This repository contains the scripts and configuration needed to spin up and maintain a local instance of a serverless platform.
- Overview
- Quickstart
- Scripts
- Config
- Visualise Environment
- Log Files
- Common Environment Tasks
- Development Environment
This section gives a high level overview of the serverless local environment.
- Orchastration Scripts:
- Up/Down environment
- Build custom docker images
- Deploy lambda packages
- Create AWS resources
- Application Configs
- Log files for Docker apps & Lambda's
- ELK stack
- Development Tools Installer (OSX only)
- Integration with Weave Scope (see
Visualise Environment)
- Mock AWS Services (SQS, S3, SNS, Lambda etc.)
- Mock ALB for AWS Lambda Functions
See the serverless-env/README.md file for more information on services, URLs and config
- AWS services are mocked using localstack, which does not 100% reflect real world AWS behaviour
- AWS Lambda's run inside localstack using Docker containers
- You will need to allow docker to consume a decent amount of memory, localstack alone consumes 4GB of RAM when all services are enabled
-
Install development tools for spinning up the environment, see:
Development Environment -
If using Docker for Mac or Windows, ensure it is configured to be able to use at least
8GBof your machine's RAM, to configure this: click the docker icon -> Perferences... -> General -> Memory -
If you have a
~/.aws/configfile, ensure it is set up to match the values inserverless-env/config/aws-config.env -
Then run:
./up
-
Once this is complete you can access services on localhost
-
You can destroy your environment by running:
./down
You can run selectively deploy parts of the local environment using the below scripts:
Note: all scripts reside in the scripts directory
-
up-env.sh: Bring up docker services, create AWS resources and deploy Lambda Functions -
up-aws.sh: Bring up localstack, create AWS resources and deploy Lambda Functions -
