gitfw(alias gf)
gitfw is a cli-tool that helps develop make sure the team is all in agreement; to ensure the team is on the same page, an agreed upon Git workflow should be developed or selected.
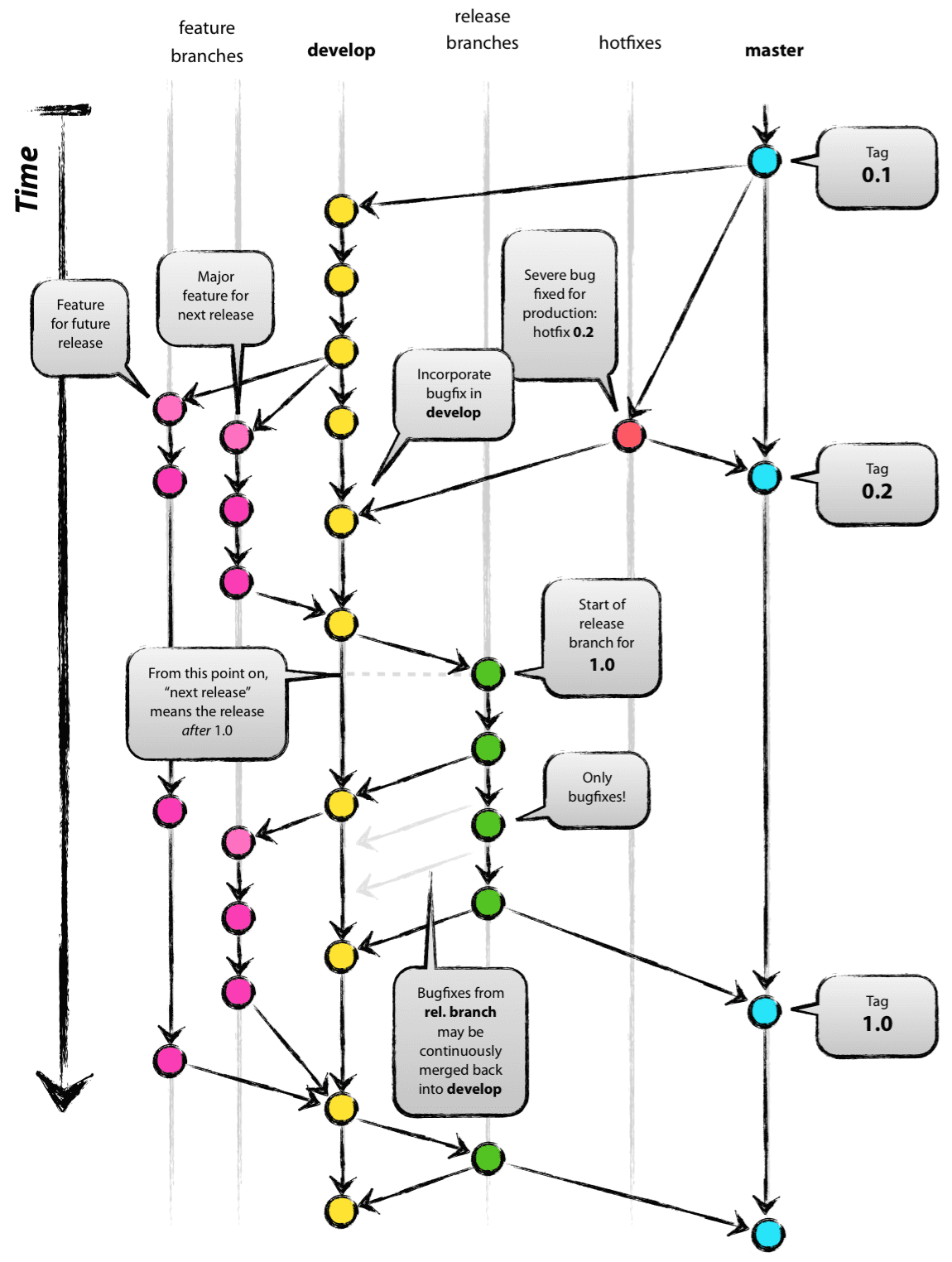
What Is Gitflow Workflow
The overall flow of Gitflow is:
- A develop branch is created from master
- A release branch is created from develop
- Feature branches are created from develop
- When a feature is complete it is merged into the develop branch
- When the release branch is done it is merged into develop and master
- If an issue in master is detected a hotfix branch is created from master
- Once the hotfix is complete it is merged to both develop and master
- Gitflow Workflow Reference article,Thanks
Installation
npm install -g gitfw
or
yarn global add gitfwAnd gitfw will be installed globally to your system path.
Usage
For CLI options, use the -h (or --help) argument:
gitfw -h
Usage: gitfw [options] [command]
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
-h, --help output usage information
Commands:
acmp|cm [options] [msg] one line command commit code
branch|br [brname] [baseBranch] checkout new branch by other branch(default develop branch)
start|s [options] start iterating and branch switching
finsh|f [options] [tagVersion] finsh iterating and branch switching,[tagVersion] is optional, default is the branch name without package prefix, but must be the
same as the version in package.json.1.gitfw acmp [options] [msg]
If you like to submit code using the git command line,gitfw is a fast and convenient way to submit code.as follows:
$ gitfw acmp -h
Usage: acmp|cm [options] [msg]
one line command commit code
Options:
--feat Add new feature
--fix Fix bug, hotfix
--style Document related
--docs Style modification, word modification, formatting, etc.
