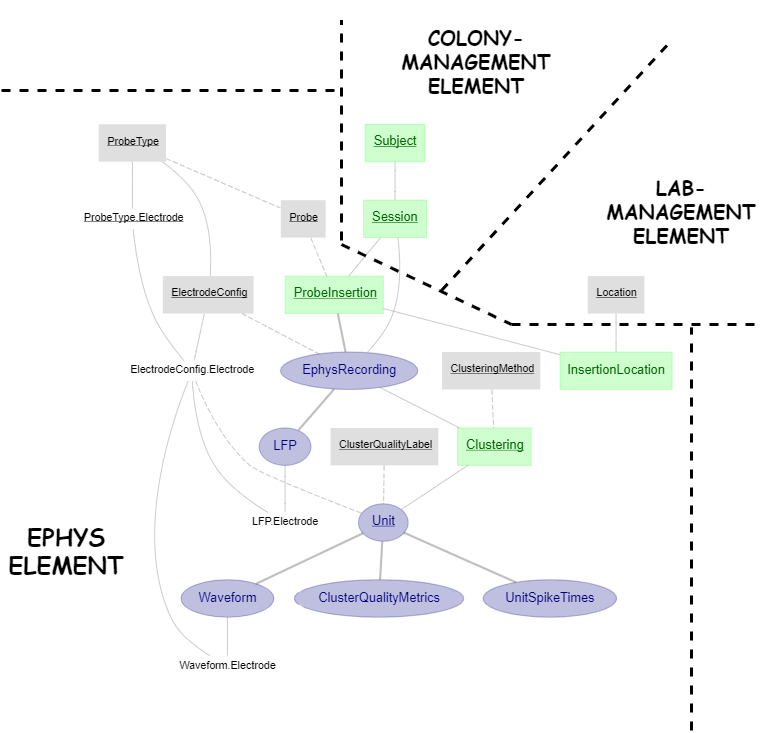
Build a full ephys pipeline using the canonical pipeline elements
This repository provides demonstrations for:
- Set up a pipeline using different pipeline modules (see here)
- Ingestion of data/metadata based on:
- predefined file/folder structure and naming convention
- predefined directory lookup methods (see here)
- Ingestion of clustering results (built-in routine from the ephys pipeline module)
The electrophysiology pipeline presented here uses pipeline components from 3 DataJoint pipeline elements, lab-management, colony-management and ephys, assembled together to form a fully functional pipeline.
Clone this repository from here
- Launch a new terminal and change directory to where you want to clone the repository to
cd C:/Projects - Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/vathes/canonical-full-ephys-pipeline - Change directory to canonical-full-ephys-pipeline
cd canonical-full-ephys-pipeline
It is highly recommended (though not strictly required) to create a virtual environment to run the pipeline.
- To create a new virtual environment named venv:
virtualenv venv - To activated the virtual environment:
- On Windows:
.\venv\Scripts\activate - On Linux/macOS:
source venv/bin/activate
- On Windows:
note: if virtualenv not yet installed, do pip install --user virtualenv
From the root of the cloned repository directory:
pip install .
At the root of the repository folder,
create a new file dj_local_conf.json with the following template:
{
"database.host": "hostname",
"database.user": "username",
"database.password": "password",
"database.port": 3306,
"connection.init_function": null,
"database.reconnect": true,
"enable_python_native_blobs": true,
"loglevel": "INFO",
"safemode": true,
"display.limit": 7,
"display.width": 14,
"display.show_tuple_count": true,
"custom": {
"database.prefix": "db_",
"ephys_data_dir": "C:/data/ephys_data_dir"
}
}Specify database's hostname, username and password properly.
Specify a database.prefix to create the schemas.
Setup your data directory following the convention described below.
If you install this repository in a virtual environment, and would like to use it with Jupyter Notebook, follow the steps below:
Create a kernel for the virtual environment
pip install ipykernel
ipython kernel install --name=full-ephys
At this point the setup/installation of this pipeline is completed. Users can start browsing the example jupyter notebooks for demo usage of the pipeline.
jupyter notebook
The pipeline presented here is designed to work with the directory structure and file naming convention as followed
root_data_dir/
└───subject1/
│ └───session0/
│ │ └───imec0/
│ │ │ │ *imec0.ap.meta
│ │ │ └───ksdir/
│ │ │ │ spike_times.npy
│ │ │ │ templates.npy
│ │ │ │ ...
│ │ └───imec1/
│ │ │ *imec1.ap.meta
│ │ └───ksdir/
│ │ │ spike_times.npy
│ │ │ templates.npy
│ │ │ ...
│ └───session1/
│ │ │ ...
└───subject2/
│ │ ...
-
root_data_dir is configurable in the
dj_local_conf.json, undercustom/ephys_data_dirvariable -
the subject directories must match the identifier of your subjects
-
the session directories must match the following naming convention:
*subject_mmddyy_HHMMSS*(wheremmddyy_HHMMSSis the datetime of the session) -
the probe directories must match the following naming convention:
*imec[0-9](where[0-9]is a one digit number specifying the probe number) -
a neuropixels meta file is required per probe folder, with the following naming convention:
*imec[0-9].ap.meta
Once you have your data directory configured with the above convention, populating the pipeline with your data amounts to these 3 steps:
-
Insert meta information - modify and run this script to insert meta information (e.g. subject, equipment, etc.)
-
Import session data - run:
python my_project/ingestion.py
-
Import clustering data and populate downstream analyses - run:
python my_project/populate.py
Rerun step 2 and 3 every time new subjects, sessions or clustering data become available. In fact, step 2 and 3 can be executed as scheduled jobs that will automatically process any data newly placed into the root_data_dir