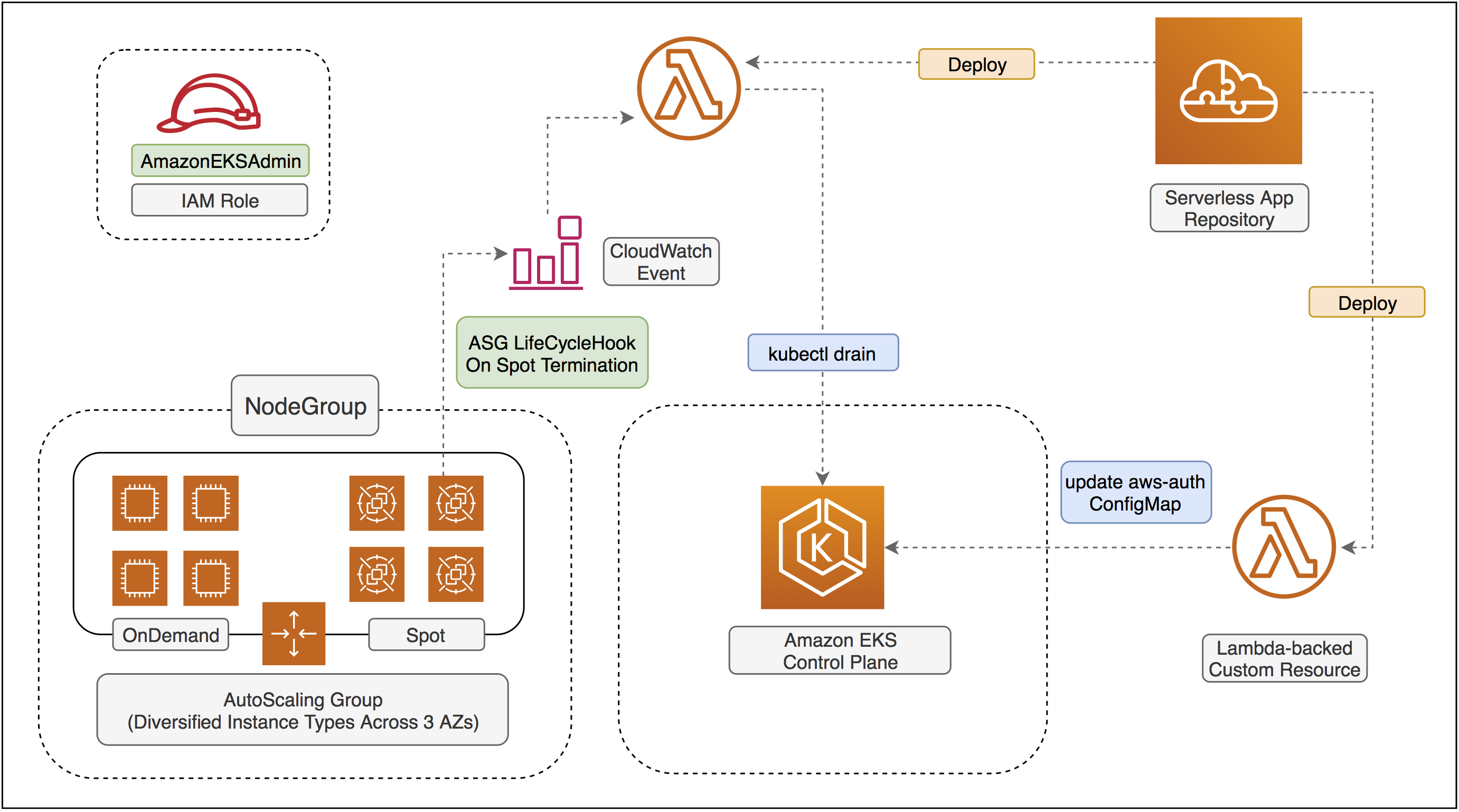
Reference architecture of Amazon EKS with modern cloudformation templates.
This project aims to help you provision a ready-to-use Amazon EKS cluster by simply launching a cloudformation template with nested stacks. Supper easy and hassel-free!
- Creates both Amazon EKS
clusterandNodeGroupin a single cloudformatoin template with nested stacks. - Abstracts away the CLI control in the
Makefile- simplymake create-eks-cluster,make update-eks-clusterandmake delete-eks-cluster. That's all. - Fully support the latest Autoscaling Group features to hybrid on-demand and spot instances with mixed types and purchase options.