build-custom-images.sh: Build any custom docker images not available on Docker Hub (including custom services); this script pulls a git repo and builds theDockerfileinside. You can pass the--imageflag with a docker image name to build one image only; e.x.--image my-api -
deploy-lambda-functions.sh: Deploy Lambda Functions to localstack; this script using a local or http(s) package. You can pass the--functionflag with a function name to deploy one function only; e.x.--function api
By default the above scripts will not create a service or resources that already exist, pass various --clean options to scripts to recreate existing resources. Run ./up --help to view options.
The config directory holds .env files which provide configuration for the scripts in this repo.
aws-services: Required AWS resourcescustom-images: Custom docker image definitionslambda-functions: Lambda function definitions
See the config file for more info.
The default environment setup includes several web-apps that are useful for understanding and debugging the platform.
An ELK stack is installed as part of the local environment. It will ingest log files from docker applications and lambda functions. These are parsed to provide some key metadata, such as:
- HTTP Requests (path, method, query string)
- Lambda Stats (request id, duration, memory used)
- Platform Type (docker, lambda)
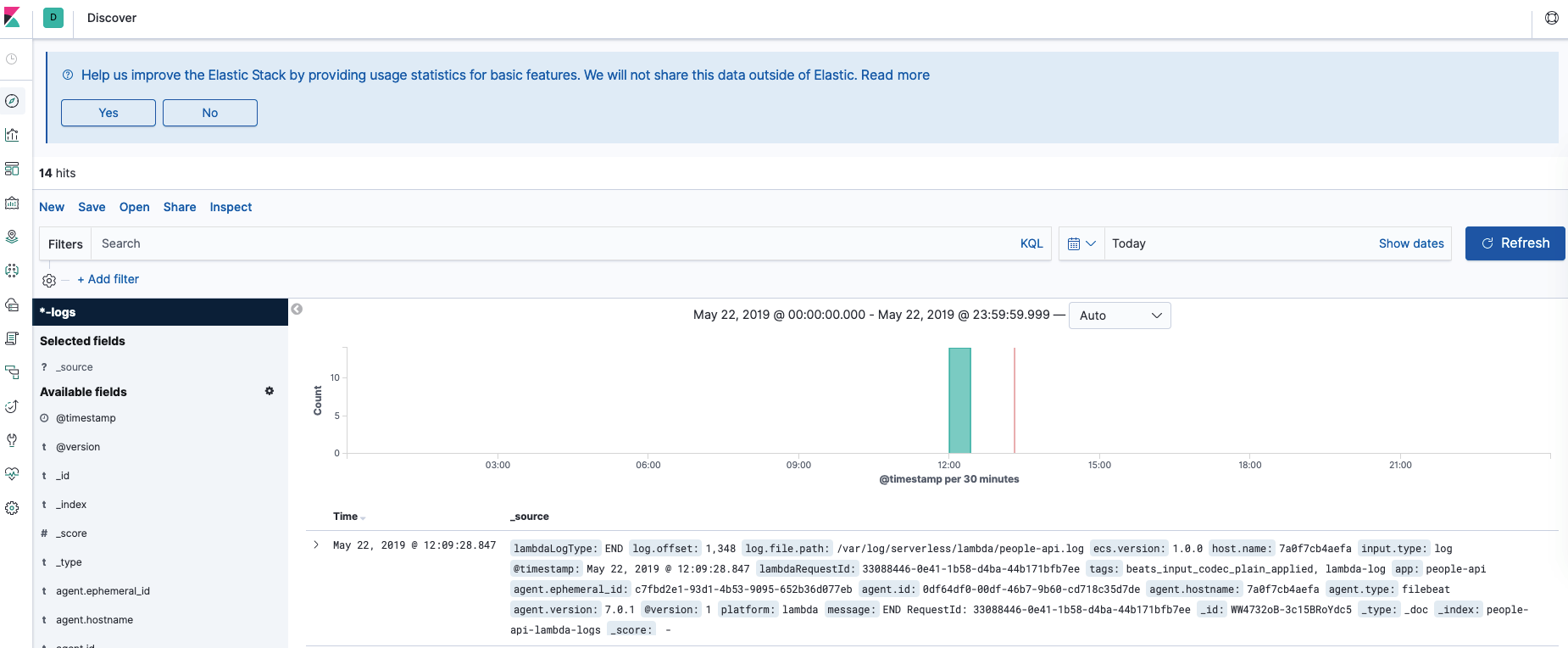
- Go to http://localhost:5601/app/kibana#/management/kibana/index_patterns/
- Create a new index pattern, using the pattern:
*-logs - Use
@timestampfor the time filter field - You can now discover logs and start querying by going to http://localhost:5601/app/kibana#/discover?_g=(refreshInterval:(pause:!t,value:0),time:(from:now%2Fd,to:now%2Fd))
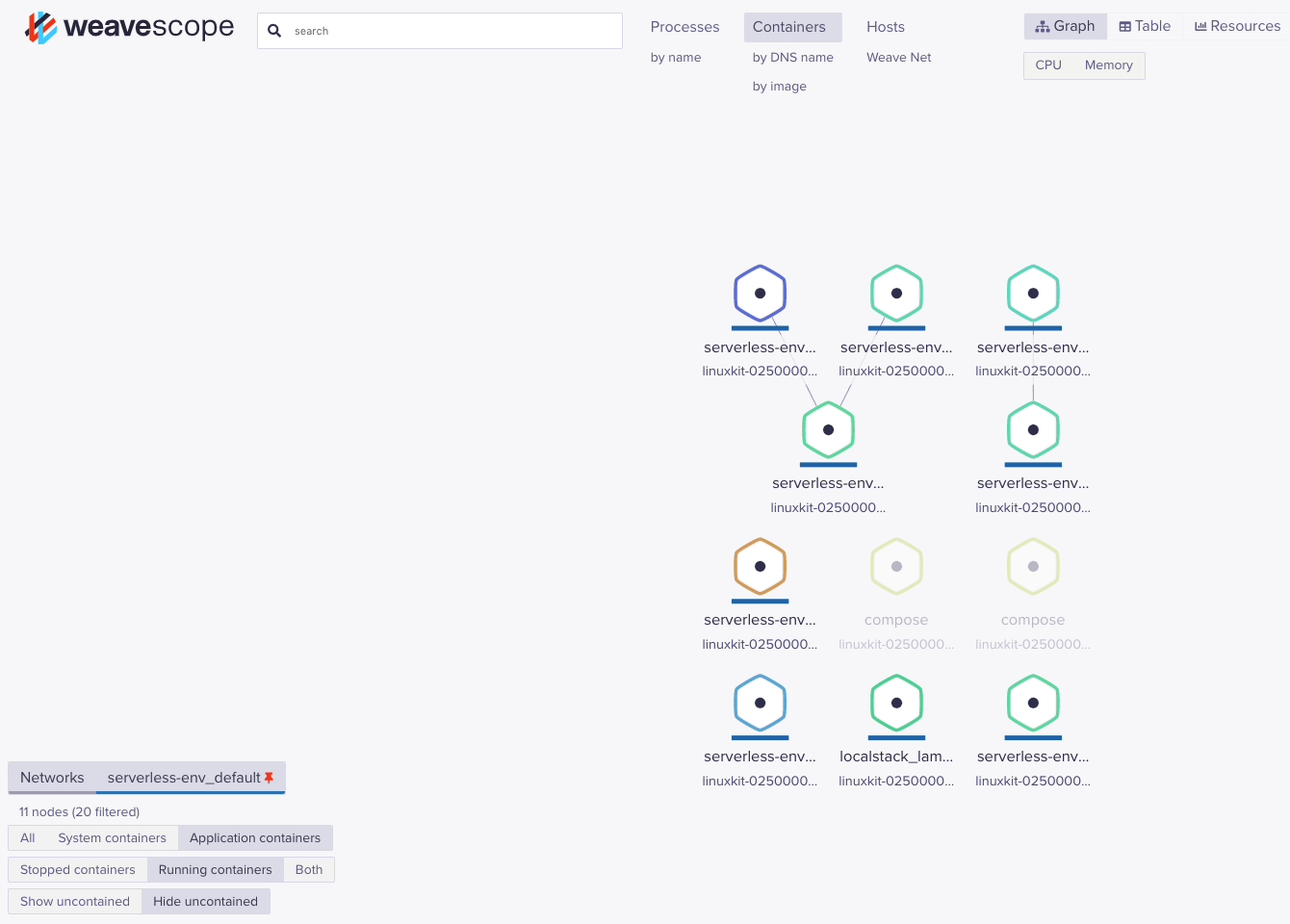
Scope is a powerful Docker infastructure visualisation and querying tool. It exposes a web ui which shows all containers, network connections, volumes, processes, environment variables and much more.
