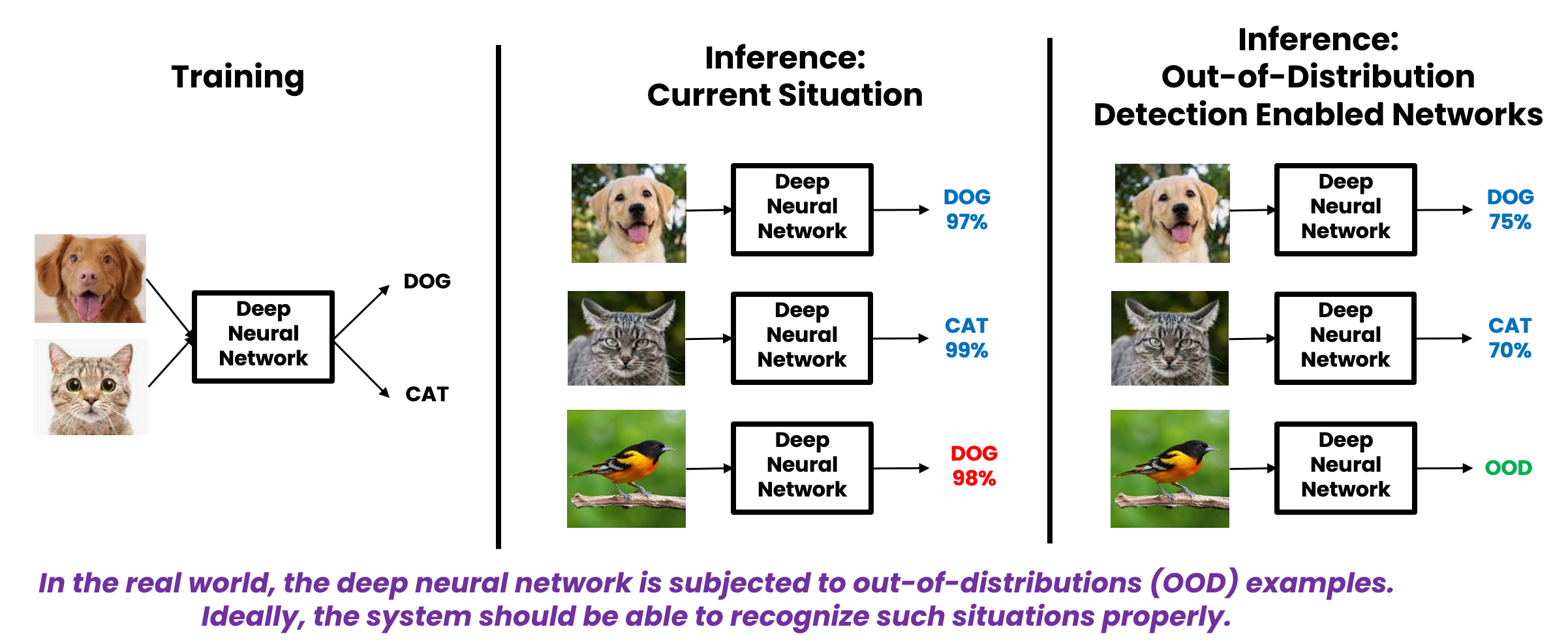
TRAIN OR FINE-TUNE
Train your model from scratch or fine-tune a pretrained model using the losses provided in this library to improve out-of-distribution detection and uncertainty estimation performances.
CALIBRATE
Calibrate your model to produce enhanced uncertainty estimations.
DETECT
Detect out-of-distribution data using the defined score type and threshold.
- Model Independent:
Use models from timm library or whatever you want.
- Data Independent:
Most cases work for any type of media (e.g., image, text, audio, and others).
- Large-Scale Models and Data:
Train using large-scale models and data (e.g., ImageNet).
- Efficient Inferences:
The trained models are as efficient as the ones trained using the cross-entropy loss.
- Hyperparameter-Free:
There is no hyperparameter to tune. "You only train once" (YOTO).
- Standard Interface:
Use the same API to train models with improved robustness using different losses.
- No Need for Additional Data:
The losses used in this library do not require collecting or using additional data.
- Temperature Calibration:
Calculate the Uncertainty Estimation and update the temperature of the output last layer.
- Scalability: More data, Bigger Models, Better Results!
Entropic losses perform better and better as the size of the data and model increase.
- Threshold Computation:
Compute the threshold for deciding regarding out-of-distribution examples.
- Scores Computation:
Compute the scores opting from a set of many different types available.
- Detect Out-of-Distribution:
Detect out-of-distribution examples using the computed scores.