- The cloudformation stack will help you automate the configuration on
aws-auth-cmConfigMap with AWS Lambda-backedcustom resource. - No need to provision SpotFleet anymore.
- On-demand instances will have node label lifecycle=OnDemand
- Spot instances will have node label lifecycle=Ec2Spot and a spotInstance=true:PreferNoSchedule taint
- NVIDIAGPU=1 node label will be created for all GPU instances on nodegroup creation
- support passing
ExtraNodeLabels(#3) - Support private subnets
- Support non-RFC1918 IP/CIDR VPC subnets
- Select the latest EKS-optimized AMI for Amazon Linux from a Lambda-backed cloudformaiton custom resource. This help you always use the latest EKS-Optimized AMI.
- Support pahud/eks-lambda-drainer to help you
drainthe pods on terminating spot instances to protect your online workload. Just passEnableNodeDrainer=yesto themakecommand to install the plug-in straight from SAR. - Support the latest Amazon EC2 Instance Connect with web SSH capabilities(details)
Create a AmazonEKSAdminRole IAM Role manually and we will use thie role to
- deploy the cloudformaiton stacks
- execute the Lambda function as custom resource to help you configure the
aws-authConfigMap so the nodes in the nodegroup can register themselves to the control plane. kubeclwill call Amazon EKS control plane as this IAM role for RBAC Auth.
$ aws iam create-role --role-name AmazonEKSAdminRole --assume-role-policy-document file://assume-role-policy.json
$ aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name AmazonEKSAdminRole --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2FullAccess
$ aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name AmazonEKSAdminRole --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
$ aws iam put-role-policy --role-name AmazonEKSAdminRole --policy-name EKSAdminExtraPolicies --policy-document file://eks-admin-iam-policy.jsonget the role arn string. We will use the arn later.
$ aws iam get-role --role-name AmazonEKSAdminRole --query 'Role.Arn' --output text
arn:aws:iam::903779448426:role/AmazonEKSAdminRoleCreate a custom.mk file as your configuration file like this and leave Makefile untouched.
CLUSTER_STACK_NAME ?= eksdemo
SSH_KEY_NAME ?= 'aws-pahud'
EKS_ADMIN_ROLE ?= arn:aws:iam::903779448426:role/AmazonEKSAdminRole
REGION ?= us-west-2
VPC_ID ?= vpc-c7635ea0
SUBNET1 ?= subnet-0f247a2b289129708
SUBNET2 ?= subnet-0da5823de42ae81f9
SUBNET3 ?= subnet-02858661648d4840a
InstanceTypesOverride ?= 't3.medium,m4.large,m5.large'
OnDemandBaseCapacity ?= 2
NodeAutoScalingGroupMinSize ?= 10
NodeAutoScalingGroupDesiredSize ?= 12
NodeAutoScalingGroupMaxSize ?= 20
NodeVolumeSize ?= 50
The parameters in custom.mk file will override the content of Makefile for customization.
- CLUSTER_STACK_NAME - the stack name and cluster name. default:
eksdemo - SSH_KEY_NAME - Your existing SSH keypair name in AWS EC2 console. default:
aws-pahud(please update this value) - REGION - The region code to deploy your EKS cluster. default:
ap-northeast-1 - VPC_ID - The VPC ID to deploy your nodegroup
- EKS_ADMIN_ROLE - The
AmazonEKSAdminRolearn described above. - SUBNET1 The 1st subnet ID to deploy your nodegroup
- SUBNET2 The 2nd subnet ID to deploy your nodegroup
- SUBNET3 The 3rd subnet ID to deploy your nodegroup
- InstanceTypesOverride Instance types for your ASG
- OnDemandBaseCapacity On-Demand base capacity
- NodeAutoScalingGroupMinSize ASG min size
- NodeAutoScalingGroupDesiredSize ASG desired size
- NodeAutoScalingGroupMaxSize ASG max size
- NodeVolumeSize Default node volume size
OK. Let's create the complete Amazon EKS cluster and nodegroup
$ make create-eks-clusterYou may override the default values like this
$ REGION=ap-northeast-1 EKS_ADMIN_ROLE=arn:aws:iam::903779448426:role/AmazonEKSAdminRole CLUSTER_STACK_NAME=eksdemo10 make create-eks-clusteror if you intend to run your nodegroup in private subnets and disable the auto-assign-public-ip completely for your nodes.
