pktstat is a simple replacement for ncurses-based pktstat. On Linux platform it uses AF_PACKET, and on other platforms it uses generic PCAP live wire capture. It does not rely on any special/recent Linux kernel features (AF_PACKET is a feature from Linux kernel v2.2, from 1999) and is even cross-compatible with other Unix platforms such as Darwin, since it fallbacks to generic PCAP for non-Linux architectures.
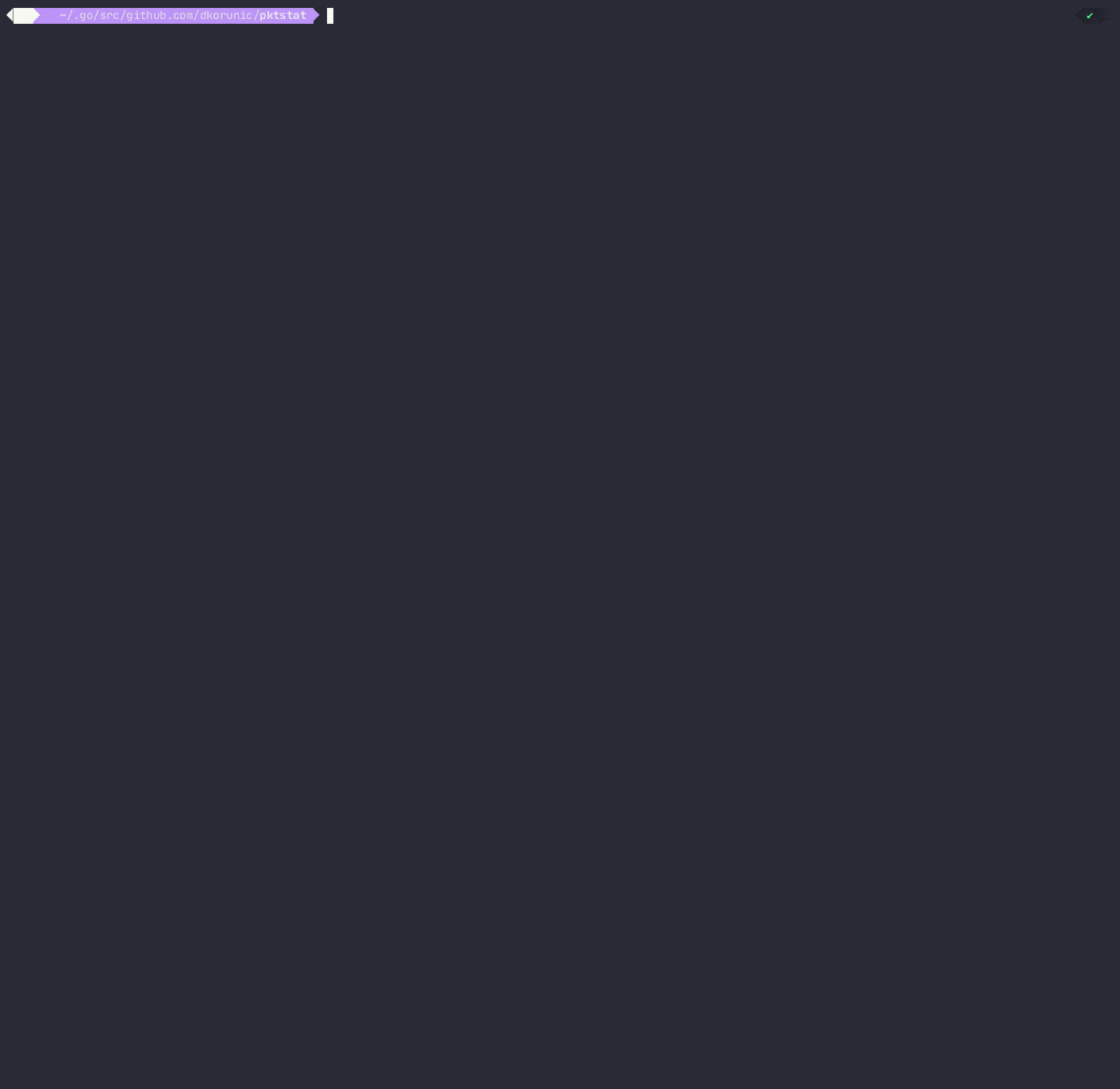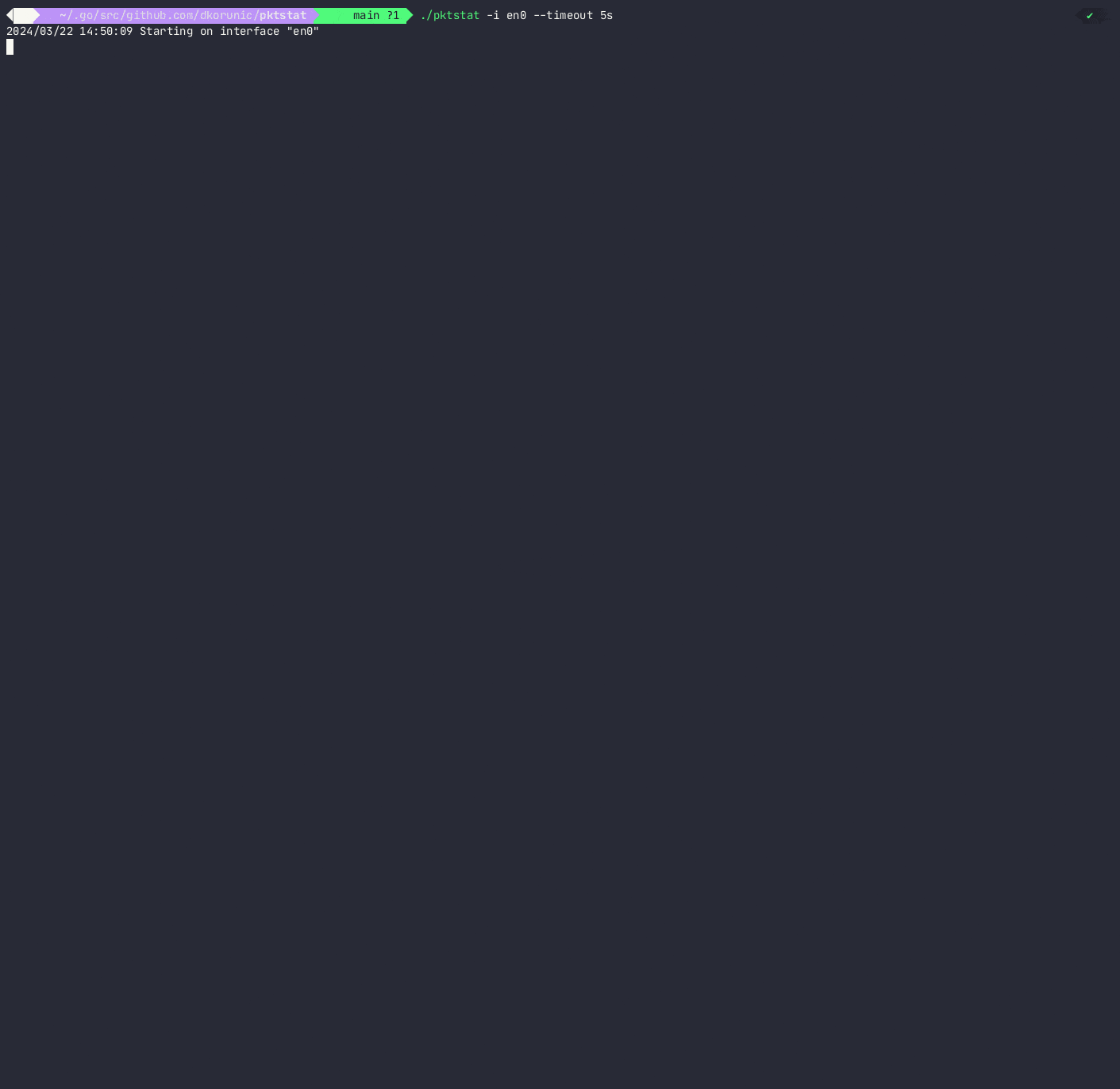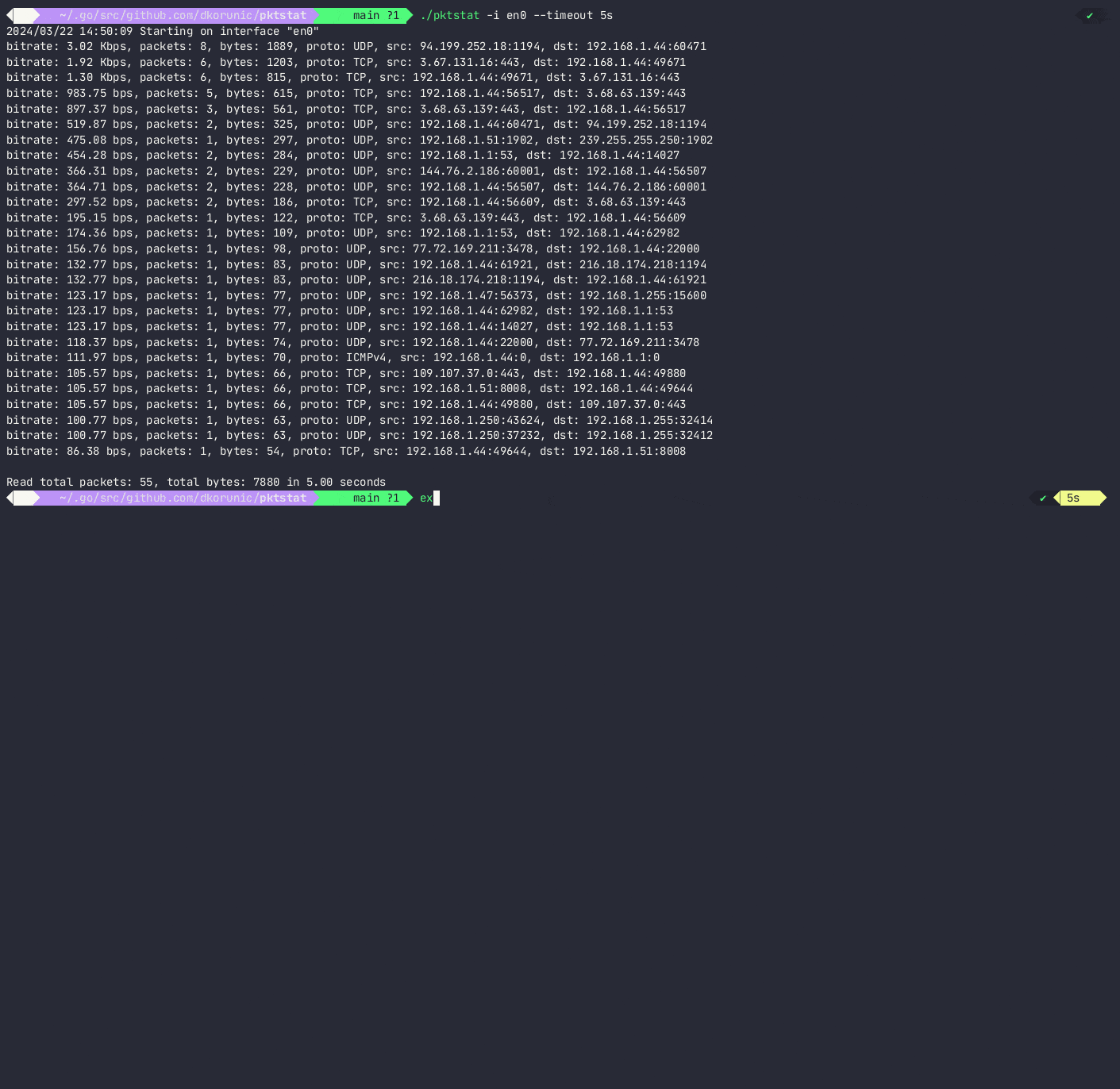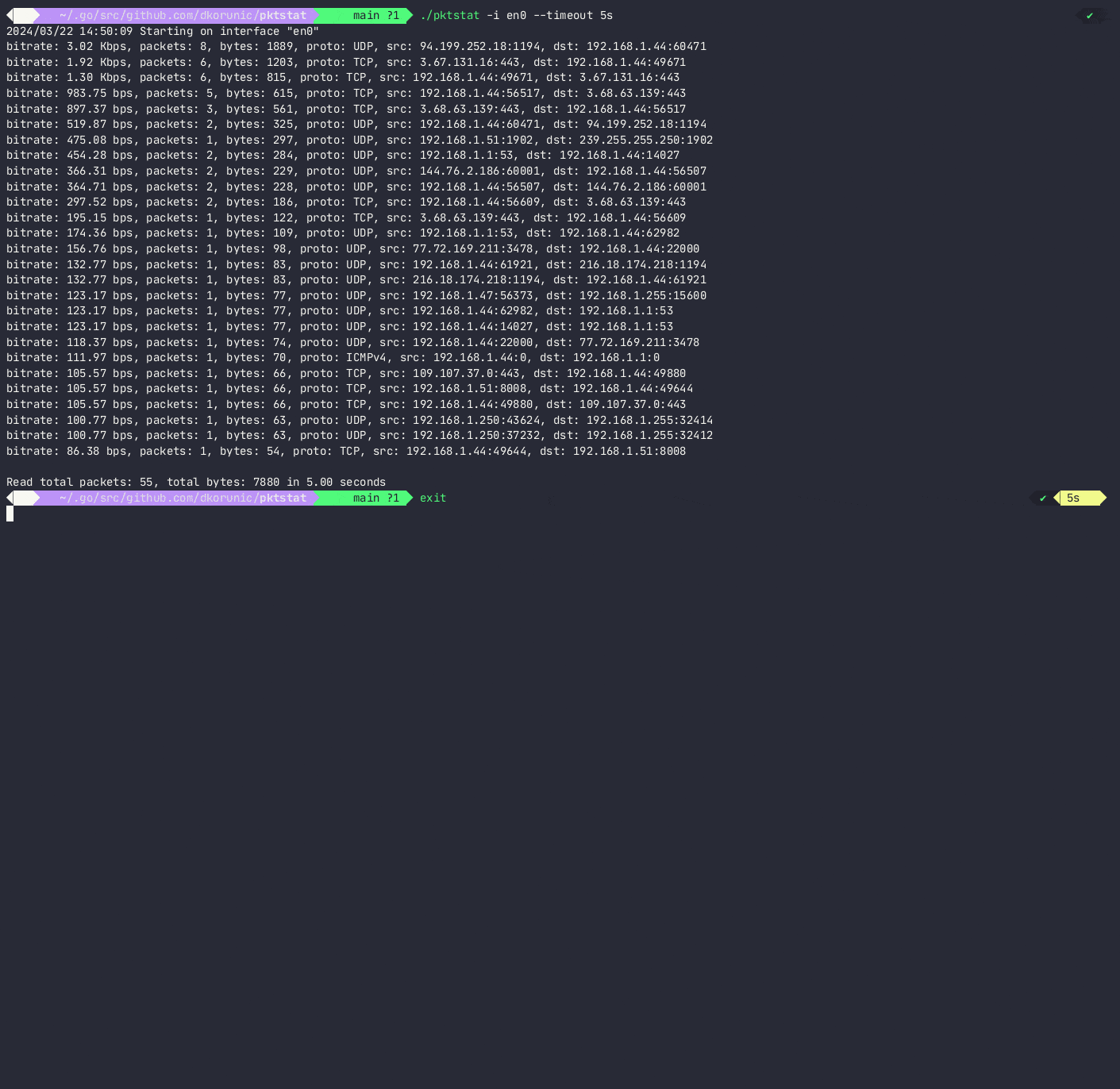
