最近在研究Binder架构,由于本人比较菜,只分析代码逻辑无法很清楚的了解其中的数据流向以及数据结构,所以想整理一套简单的调试工具帮助我来分析,我一共尝试过三种方法:
- 直接使用GDB调试(本人比较菜用的很不顺手)
- Eclipse+GDB,效果很好,配置起来有点复杂
- AndroidStudio+LLDB,这是用着效果最好
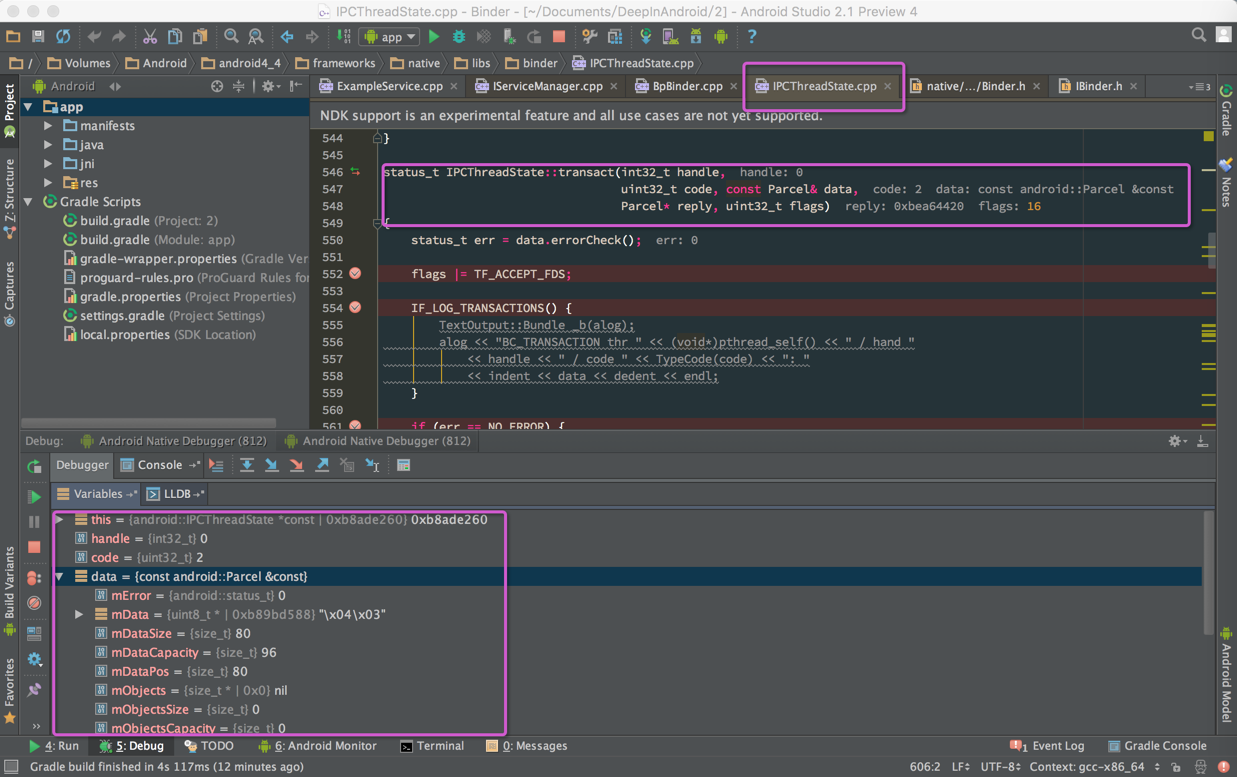
先来看一下我们可以调试到什么程度
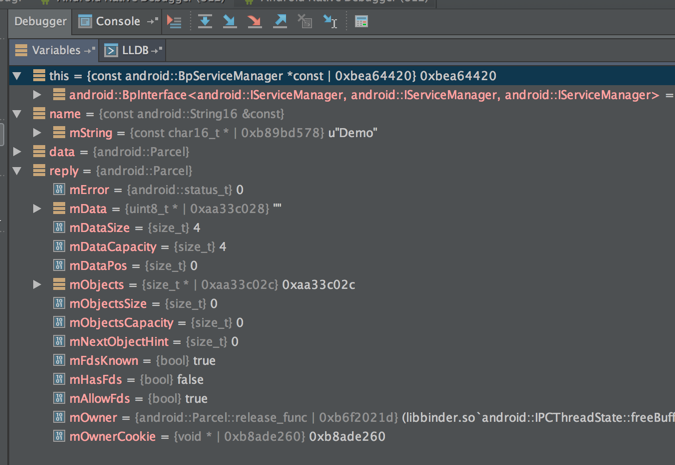
从上图中可以看到调试IPCThreadState.cpp的过程,我们可以看到参数的值,以及各个变量的结构和对应的值
下面描述一下环境搭建过程.