$ ASGAutoAssignPublicIp=no make create-eks-clusterTo specify a specific Amazon EKS cluster version(1.11 , 1.12 or 1.13):
$ ClusterVersion=1.13 make create-eks-cluster (if you don't specify ClusterVersion, it will create the latest version for you)
response
{
"StackId": "arn:aws:cloudformation:ap-northeast-1:903779448426:stack/eksdemo10/b3ebf5c0-3395-11e9-bfb3-0a4b1943673a"
}
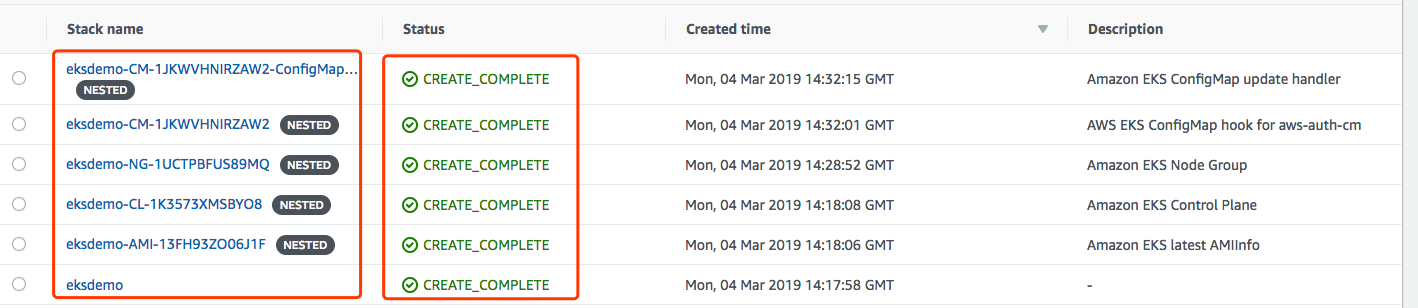
Behind the scene, a cloudformation stack with nested stacks will be created:
- eksdemo - the primary stack
- eksdemo-CL- - the control plane and security group
- eksdemo-AMI- - EKS-Optimized AMI info for Amazon EKS
- eksdemo-NG- - the nodegroup
- eksdemo-CM- - the custom resource to update the
aws-authConfigMap - eksdemo-CM-xxx- - the custom resource lambda function as
AWS::Serverless::Applicationresource fromSAR(Serverless Application Repository) - eksdemo-Drainer-* - the
eks-lambda-drainerapp installed from SAR public repo.
Now cloudformation stack is created. The Amazon EKS cluster will only be able to administratered via kubectl as AmazonEKSAdminRole IAM role. However, according to our
assume-role-policy.json, only the following identities are allowed to assume to this role:
- Lambda service(
lambda.amazonaws.com) - Cloudformation service(
cloudformation.amazonaws.com)
We need to grant our current IAM identity to assume this role(i.e. AmazonEKSAdminRole)
Let's check our current identity
$ aws sts get-caller-identity
{
"Account": "903779448426",
"UserId": "AIDAJQENSMB5TSS54VEB2",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::903779448426:user/pahud"
}(please note your Account and Arn string would be different from mine)
Let's edit assume-role-policy.json file from the local repo:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
},
{
"Sid": "",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "cloudformation.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::903779448426:root"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
This will allow all IAM user from AWS Account ID 903779448426 be able to assume this role.
If you prefer to restrict to a single IAM user, for example pahud:
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::903779448426:user/pahud"
}
And of course you can specify multiple IAM users in Principal
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::903779448426:user/pahud",
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::903779448426:user/emilie"
}
OK let's update the assume role policy
$ aws iam update-assume-role-policy --role-name AmazonEKSAdminRole --policy-document file://assume-role-policy.jsonTry assume this role with aws assume-role like this
$ aws sts assume-role --role-arn arn:aws:iam::903779448426:role/AmazonEKSAdminRole --role-session-name test
{
"AssumedRoleUser": {
"AssumedRoleId": "AROAJCL4US4TE3MXZM272:test",
"Arn": "arn:aws:sts::903779448426:assumed-role/AmazonEKSAdminRole/test"
},
"Credentials": {
"SecretAccessKey": "...",
"SessionToken": "...",
"Expiration": "2019-02-20T08:19:58Z",
"AccessKeyId": "..."
