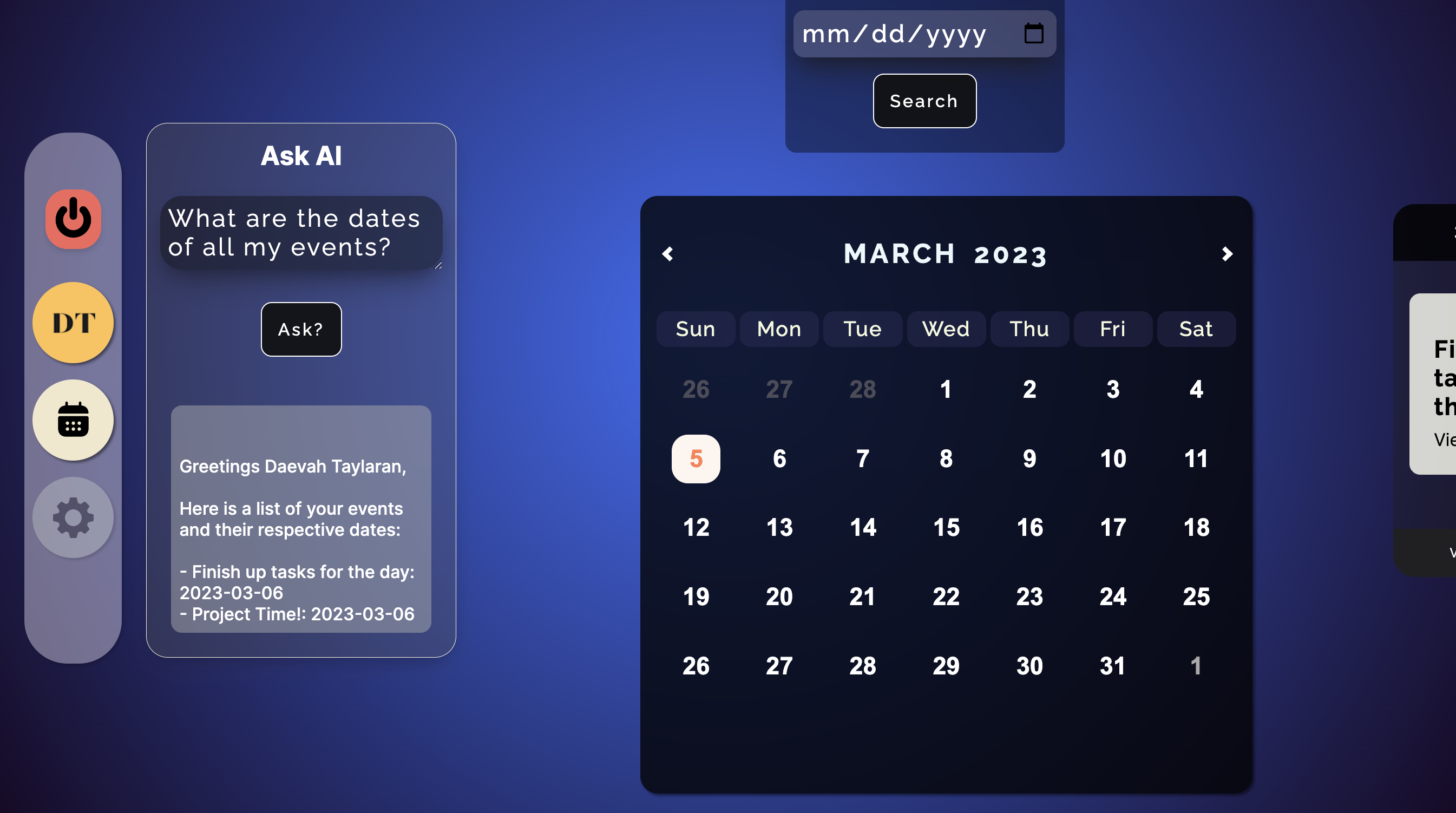
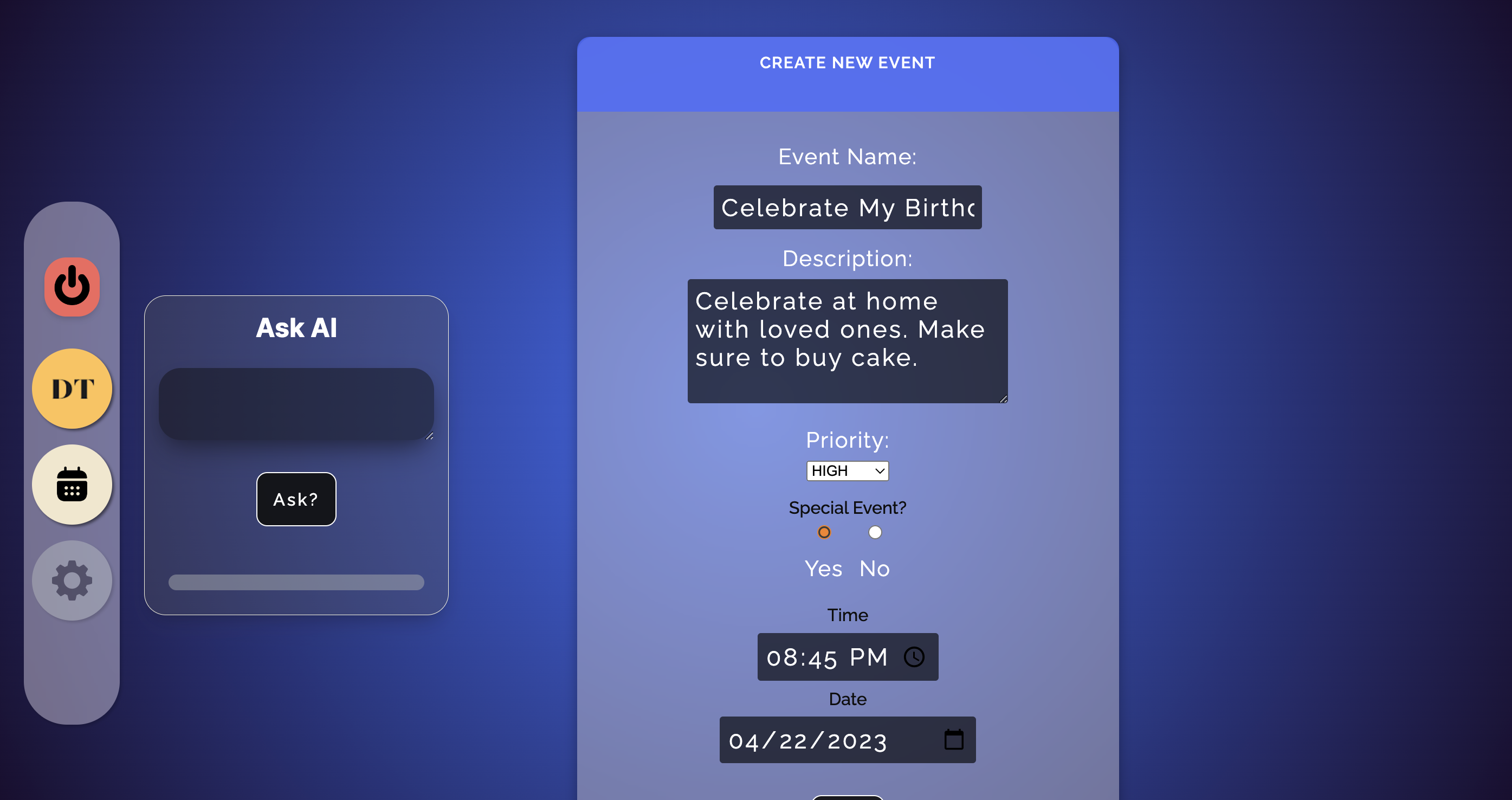
A simple task management application, where users are able to manage events/tasks by utilizing a calendar view, as well as input dates, and access their data using an AI assistant. In addition to being able to manually create, read, update, and delete personal events, the AI assistant is able to suggest events, locations, and retrieve the user's data according to user's commands.
