This tool makes building 3D printed custom split keyboard cases (and plates) easy, if you can use Inkscape, you can build a keyboard case.
You must have Inkscape and OpenSCAD installed, that's it!
All the work is done in template.svg using Inkscape.
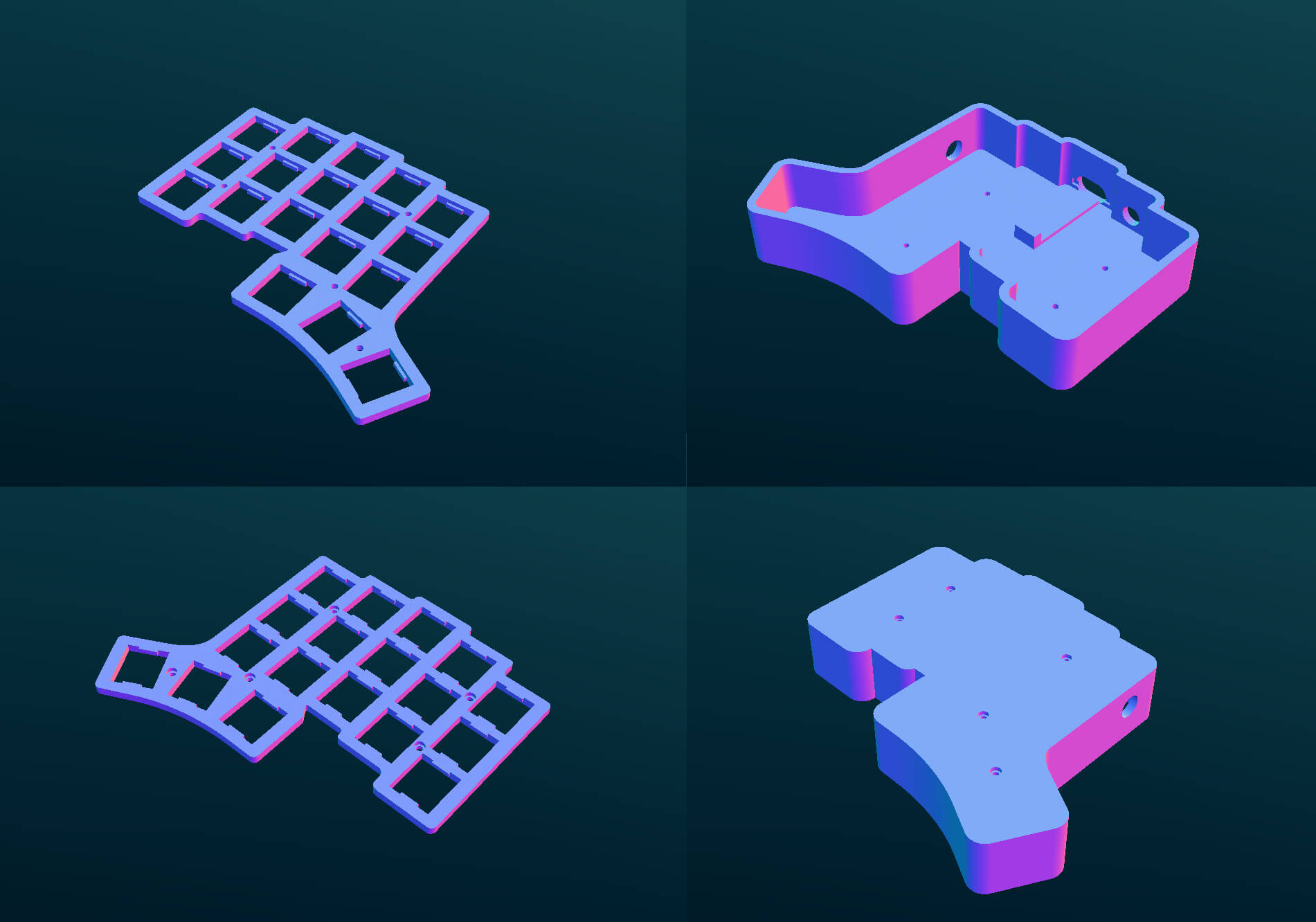
We need to create and export four SVG files from the template, kb_plate_locking.svg makes up the top half of the key plate that the switches can lock into, kb_plate_open.svg makes the bottom half of the plate, kb_case_wall.svg is the walls of the case, kb_case_bottom is the inside bottom of the case, and kb_case_bottom_outer is the counter-sunk portion of the case bottom. These four SVG files will be converted by OpenSCAD to two STL files, case and plate. You'll need some 8mm or 10mm standoffs and 2mm screws to attach the plate to the case.