- State-of-the-art:
SOTA results for out-of-distribution detection and uncertainty estimation.
| Loss [Score] | Class (ACC) | Near OOD (AUROC) |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Entropy [MPS] | 69.9 | 52.4 |
| DisMax [MMLES] | 69.6 | 75.8 |
pip install robust-deep-learning# Import the robust deep learning library as rdl
import robust_deep_learning as rdl
#####################################################################################################
#####################################################################################################
# Training or Fine-tuning
#####################################################################################################
#####################################################################################################
#########################################################
# Option 1: Creating a custom model and defining the loss
#########################################################
# Create from a model definition file.
# For example, import a class "Model" from a model definition file.
model = Model()
# Load a pretrained model if fine-tuning rather than training from scratch (random weights).
# model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pre_trained_file_name, map_location="cuda:" + str(args.gpu)))
# Chance the output last layer of the model with the desired loss first part.
# If the name of the output last layer of the model is unknown, print it with "print(model)".
# For example, if the output last layer is called "classifier":
# "model.classifier = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)"
# Then, replace this output layer (usually a linear layer) by adding the following line:
model.classifier = rdl.DisMaxLossFirstPart(num_features, num_classes)
# Replace the Cross-Entropy Loss.
# The first argument is the name of the output last layer of the model used above.
# In case of training using a not too constrained model on image data, pass an add-on.
# Currently, only DisMax has one add-on called "FPR".
# Otherwise, do not pass add-on or simple pass "add_on=None".
criterion = rdl.DisMaxLossSecondPart(model.classifier, add_on="FPR", gpu=None)
#######################################################
# Option 2: Creating a timm model and defining the loss
#######################################################
# For using a model from timm lib, use "create_model" functionality.
# It is possible to start from a pretrained model to fine-tune using the desired loss.
model = timm.create_model('resnet18', pretrained=False)
# Chance the output last layer of the model with the desired loss first part.
# If the name of the output last layer of the model is unknown, print it with "print(model)".
# For example, if the output last layer is called "fc":
# "model.fc = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)"
# Then, replace this output layer (usually a linear layer) by adding the following line:
model.fc = rdl.DisMaxLossFirstPart(model.get_classifier().in_features, num_classes)
# Replace the Cross-Entropy Loss.
# The first argument is the name of the output last layer of the model used above.
# In case of training using a not too constrained model on image data, pass an add-on.
# Currently, only DisMax has one add-on called "FPR".
# Otherwise, do not pass add-on or simple pass "add_on=None".
criterion = rdl.DisMaxLossSecondPart(model.fc, add_on="FPR", gpu=None)
############################
# Checking the training loop
############################
for epoch in epochs:
# Training loop
for inputs, targets in in_data_train_loader:
# In the training loop, add the line below for preprocessing before forwarding.
# This is only required if using add_on other than None. Otherwise, this line is not needed.
inputs, targets = criterion.preprocess(inputs, targets)
# The three below lines are usually found in the training loop!
# These lines must not be changed!
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
loss.backward()
#####################################################################################################
#####################################################################################################
# Uncertainty Estimation
#####################################################################################################
#####################################################################################################
#############
# Calibrating
#############
# Get outputs, labels, accuracy, expected calibration error (ECE), and negative log-likelihood (NLL).
results = rdl.get_outputs_labels_and_metrics(model, in_data_val_loader, gpu=None)
# Calculate probabilities and verify the values returned above.
probabilities = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=1)(results["outputs"])
print(probabilities)
print(results["acc"], results["ece"], results["nll"])
# Calibrate the temperature passing the output last layer, the model, and the validation set.
# Choose the metric to optimize. For example, "ECE" (the only option for now).
rdl.calibrate_temperature(model.classifier, model, in_data_val_loader, optimize="ECE", gpu=None)
#rdl.calibrate_temperature(model.fc, model, in_data_val_loader, optimize="ECE")
# Verify the novel value of the temperature of the output last layer.
print(model.classifier.temperature)
######################
# Verifing calibration
######################
# Get the results again using the calibrated model.
results = rdl.get_outputs_labels_and_metrics(model, in_data_val_loader, gpu=None)
# Verifiy the probabilities, ECE, and NLL are improved regarding the now calibrated model.
probabilities = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=1)(results["outputs"])
print(probabilities)
print(results["acc"], results["ece"], results["nll"])
####################################################################################################
####################################################################################################
# Out-of-Distribution Detection
####################################################################################################
####################################################################################################