- Navigation bar allows for easy navigation between calendar view, day view, settings, and log out
- Allows users the option to delete all their events saved in the application
- Change main background color of the app
- Allows users to view the calendar, interact with the calendar and view their personal events upon clicking on a day on the calendar.
- User can interact with the calendar to change the months and years accordingly
- A Date input is provided as an alternate option to look for a specific date
- The current day is highlighted on the calendar
- Users are able to view and create an event for any day of the year
- A Day View allows users to edit, delete, and create more events
- High priority and special events are given their own section on the day view
- Users are able to request their events from a virtual assistant, as well as ask it for suggestions and any other questions that could better assist a user in managing events, ideas, and plans.
- JavaScript
- HTML
- CSS
- NodeJS
- Express
- MongoDB, Mongoose
- Vanilla Calendar API
- OpenAI API
- Add additional task types, where users are able to check off a list of tasks if completed
- Give users the option to specify deadlines
- Give users the option to create tags to include as an option to events for better organization of events/tasks
- Sort events in ascending and descending order
- Able to utilize grabbing the document’s URL to perform get requests
- The Vanilla Calendar API I used had a built in setting that allows developers to set specific months and years
- A blocker I had earlier was that the calendar would re-render back to the current month after clicking a day on another month
- Solution: used document.URL and implemented the split method, to access the target month and year, to display on the calendar every new render
settings: {
selected: {
month: document.URL.split('date').length === 1 ? new Date().getMonth() : document.URL.split('date')[1].split('-')[1] - 1,
year: document.URL.split('date').length === 1 ? new Date().getFullYear() : Number(document.URL.split('date')[1].split('-')[0].slice(1))
}- I had to find a way around using import statement on Express. Easier to implement once we transition to using the React front end library, but for now, I was able to load the calendar using the script tags on the header.ejs partial
- Performed a GET request using the dates attribute that the calendar library provided and jquery's $.get() method to GET a show preview of the day clicked on the calendar
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', (e) => {
const calendar = new VanillaCalendar('#calendar', {
actions: {
clickDay(event, dates) {
event.target.setAttribute("type", "submit");
$.get(`/dashboard/show?date=${dates}`, function(data, status) {
window.location = `/dashboard/show?date=${dates}`;
})
}- Saw firsthand how much more efficient task management can be when there is immediate assistance that can help gather information, give suggestions, and provide specific data
- The process of setting up configuration and storing API keys in a .env file for OpenAI was very similar to the configuration proccess of Google OAuth 2.0 and MongoDB
- Initially had some blockers with finding out how to receive the response from the virtual assistant once performing a POST request to the API, using the input textarea to provide a prompt to the OpenAI on the client side
<h2>Ask AI</h2>
<form action="<%=url%>" method="POST" class="flex-col">
<textarea type="text" name="message"></textarea>- On the server side, I was able to specify the role of the AI model, as a personal assistant that can make suggestions and retrieve the user's events if asked for them. OpenAI API allows developers to fine tune the prompt for the AI model.
askGPT: async (req) => {
let user = req.user;
let events = await Event.find({user: req.user});
let today = new Date();
let message = req.body.message;
const response = await openai.createCompletion({
model: "text-davinci-003",
prompt: `You are a personal assistant. Give suggestions, locations, tasks, events if asked. Present lists in a bullet format. Greet with a message for ${user}. Look up ${events} and its properties if asked. Refer to ${today} if asked about date or time. >${message}?`,
max_tokens: 300,
temperature: 0.45,
});
if (response.data) {
if (response.data.choices) {
return response;
}