String, // formatted address
bounds: [
[Number, Number], // s, w - lat, lon
[Number, Number], // n, e - lat, lon
],
raw: {}, // raw provider result
}The contents of the raw property differ per provider. This is the unprocessed
result from the 3th party service. This property is included for developer
convenience. leaflet-geosearch does not use it. If you need to know the
contents of this property, you should check the 3th party developer docs. (or
use your debugger)
When OpenStreetMap does not match your needs; you can also choose to use the
Bing, Esri, Google LocationIQ, or OpenCage providers. Those providers do however require API
keys. See the documentation pages on the relevant organisations on how to obtain
these keys.
In case you decide to write your own provider, please consider submitting a PR to share your work with us.
Providers are unaware of any options you can give them. They are simple proxies
to their endpoints. There is only one special property, and that is the params
option. The difference being; that params will be included in the endpoint url.
Often being used for API KEYS, where as the other attributes can be used for
provider configuration.
note: Bing services require an API key. Obtain here. For more options and configurations, see the MSDN developer docs.
import { BingProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const provider = new BingProvider({
params: {
key: '__YOUR_BING_KEY__'
},
});For more options and configurations, see the ArcGIS developer docs.
import { EsriProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const provider = new EsriProvider();note: Google services require an API key. Obtain here. For more options and configurations, see the Google Maps developer docs.
import { GoogleProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const provider = new GoogleProvider({
params: {
key: '__YOUR_GOOGLE_KEY__',
},
});For more options and configurations, see the OpenStreetMap Nominatim wiki.
import { OpenStreetMapProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const provider = new OpenStreetMapProvider();note: LocationIQ services require an API key. Obtain here. For more options and configurations, see the LocationIQ developer docs.
import { LocationIQProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const provider = new LocationIQProvider({
params: {
key: '__YOUR_LOCATIONIQ_KEY__',
},
});note: OpenCage services require an API key. Obtain here. For more options and configurations, see the OpenCage developer docs.
import { OpenCageProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const provider = new OpenCageProvider({
params: {
key: '__YOUR_OPENCAGE_KEY__',
},
});This project comes with a leaflet control to hook the search providers into
leaflet. The example below uses the OpenStreetMap Provider, but you can exchange
this with on of the other included providers as well as your own custom made
providers. Remember to setup the provider with a key when required (Google and
Bing for example).
import L from 'leaflet';
import { GeoSearchControl, OpenStreetMapProvider } from 'leaflet-geosearch';
const provider = new OpenStreetMapProvider();
const searchControl = new GeoSearchControl({
provider: provider,
});
const map = new L.Map('map');
map.addControl(searchControl);There are some configurable options like setting the position of the search input and whether or not a marker should be displayed at the position of the search result.
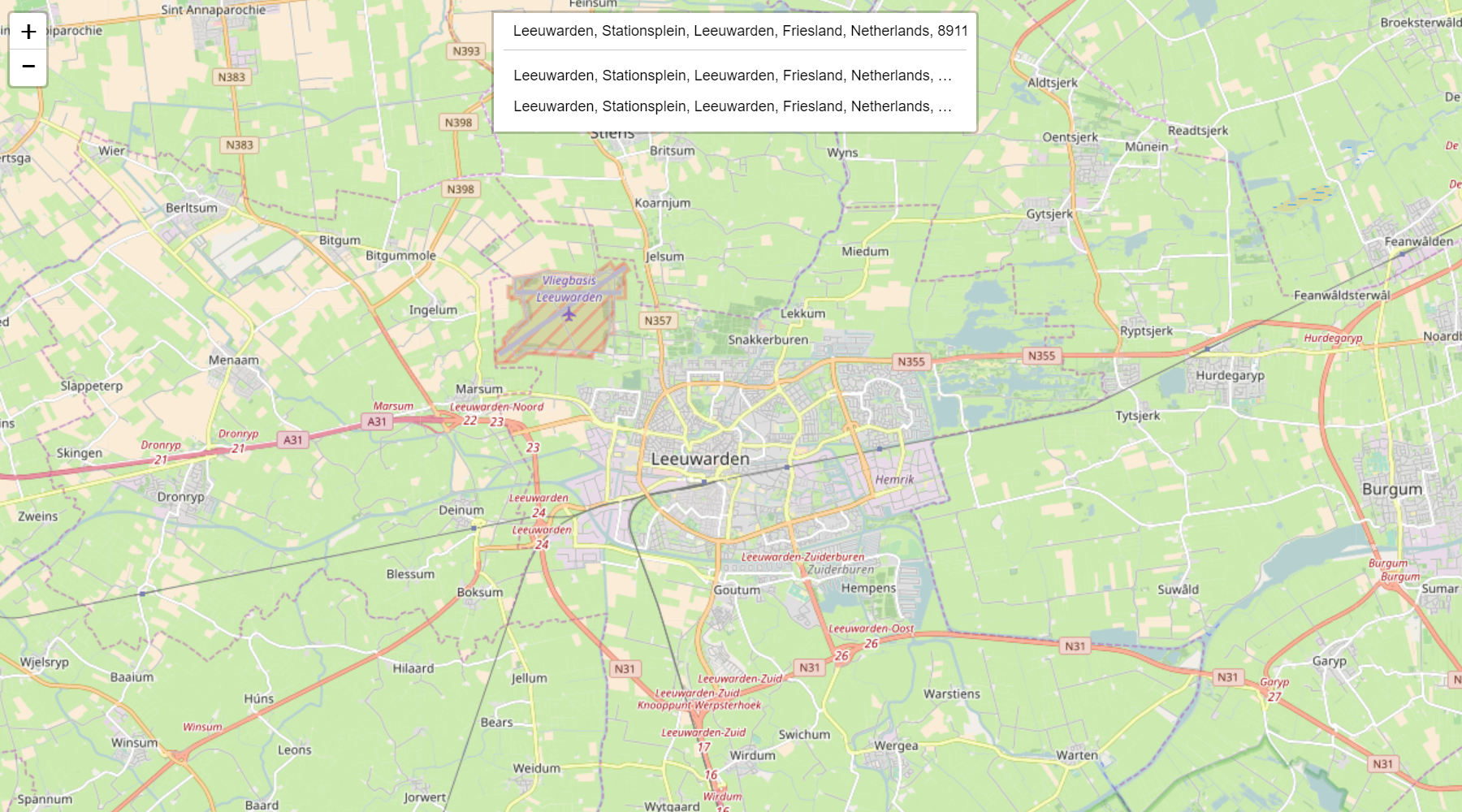
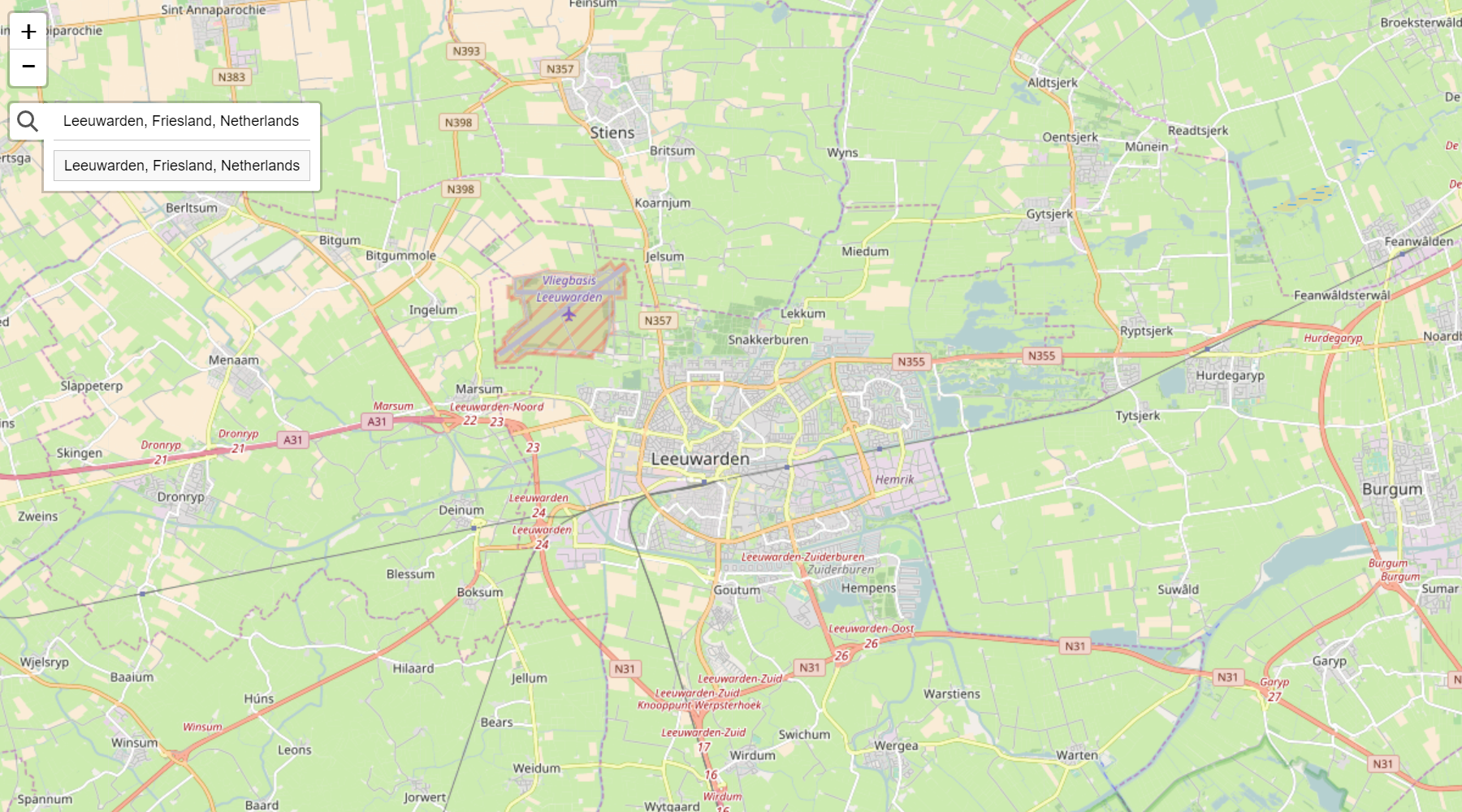 There are two visual styles of this control. One is the more 'leaflet-way' by
putting the search control under a button (see image above). And one where the
search control is permanently shown as a search bar (see image under
using with LeafletJS).
There are two visual styles of this control. One is the more 'leaflet-way' by
putting the search control under a button (see image above). And one where the
search control is permanently shown as a search bar (see image under
using with LeafletJS).
Render style
This render style can be set by the optional style option.
new GeoSearchControl({
provider: myProvider, // required
style: 'bar', // optional: bar|button - default button
}).addTo(map);AutoComplete
Auto complete can be configured by the parameters autoComplete and
autoCompleteDelay. A little delay is required to not DDOS the server on every
keystroke.
new GeoSearchControl({
provider: myProvider, // required
autoComplete: true, // optional: true|false - default true
autoCompleteDelay: 250, // optional: number - default 250