At the end of the execution program will display per-IP and per-protocol (IPv4, IPv6, TCP, UDP, ICMPv4 and ICMPv6) statistics sorted by per-connection bps, packets and (source-IP:port, destination-IP:port) tuples.
Note that typically pktstat with AF_PACKET is reasonably fast and works without packet loss up to several thousand packets per second but for higher traffic volume it is better to use pktstat-bpf solution that is implemented as Linux eBPF program and operates nearly at wire-speed with no impact to the production system and/or no packet loss.
Sniffing traffic typically requires root privileges, but it is also possible to run rootless and set specific CAP_NET_ADMIN and CAP_NET_RAW capabilities:
$ setcap cap_net_raw,cap_net_admin=eip pktstatNAME
pktstat
FLAGS
-?, --help display help
-v, --add_vlan if true, add VLAN header
-j, --json if true, output in JSON format
--version display program version
-s, --snaplen INT snaplen (if <= 0 uses 65535) (default: 0)
-b, --bufsize INT interface buffersize in MB (default: 8)
-f, --filter STRING BPF filter
-i, --iface STRING interface to read from (default: any)
-t, --timeout DURATION timeout for packet capture (default: 0s)By default pktstat listens to all interfaces without any BPF filter. It is possible to specify interface with --iface and specify a BPF filter either including or excluding needed traffic, for instance --filter "not port 22".
Timeout --timeout will stop execution after a specified time, but it is also possible to interrupt program with Ctrl C, SIGTERM or SIGINT.
With --json it is possible to get traffic statistics in JSON format.