########################
# Estimating performance
########################
# Define a score type. Typically, the best/recommended option for the loss you are using.
score_type = "MMLES"
# Evaluate the out-of-distribution detection performance passing loaders.
ood_metrics = rdl.get_ood_metrics(
model, in_data_val_loader, out_data_loader, score_type, fpr=0.05, gpu=None)
# Optionally, first get in-data scores:
results = rdl.get_outputs_labels_and_metrics(model, in_data_val_loader, gpu=None)
in_data_scores = rdl.get_scores(results["outputs"], score_type)
# Second, get out-data scores:
results = rdl.get_outputs_labels_and_metrics(model, out_data_loader, gpu=None)
out_data_scores = rdl.get_scores(results["outputs"], score_type)
# Then, finally, evaluate the out-of-distribution detection performance passing scores.
ood_metrics = rdl.get_ood_metrics_from_scores(in_data_scores, out_data_scores, fpr=0.05)
######################################
# Detecting (still testing this part))
######################################
# Before detecting, it is necessary to compute the thresholds.
thresholds = rdl.get_thresholds(model, in_data_val_loader, score_type, gpu=None)
# Optionaly, it is possible to compute the threshold using in-data scores.
#thresholds = rdl.get_thresholds(results["outputs"], score_types="MMLES")
thresholds = rdl.get_thresholds_from_scores(in_data_scores) # guarder
# After calculating thresholds, detection may be performed.
# Some test input may be obtained using: input = next(iter(in_data_val_loader))
ood_detections = rdl.get_ood_detections(model, inputs, thresholds, fpr="0.05", gpu=None)The following losses are implemented:
- Isotropy Maximization Loss arXiv conference version journal version
- Enhanced Isotropy Maximization Loss arXiv
- Distiction Maximization Loss arXiv
The following scores are implemented:
- Maximum Probability Score
- Entropic Score arXiv conference version journal version
- Minimum Distance Score arXiv
- Maximum Mean Logit Entropy Score arXiv
Install the requirements to reproduce the experiments of this library:
pip install -r requirements.txtPlease, move to the data directory and run all the prepare data bash scripts:
# Download and prepare out-of-distrbution data for CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 datasets.
./prepare-cifar.sh
# Download and prepare out-of-distrbution data for ImageNet.
./prepare-imagenet.shRun the experiments:
./run_cifar100_densenetbc100.sh*
./run_cifar100_resnet34.sh*
./run_cifar100_wideresnet2810.sh*
./run_cifar10_densenetbc100.sh*
./run_cifar10_resnet34.sh*
./run_cifar10_wideresnet2810.sh*
./run_imagenet1k_resnet18.sh*Analize the results:
./analize.shPlease, cite our papers if you use our losses in your work:
@INPROCEEDINGS{9533899,
author={Macêdo, David and Ren, Tsang Ing and Zanchettin, Cleber and Oliveira,
Adriano L. I. and Ludermir, Teresa},
booktitle={2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)},
title={Entropic Out-of-Distribution Detection},
year={2021},
pages={1-8},
doi={10.1109/IJCNN52387.2021.9533899}
}@ARTICLE{9556483,
author={Macêdo, David and Ren, Tsang Ing and Zanchettin, Cleber and Oliveira,
Adriano L. I. and Ludermir, Teresa},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems},
title={Entropic Out-of-Distribution Detection:
Seamless Detection of Unknown Examples},
year={2022},
volume={33},
number={6},
pages={2350-2364},
doi={10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3112897}
}@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-2105-14399,
author = {David Mac{\^{e}}do and
Teresa Bernarda Ludermir},
title = {Enhanced Isotropy Maximization Loss:
Seamless and High-Performance Out-of-Distribution Detection
Simply Replacing the SoftMax Loss},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2105.14399},
year = {2021},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.14399},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2105.14399},
timestamp = {Wed, 02 Jun 2021 11:46:42 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-2105-14399.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-2205-05874,
author = {David Mac{\^{e}}do and
Cleber Zanchettin and
Teresa Bernarda Ludermir},
title = {Distinction Maximization Loss:
Efficiently Improving Out-of-Distribution Detection and Uncertainty Estimation
Simply Replacing the Loss and Calibrating},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2205.05874},
year = {2022},
url = {https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2205.05874},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2205.05874},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2205.05874},
timestamp = {Tue, 17 May 2022 17:31:03 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-2205-05874.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-2208-03566,
author = {David Mac{\^{e}}do},
title = {Towards Robust Deep Learning using Entropic Losses},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2208.03566},
year = {2022},
url = {https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2208.03566},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2208.03566},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2208.03566},
timestamp = {Wed, 10 Aug 2022 14:49:54 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-2208-03566.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}