}).addTo(map);Show result
There are a number of options to adjust the way results are visualized.
new GeoSearchControl({
provider: myProvider, // required
showMarker: true, // optional: true|false - default true
showPopup: false, // optional: true|false - default false
marker: { // optional: L.Marker - default L.Icon.Default
icon: new L.Icon.Default(),
draggable: false,
},
popupFormat: ({ query, result }) => result.label, // optional: function - default returns result label
maxMarkers: 1, // optional: number - default 1
retainZoomLevel: false, // optional: true|false - default false
animateZoom: true, // optional: true|false - default true
autoClose: false, // optional: true|false - default false
searchLabel: 'Enter address', // optional: string - default 'Enter address'
keepResult: false // optional: true|false - default false
});showMarker and showPopup determine whether or not to show a marker and/or
open a popup with the location text.
marker can be set to any instance of a (custom) L.Icon.
popupFormat is callback function for displaying text on popup.
maxMarker determines how many last results are kept in memory. Default 1, but
perhaps you want to show the last x results when searching for new queries as
well.
retainZoomLevel is a setting that fixes the zoomlevel. Default behaviour is to
zoom and pan to the search result. With retainZoomLevel on true, the map is
only panned.
animateZoom controls whether or not the pan/zoom moment is being animated.
autoClose closes the result list if a result is selected by click/enter.
keepResult is used to keep the selected result in the search field. This prevents markers to disappear while using the autoClose feature.
Events
geosearch/showlocation is fired when location is chosen from the result list.
map.on('geosearch/showlocation', yourEventHandler)geosearch/marker/dragend is fired when marker has been dragged.
map.on('geosearch/marker/dragend', yourEventHandler)Checkout the providers to see how easy it is to write your own. For research it
can be interesting to see the difference between Bing and the others; because
Bing does not support CORS, and requires jsonp to be used instead.
In case you decide to write your own provider, please consider submitting a PR to share your work with us.