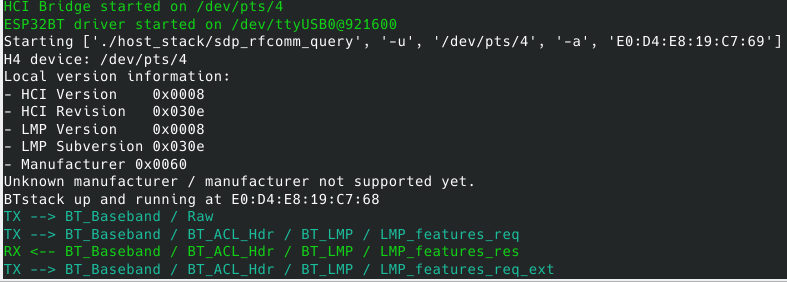
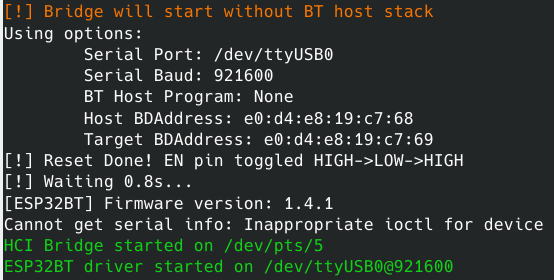
BrakTooth ESP32 BR/EDR Active Sniffer/Injector
Simple "Monitor mode" for Bluetooth Classic. Sniff or inject BR/EDR Baseband packets in ESP32 BT connections.
This is a reverse engineered active BR/EDR sniffer and ESP32 patching framework (soon to be open-sourced), which can be used to explore the Bluetooth (BT) BR/EDR interaction between ESP32 controller and a remote target.
Differently than passive sniffers, which do not interact with the BT network (piconet), the active sniffer connects itself to the remote BT device (BR/EDR target) and allows testing the BT protocol down to the Baseband layer while guided by a BT host stack such as blue-kitchen. The BrakTooth sniffer supports cheap boards such as ESP32-DOIT ($4) or ESP32-DevKitC ($10).
Table of Contents
- Simplified Setup Overview
- 1) Installation
- 2) Usage Instructions
- 3) Customising BT Host programs (Profiles)
- Software Architecture of BrakTooth Sniffer
- Features Overview
- Acknowledgements
Simplified Setup Overview
1) Installation
A. Install Linux requirements (Ubuntu 18.04 / 20.04)
git clone https://github.com/Matheus-Garbelini/esp32_bluetooth_classic_sniffer
cd esp32_bluetooth_classic_sniffer
./requirements.sh # (sudo required) Installs latest wireshark and standalone python3 runtime
./build.sh # Build BT Host programs and Wireshark h4bcm dissectorB. Flash custom firmware to ESP32
Before starting to use BrakTooth Sniffer, you need to upload a custom firmware to your ESP32 board:
./firmware.py flash /dev/ttyUSB0 # Change ttyUSB0 to match your port name2) Usage Instructions
Usage: BTSnifferBREDR.py [OPTIONS]
Options:
--port TEXT Serial port name (/dev/ttyUSBx for Linux)
--host TEXT BDAddress of local host (default: E0:D4:E8:19:C7:68)
--target TEXT BDAddress of remote target (ex: a8:96:75:25:c2:ac)
--live-wireshark Opens Wireshark live session
--live-terminal Show a summary of each packet on terminal
--bridge-only Starts the HCI bridge without connecting any BT Host stack
--help Show this message and exit.You can start the sniffer in as either master or slave role. If you use add --target argument, the sniffer will attempt a connection to your remote target. Otherwise, it will just wait for someone to connect to it.
Lastly, the --bridge-only only creates the HCI pseudo terminal (/dev/pts/x) so ESP32 can operate as a standard HCI BT controller. You can use this feature to connect any other BT host stack to ESP32.
Example 1 - Connect to remote target (Master Role)
./BTSnifferBREDR.py --port=/dev/ttyUSB0 --target=E0:D4:E8:19:C7:69 --live-terminal --live-wiresharkExample 2 - Wait for BT connection (Slave Role)
./BTSnifferBREDR.py --port=/dev/ttyUSB0 --live-terminal --live-wiresharkExample 3 - HCI Bridge Mode (connect with other BT Host stack)
./BTSnifferBREDR.py --port=/dev/ttyUSB0 --bridge-only --live-terminal --live-wireshark3) Customising BT Host programs (Profiles)
Since BrakTooth sniffer uses a BT host stack to guide connectivity, the following modified BlueKitchen examples are used:
- host_stack/sdp_rfcomm_query - This program initiates connection with slave device and attempts to perform SDP scanning and pairing.
- host_stack/spp_counter - This program wait for connections and establish a spp (serial port) connection with the master device.
You can modify or add BT profiles to the current programs by following the official documentation of BlueKitchen. Note that folder host_stack/bluekitchen/example/ already contain some profile examples.
Software Architecture of BrakTooth Sniffer
The custom ESP32 BR/EDR Sniffer/Injector firmware communicates with the host system over a USB serial port and waits to receive custom commands or HCI commands. At startup, an HCI bridge is created to separate BrakTooth custom protocol from standard HCI commands sent or received from ESP32. Once the "RX/TX Sniffer" feature is enabled on the ESP32 firmware, Baseband packets are directly forwarded to BTSnifferBREDR.py script which simply decodes sniffed packets over the custom protocol and prints them via Scapy and/or dumps to Wireshark via live capture and to logs folder.
Features Overview
- RX/TX Sniffer: Dumps Baseband packets and forwards them to the host. Supported packets:
- Baseband Header
- NULL/POLL from remote target
- FHS (no scapy layer for now)
- EIR (no dissection for now)
- ACL Header
- LMP
- TX Interception: This allows the host PC to modify TX packets in real-time before over-the-air transmission from ESP32. It requires however, an ESP32 board with high-speed USB such as ESP-PROG or ESP-WROVER-KIT. Both of them have a FTD2232H USB to UART controller, which allows reduced USB pooling latency of 125us. (disabled for now, sorry).
- TX Injector: This allows the host to inject BR/EDR packets immediately after the BT paging procedure and on every transmission slot (i.e. every 1.25ms) subjected to waits if there is something in ESP32 internal LMP queue. (disabled for now, sorry).
- RX/TX Bypass: Effectively "blinds" ESP32 BT stack from receiving or transmitting LMP packets after the paging procedure. One can use this to construct a standalone LMP state machine on the host and with Scapy 🙂. This feature could enable something similar to what has been done in SweynTooth nRF52 dongle, but for BR/EDR.
- ROM Patcher: Installs ROM hooks from inside the firmware.
- HCI IN/OUT: Standard communication interface with the BT Host stack. A third-party stack such as bluekitchen.
Acknowledgements
The dissection of Baseband packets extends the InternalBlue Broadcom Wireshark Dissector. Specifically, the dissection extended the h4bcm Wireshark plugin to support a few more BT layers and our custom ESP32 metadata header. Thanks @jiska2342.
Thanks to all the following open-source projects:
- Special thanks to @Ebiroll for his maintenance on Xtensa Module for Ghidra
- @mringwal for the excellent open-source BlueKitchen BT Host Stack
- InternalBlue Project
- Scapy Packet Manipulation Library
- Wireshark Project