- Key Layout - Clone the "keycode with clearance" to layout your keys, the black boxes should be touching but not overlapping.
kb_plate_locking.svg- Clone the layout, draw an outline around all the keys with the pen tool, this is the plate part of the case where the switches mount (use the "Corners" path effect to round out the edges if desired, make sure to do "path" > "object to path" after). Add counter-sunk screw holes between the keyholes, the "screw hole" bit in the template is for 2mm machine screws, adjust it as needed.kb_plate_open.svg- Clone the plate locking part you just made, you can now ungroup all the "keycode with clearance" parts (ctrl+a to select all, ctrl+shift+g to ungroup), delete everything except "keyhole locking" from the plate locking part, and everything but the "keyhole open" from the plate open part. Switch the counter-sunk screw holes with non counter-sunk.kb_case_wall.svg- Clone the plate bottom outline and screw holes, use the "offset" path effect with a value of 1mm, this gives the plate a little bit of room to fit into the inner wall of the case, then do "path" > "object to path". Clone the outline in place with "ctrl + d" to make the outer wall of the case, then do another offset of 3mm, for the width of the case wall, "path" > "object to path" again on that one. (we will delete the screw holes after the next step, but we need them for the case bottom).kb_case_bottom.svg- Clone the case wall and delete the inner outline, delete the screw holes from the case wall.kb_case_bottom_outer.svg- Clone case bottom, swap the screw holes with the counter sunk ones.- For each part created above, clone it, run "path" > "object to path", then "path" > "combine", then "file" > "export", choose "selection", choose "svg" for the filetype, and save to the
srcfolder with the appropriate filename.
- Run
build.shto create STL files in theoutputfolder, or open the OpenSCAD files to tweak parameters and export STL files manually.- Note: If the ports in the case don't line up, you'll need to adjust their location in OpenSCAD via parameters.
- You'll need to mirror both parts to print the other half for split keyboards, you can do this with modern slicers such as PrusaSlicer.
- Print them up and build yourself a keyboard!
show_voids: If true will show ports and slots as solids for assistance in positioning (because you can't see voids if they're outside the part body), set to false to make them voids for printingwall_height: Height of the case wall, should be above the plate so bottom of keycaps sit flush, default value of20.6works well with 8mm standoffsbottom_thickness: Thickness of the case bottom, the last 1.5mm will be the counter-sunk portion, so the total screw hole depth isbottom_thickness- 1.5mmcontroller_pcb_axis_rotation: PCB mount, Set to0for back or front,90for left or right sidecontroller_pcb_x_offset: PCB mount, move left or right in planecontroller_pcb_y_offset: PCB mount, move forward or backward in planecontroller_pcb_thickness: Thickness of PCB, the default should work fine for most boardscontroller_pcb_width: Width of PCB, the default is Pro Micro / Elite-C sizecontroller_pcb_length: Length of PCB, the default is Pro Micro / Elite-C sizecontroller_pcb_riser_width: PCB riser, this gives clearance for solder joints on the bottom of PCB, lower number here gives more clearance on the sidescontroller_pcb_riser_height: PCB riser, higher number here gives more clearance underneathcontroller_pcb_plug_depth: Controls how deep into the case wall to cut for the USB port to be flush, higher number here is a deeper cut (closer to outside wall)controller_usb_port_width: Width of USB port openingcontroller_usb_port_height: height of USB port openingcontroller_usb_port_depth: Length of USB port opening (void)trrs_jack_hole_size: Diameter of hole for TRRS jacktrrs_jack_axis_rotation: Set to0for back or front,90for left or right sidetrrs_jack_x_offset: Move TRRS jack hole left or right in planetrrs_jack_y_offset: Move TRRS jack hole forward or backward in planetrrs_jack_z_offset: Move TRRS jack hole up or down in planereset_button_hole_size: Diameter of reset button holereset_button_axis_rotation: Set to0for back or front,90for left or right sidereset_button_x_offset: Move reset button hole left or right in planereset_button_y_offset: Move reset button hole forward or backward in planereset_button_z_offset: Move reset button hole up or down in plane