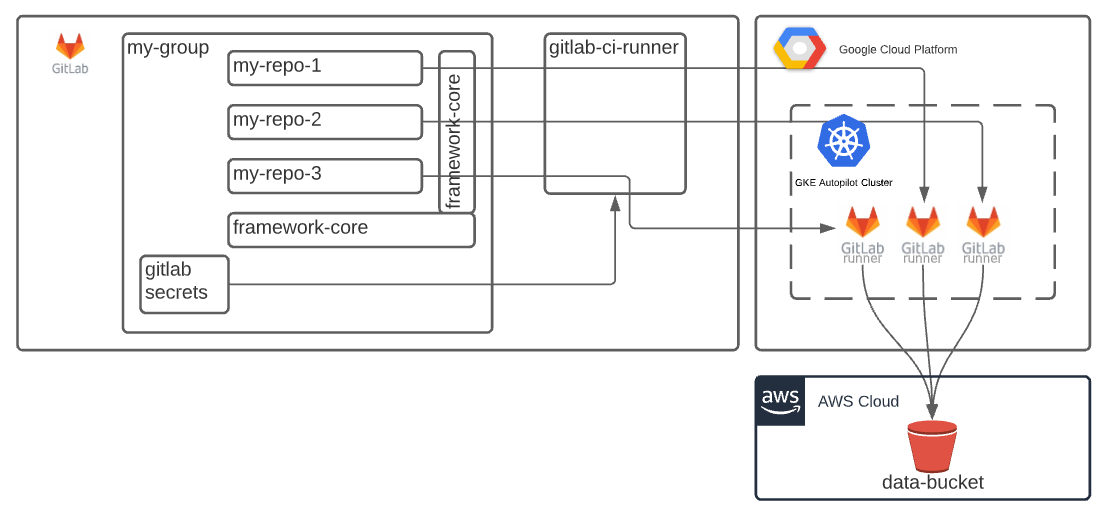
This documentation describes a GitOps oriented data lake.
The data is stored in Amazon S3 and contains the following types of assets
{
// Raw dataset
`s3://data-bucket/asset/${repo}/${branch}/data/${yyyy}-${mm}-${dd}.csv.gz`: '<gzipped csv data>',
// Metadata file indicating the location of the latest dataset
`s3://data-bucket/asset/${repo}/${branch}/metadata/latest`: latest.grosRef.serialize(),
// Downstream Dependency location
`s3://data-bucket/dependency/${repo}/${branch}/downstreams/${urlencode(`${repo}/${branch}`)}`: dep3.grosRef.serialize(),
// Audit logs containing information on the downstreams dependent on a dataset
`s3://data-bucket/dependency/${repo}/${branch}/${yyyy}-${mm}-${dd}/downstreams/${urlencode(`${dep3.repo}/${dep3.branch}`)}`: dep3.grosRef.serialize(),
// Audit logs containing information on the upstream datasets used to produce this dataset
`s3://data-bucket/dependency/${repo}/${branch}/${yyyy}-${mm}-${dd}/metadata/${yyyy}-${mm}-${dd}.json`: {
"gros_ref": this.grosRef.serialize(),
"upstreams": [
dep1.grosRef.serialize(),
dep2.grosRef.serialize(),
]
},
}To retrieve datasets in the data lake, you can use a URI style protocol in the pandas.read_csv function.
Example:
import gros
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('gros://my-branch/my-repo:latest')The URI is in the following format:
gros://$repo[/$branch]?[:$tag]?
where:
repo(required) is the name of the repo(the project slug) that produced the data
branch(optional) is the branch of code that produced the data. Defaults to master.
tag(optional) is:
- indicating that it's sourcing the the latest dataset as a real-time dependency. This pipeline will be run whenever its upstream has new data.
latestindicating that it's using the latest dataset. The pipeline will not be triggered on new data.- a date string in
YYYY-mm-ddformat - a
signed intallows selecting datasets by earliest to latest
The pipelines are run on GitLab CI Runners on a Kubernetes Cluster. The CI jobs have credentials in order to run downstream pipelines using GitLab multi-project features. When pipelines are run, datasets are retrieved from the data lake using a single API. This API logs the datasets accessed during the job run. If a dataset is retrieved using an empty tag, it is recognized as an upstream dependency and will be run when the upstream dataset is updated.
This strategy benefits from pipeline logs, source code, and secrets management being consolidated behind a single pane of glass. The infrastructure uses a GKE Autopilot cluster and auto-scales the node count based on the needed CPU and RAM. After jobs complete running, the resources are automatically scaled down by the platform for cost savings. This strategy leads to a scaleable, but low-maintenance data lake that can support complex pipeline logic and easy access to datasets in an interactive notebook environment.