}
}
If you get the response like this then you are allowed to assume role to AmazonEKSAdminRole.
download the latest kubectl binary
For example, in Linux
$ curl https://amazon-eks.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/1.13.7/2019-06-11/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl -o kubectl
$ chmod +x $_
$ sudo mv $_ /usr/local/bin/check Amazon EKS document about install kubectl and getting started and download the two binaries of latest version.
run update-kubeconfig
$ aws --region ap-northeast-1 eks update-kubeconfig --name eksdemo --role-arn arn:aws:iam::903779448426:role/AmazonEKSAdminRoleresponse
Updated context arn:aws:eks:ap-southeast-1:903779448426:cluster/eksdemo in /home/ec2-user/.kube/config
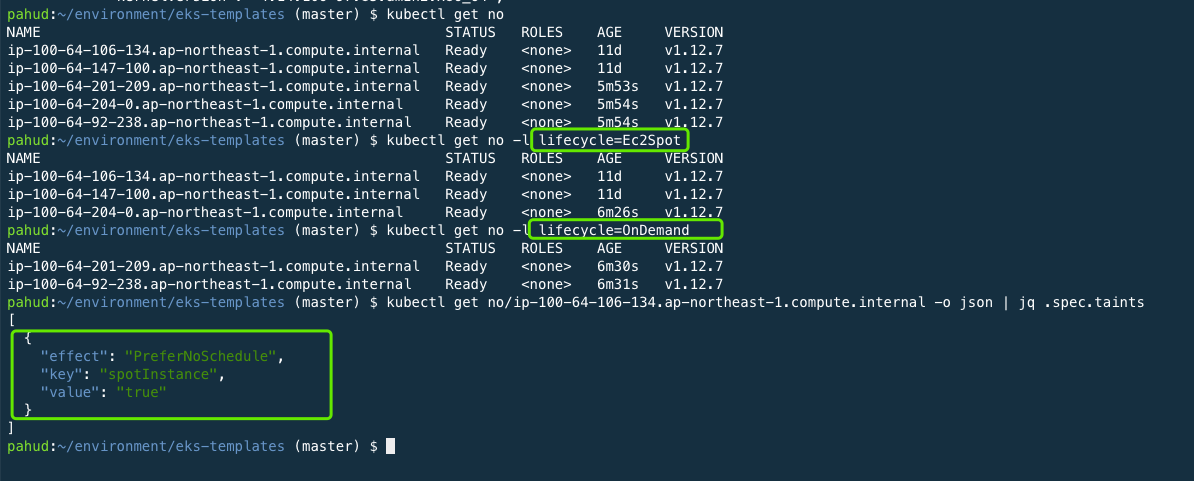
try list the nodes
$ kubectl get no
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-100-64-182-62.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 1m v1.13.7-eks-c57ff8
ip-100-64-71-142.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 1m v1.13.7-eks-c57ff8Your cluster is ready now.
update from 1.12 to 1.13
$ ClusterVersion=1.13 make update-eks-clusterupdate from 1.11 to 1.12
$ ClusterVersion=1.12 make update-eks-clusterBy default, all the on-demand instances will have lifecycle=OnDemand label while spot instances will have lifecycle=Ec2Spot. Use the node selector to better schedule your workload
Additionally, all the spot instances have a spotInstance=true:PreferNoSchedule taint. To deploy your Pod on spot instances, use the node label selector to specify lifecycle=Ec2Spot, otherwise the pod will not be scheduled on the spot instances unless it has relevant toleration. (Taint and Toleration in Kubernetes).
From time to time you may need to update your nodegroup with the latst Amazon EKS-optimized AMI, especially when there's a new security patch like this and a new AMI is released. No bother to specify the latest AMI ID - just kick off the nodegroup rolling update with the latest Amazon EKS-optimized AMI.
# force AMI check and update(if any)
$ UPDATE_AMI=1 make update-eks-clusterTo enable the pahud/eks-lambda-drainer support as the plug-in and install the drainer from SAR,
just pass EnableNodeDrainer=yes to the make command. e.g.
$ EnableNodeDrainer=yes make create-eks-clusterA Drainer cloudformation nested stack will be created and install the eks-lambda-drainer from SAR for you. All the
spot instance termination will be watched and handled by the provided Lambda function. Easy peasy!