It is especially good at inspecting the connections between services.
If you installed the dev tools using scripts/install-dev-tools.sh or manually installed scope, it is accessible @ http://localhost:4040
Note: You can filter by image name or network to see only the serverless-env environment
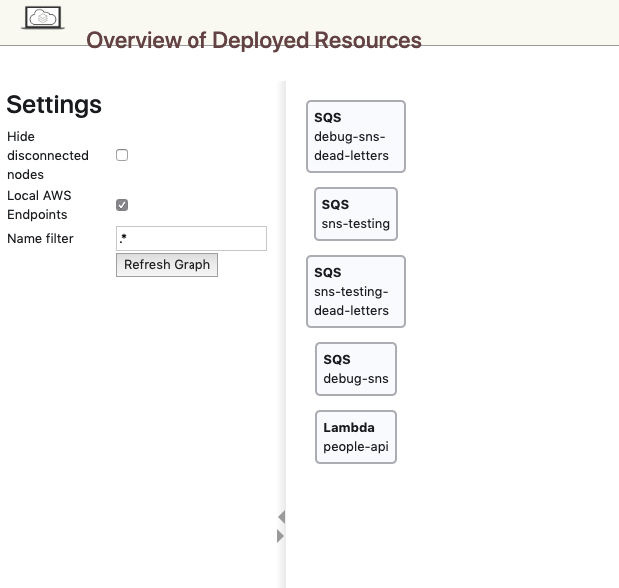
AWS services are provided by the localstack stack, it exposes a simple UI for quickly viewing deployed AWS resources @ http://localhost:8888
All docker applications and lambda functions will produce log files. You can find these @ serverless-env/.volumes/logs
Docker log files are generated by the logging libraries of the applications themselves (log4j, dropwizard etc.) and can be tweaked in the app config files.
By default all Lambda Functions will emit logs to Cloudwatch Logs, which is hosted locally by the aws service.
The lambda_logger service uses the serverless-env/scripts/lambda-logger/monitor-lambda-logs.sh script to poll Cloudwatch, writting log event lines to log files in serverless-env/.volumes/logs/lambda. Each lambda will generate an individual log file.
As described in the Kibana section, an ELK stack is installed locally for you.
The stack is configured to ingest logs from docker apps and lambda functions automatically and index these in elasticsearch.
Below is the workflow for indexing log events:
-
Logs are generated by docker applications and the
lambda_loggerservice (see Lambda) -
Logs files are saved in
serverless-env/.volumes/logs -
The
filebeatservice monitors thelambda&dockerdirectories for new logs files and log file changes (seeserverless-env/config/elk/filebeat.yml) -
filebeatsends these log file events to thelogstashservice, using grok patterns to parse log lines and assign tags (seeserverless-env/config/elk/logstash.conf) -
logstashsends all successfully parsed events to theelasticsearchservice -
At this point data can be manually queried or the
kibanaservice can be used to discover log events
This sections shows how to preform common tasks in the serverless local envrionment.
A convience wrapper around the docker-compose package is in the root directory:
Soft Restart (restart container process):
./docker-compose restart api
Hard Restart (recreate container):
./docker-compose up --force-recreate api
Note: when you restart the aws service you will lose some resources as they only persist in memory
./docker-compose logs api
Tail:
./docker-compose logs --tail 10 api
Follow (can be combined with tail):
./docker-compose logs --follow api
There is a script scripts/get-lambda-logs.sh that will dump out log messages from a Lambda Function using Cloudwatch:
./scripts/get-lambda-logs.sh --function metadata-service
See the --help options for more info on how to tail and watch logs.
Also, logs can be manually queried using the ./aws command line:
./aws logs filter-log-events --log-group-name /aws/lambda/<name-of-lambda>A list of log groups can be found by running:
./aws logs describe-log-groupsRemember that a lambda log group will not be created until the first request for that function is processed
You can open an interactive shell within a service container by running:
./docker-compose exec api /bin/sh
A convience wrapper around the awslocal package is in the root directory:
./aws s3api list-buckets
If you are running OSX a convience script is provided to install tools required:
-
Ensure your
~/.bash_profileor~/.zshrcfile is created (runecho $SHELLto see which shell you are running if unsure) -
Run:
./scripts/install-dev-tools-osx.sh --help
-
This will show you the options available
-
Run the script with your desired options to install your dev tools
If you are on another platform or want to manually install tools, you will need:
| Tool | Version | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| docker | latest | |
| python | latest | |
| pipenv | latest | |
| Weave Scope | latest | Optional, but nice debugging tool (see Visualise Environment) |