My bachelor thesis project, to fulfill a degree requirement from Bandung Institute of Technology
by Senapati S. Diwangkara, 2020
3 years after completing this project, I got messages from non-negligible amount of people interested in replicating and understanding this project. As such, I'm updating this README to include additional instruction to run the experiment in the paper.
This project was originally written in Python 3.7 and installing the requirements.txt using the contemporary version of Python would probably give you some version error.
Therefore, I'm adding a conda environment.yml with Python 3.7 and some additional MKL packages (sip, mkl_fft, and mkl_random) with the appropriate version so that you could install from requirements.txt without conflict.
- Install Conda and set it up with the
conda-forgechannel - Create an environment from the environment file:
conda env create --file environment.yml - Activate the environment:
conda activate asyncfl - Install the pip packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Run the experiment:
./train_batch.sh
This paper was published on ICITSI 2020
This work examines the effect of asynchronicity in aggregation algorithm (i.e. when the nodes' training round / epoch don't have to be in sync with one another). In particular, I'm interested in the effect of data imbalance. Intuitively speaking, if we have some true/false dataset that is split between 2 nodes, but each node only have either true or false data, and one node is faster than the other, than the trained model should perform worse than if the model is trained centrally, right? So here, we tried to verify that intuition quntitatively.
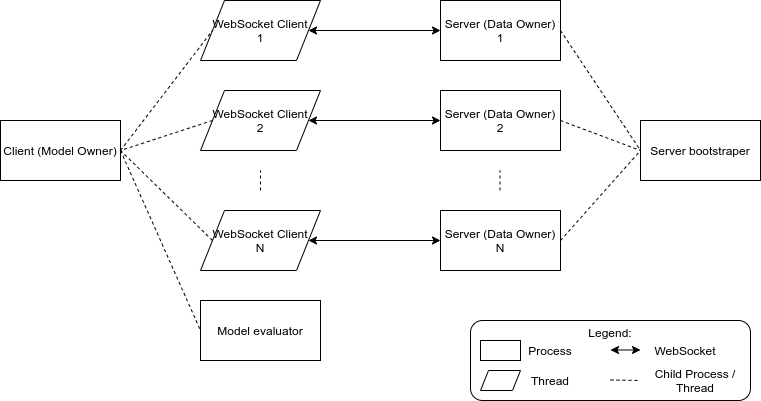
Clients are implemented in src/client.py.
It will spool up some client threads to connect to each server, and an evaluator process to evaluate the latest model periodically.
Each client threads will communicate with the evaluator process with the evaluator_q variable, that acts as a queue.
The threads will enqueue their evaluation order and they will be consumed by the evaluator process, which then will evaluate the snapshoted model and print the result.
Servers are implemented in src/servers.py.
It will split a given dataset (using src/split_dataset.py) and started the servers that will host said data.
To measure optimization performance, we use yappi as a profiler to measure how much time each function is spending.