Dilated Convolutional Networks Incorporating Soft Entity Type Constraints for Distant Supervised Relation Extraction
Source code for IJCNN 2019 paper: Dilated Convolutional Networks Incorporating Soft Entity Type Constraints for Distant Supervised Relation Extraction
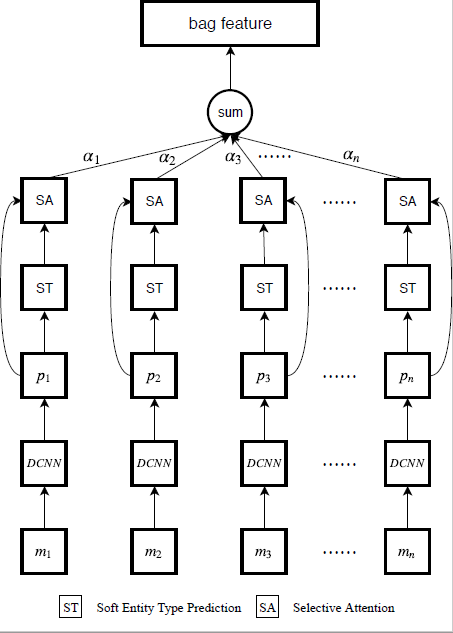
The architecture of our model, where
- Pytorch 1.0.1
- tqdm 4.31.1
- scikit-learn 0.20.3
- Compatible with Python 3.X
- Like the paper "Neural Relation Extraction with Selective Attention over Instances", we use Riedel NYT dataset for evaluation.
- Our dataset can be downloaded from here, and the extraction code is "e9zu".
- Our models can be downloaded from here, and the extraction code is "h37z".
-
Options for preprocessing, traning and testing
All options can be modified in
nre/options.py -
Preprocessing the dataset:
python preprocess.py -
Train the model:
python train.py -batch_size 160 -model_type PDCNN+TATT -gpu_num 1After training, the trained model can be found in
ckptdirectory. -
Test the model:
python test.py -batch_size 160 -model_type PDCNN+TATT -gpu_num 1 -pretrain_model ckpt/model_step_best.pt -
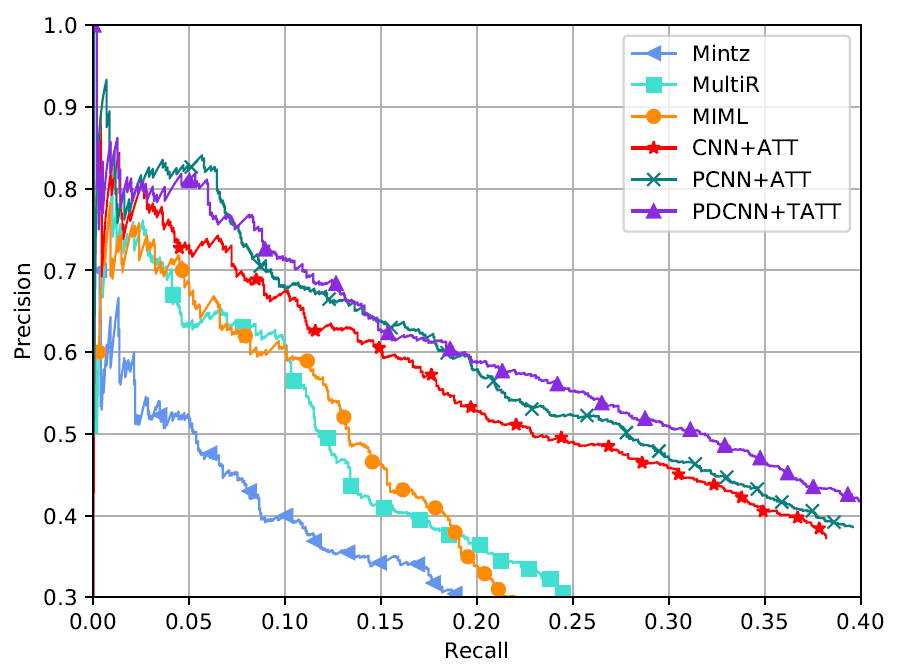
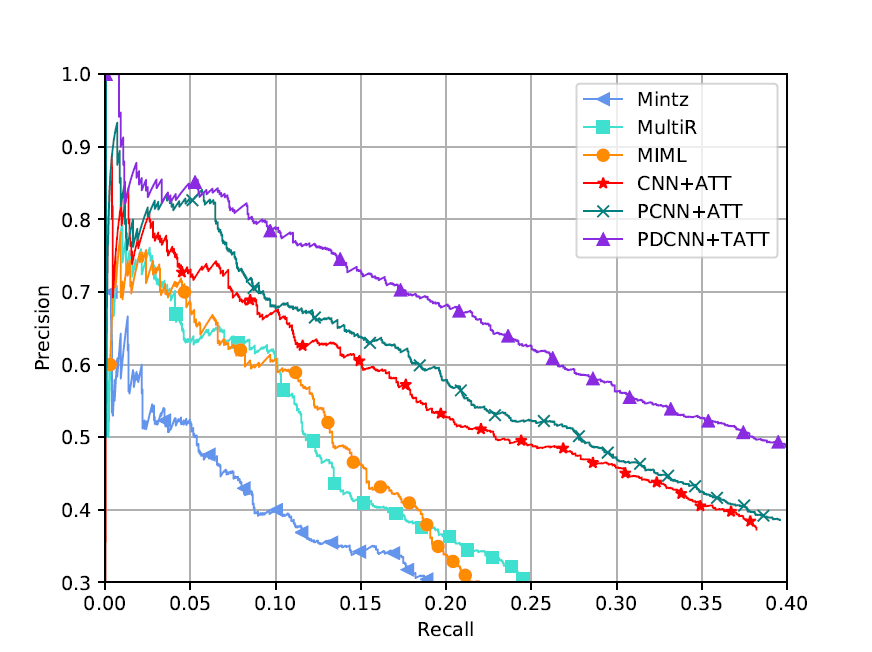
Plot precision-recall curves
python plot_tool.py -pr_data_dir pr_data/baselines
| P@N(%) | 100 | 200 | 300 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN+AVE | 67.3 | 64.7 | 58.1 | 63.4 |
| CNN+ATT | 76.2 | 68.6 | 59.8 | 68.2 |
| PCNN+AVE | 73.3 | 66.7 | 62.8 | 67.6 |
| PCNN+ATT | 76.2 | 73.1 | 67.4 | 72.2 |
| ResCNN-9 | 79.0 | 69.0 | 61.0 | 69.7 |
| DCNN+ATT | 75.2 | 72.1 | 67.0 | 71.5 |
| PDCNN+ATT | 77.2 | 77.6 | 71.4 | 75.4 |
| CNN+TATT | 79.2 | 73.1 | 66.4 | 72.9 |
| PCNN+TATT | 76.2 | 73.1 | 68.4 | 72.6 |
| DCNN+TATT | 77.2 | 70.6 | 72.1 | 73.3 |
| PDCNN+TATT | 80.2 | 76.1 | 70.8 | 75.7 |
We notice the training set used by Lin et al., 2016 has 522,611 sentences, while some recent works used the training set which has 570,088 sentences. For a fair comparison, we also conduct experiments on the latter. The following are the results:
| P@N(%) | 100 | 200 | 300 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDCNN+TATT | 83.2 | 81.1 | 76.4 | 80.2 |
Please cite the following paper if you use this code in your work.
For any clarification, please create an issue or contact huweilong@whu.edu.cn.