--refactor Refactor
--perf Improve performance
--test Test related
--chore Business-unrelated modification
--deps upgrade deps
--release Release version
--other Other modification
-h, --help output usage information
for example:
1uickly submit your code with recording and push to remote,now your branch is feature/shopcar_page,and use 'gitfw acmp --feat [msg]' to commit:
Without the gitfw extensions:
$ git add .
$ git commit -m -a 'new shopcar page'
$ git push
When using the gitfw extension:
$ gitfw acmp --feat 'new shopcar page'
* feature/shopcar_page
[feature/shopcar_page 8eaf024] feat: new shopcar page
2 files changed, 91 insertions(+), 2 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 src/shopcar.js
* [new branch] feature/shopcar_page -> feature/shopcar_page
Branch 'feature/shopcar_page' set up to track remote branch 'feature/shopcar_page' from 'origin'.
Everything up-to-date
Operation information:
- origin rmote: shopcar_page
- commit info: feat: new shopcar page
congratulations, we have completed a code submission, then use git log,you can see
feat: new shopcar page
acmp provides the option to submit information prefixes, in order to maintain a consistent submission format and distinguish the type of modification for each commit.For more details, use 'gitfw acmp -h' for instructions.
2.gitfw branch|br [options] [brname] [baseBranch]
$ gitfw branch -h
Usage:
checkout new branch by other branch(default develop branch)
$ gitfw branch hotfix/fix_style master
Switched to branch 'master'
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/master'.
Already up to date.
Switched to a new branch 'hotfix/fix_style'
3.gifs start|s [options]
$ gitfw start -h
Usage: start|s [options]
start iterating and branch switching
Options:
-f, --feature <name> Branch prefixed with feature
-x, --hotfix <name> Branch prefixed with hotfix
-r, --release <name> Branch prefixed with release
-h, --help output usage information
for example:
creating a feature/shopcar_page branch
$ gitfw start -f shopcar_page
witched to a new branch 'feature/shopcar_page'
Operation information:
- Check out a branch 'feature/shopcar_page' on 'develop' branch
- You are now on branch 'feature/shopcar_page'
4.gifs finsh|f [options]
$ gitfw finsh -h
Usage: finsh|f [options] [tagVersion]
finsh iterating and branch switching,[tagVersion] is optional, default is the branch name without package prefix, but must be the same as the version in package.json.
Options:
-f, --feature <name> Branch prefixed with feature
-x, --hotfix <name> Branch prefixed with hotfix
-r, --release <name> Branch prefixed with release
-h, --help output usage information
for example:
finsh a feature branch
gitfw finsh -f shopcar_page
Switched to branch 'develop'
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/develop'.
Already up to date.
Everything up-to-date
Deleted branch feature/shopcar_page (was 1a34759).
Operation information:
- merge the feature/shopcar_page into develop;
- delete branch feature/shopcar_page
How it works
1.Feature Branches
feature branches use develop as their parent branch. When a feature is complete, it gets merged back into develop;
Creating a feature branch
Without the gitfw extensions:
$ git checkout develop
$ git checkout -b feature/shopcar_page
When using the gitfw extension:
$ gitfw start -f shopcar_page
When you’re done with the development work on the feature, the next step is to merge the feature/shopcar_page into develop.
Finishing a feature branch
Without the gitfw extensions:
$ git checkout develop
$ git merge feature/shopcar_page
Using the gitfw extensions:
$ git flow feature finish shopcar_page
2.Release Branches
Using a dedicated branch to prepare releases makes it possible for one team to polish the current release while another team continues working on features for the next release. It also creates well-defined phases of development (e.g., it's easy to say, “This week we're preparing for version 0.1.0,” and to actually see it in the structure of the repository).
Making release branches is another straightforward branching operation. Like feature branches, release branches are based on the develop branch. A new release branch can be created using the following methods.
Creating a realse branch
Without the git-flow extensions:
$ git checkout develop
$ git checkout -b release/0.1.0
When using the git-flow extensions:
$ gitfw start -r 0.1.0
To finish a release branch, use the following methods:
Finishing a release branch
Without the gitfw extensions:
$ git checkout develop
$ git merge release/0.1.0
$ git checkout master
$ git merge release/0.1.0
$ git tag -a 0.1.0 -m 'my version 0.1.0'
$ git push origin 0.1.0
Or with the gitfw extension:
$ gitfw finsh -r '0.1.0'
3.HotFix Branches
Maintenance or “hotfix” branches are used to quickly patch production releases. Hotfix branches are a lot like release branches and feature branches except they're based on master instead of develop. This is the only branch that should fork directly off of master. As soon as the fix is complete, it should be merged into both master and develop (or the current release branch), and master should be tagged with an updated version number.
Creating a hotfix branch
Without the gitfw extensions:
$ git checkout master
$ git checkout -b hotfix/fix_pay_error
When using the git-style extensions:
$ gitfw start -x fix_pay_error
To finish a release branch, use the following methods:
Finishing a hotfix branch
Without the gitfw extensions:
$ git checkout develop
$ git merge hotfix/fix_pay_error
$ git checkout master
$ git merge hotfix/fix_pay_error
$ git tag -a 0.1.0 -m 'my version 0.1.0'
$ git push origin 0.1.0
$ git branch -D hotfix/fix_pay_error
Or with the gitfw extension:
$ gitfw finsh -x fix_pay_error 0.1.1
Summary
Here we discussed the Gitflow Workflow. Gitflow is one of many styles of Git workflows you and your team can utilize. Some key takeaways to know about Gitflow are: The workflow is great for a release-based software workflow. Gitflow offers a dedicated channel for hotfixes to production.