注:本人系统环境是Mac
进行调试的前提是我们有一套系统源码,并且已经编译完成
我编译了三个版本的代码:4.4.1_r1(本文使用的版本),5.1.0_r1,6.0.1_r1,经我测试都可以使用这种方法调试
这里不写编译过程了,具体可以查看官方文档
如果没有更改编译输出目录的话,编译完成后会在源码根目录生成out文件夹
我们需要关注的是out/target/product/generic下的东西:
Android Studio 2.1 Preview 4Gradle 2.10Android NDK r10egradle-experimental 0.7.0-alpha1
基本上都是最新的环境.
Android Studio 1.4以后就支持NDK编译了,详细的Gradle配置可以去看The new NDK support in Android Studio这篇文章,这里不在赘述,想尝试例子的可以去google 官方的github,直接导入运行即可
这里只描述一下如何使用NDK编译依赖系统库的应用.
我们都知道NDK里并没有提供Binder库的相关头文件和lib库,所以无法直接使用NDK编译Binder C++ 的程序,所以我们需要从编译好的系统目录里将需要的共享库提取出来供我们编译使用.
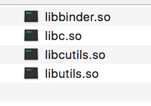
下面是我提取出来编译该Demo所使用的shared libs:
libbinder.so 是Binder的核心库,包含ServiceManager和Pracple的代码,其他三个都是libbinder.so的依赖库
除此之外还需要这些库的头文件,目录树如下:
.
├── binder ----> libbinder.so
├── core ---->别的头文件里有引用此头文件
│ └── include
│ ├── android
│ ├── corkscrew
│ ├── ctest
│ ├── cutils
│ ├── diskconfig
│ ├── ion
│ ├── log
│ ├── memtrack
│ ├── mincrypt
│ ├── netutils
│ ├── pixelflinger
│ ├── private
│ │ └── pixelflinger
│ ├── sync
│ ├── system
│ ├── sysutils
│ ├── usbhost
│ ├── utils
│ └── zipfile
├── cutils ---->libcutils.so
├── libc ----->暂时没用到
│ ├── android
│ ├── arpa
│ ├── machine
│ ├── net
│ ├── netinet
│ ├── netpacket
│ └── sys
├── log
├── system
└── utils ---->libutils.so
下面贴出gradle配置文件里系统库的配置
apply plugin: 'com.android.model.application'
model {
repositories {
libs(PrebuiltLibraries) {
libc {
headers.srcDir rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/include/libc"
binaries.withType(SharedLibraryBinary) {
sharedLibraryFile = file(rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/libs/libc.so")
}
}
binderlib {
headers.srcDir rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/include"
binaries.withType(SharedLibraryBinary) {
sharedLibraryFile = file(rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/libs/libbinder.so")
}
}
libcutils {
headers.srcDir rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/include/core/include"
binaries.withType(SharedLibraryBinary) {
sharedLibraryFile = file(rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/libs/libcutils.so")
}
}
libutils {
headers.srcDir rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/include/core/include"
binaries.withType(SharedLibraryBinary) {
sharedLibraryFile = file(rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/libs/libutils.so")
}
}
}
}
android {
compileSdkVersion = 23
buildToolsVersion = "23.0.2"
println(rootDir.absolutePath + "/binder_lib/include/libc")
defaultConfig {
applicationId "dodola.binder"
minSdkVersion.apiLevel 15
targetSdkVersion.apiLevel 22
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
buildConfigFields {
create() {
type "int"
name "VALUE"
value "1"
}
}
}
}
android.ndk {
moduleName = "binder_ndk"
cppFlags.addAll(["-Werror", "-fno-rtti", "-fno-exceptions"/*, "-std=c++11"*/])
CFlags.addAll(["-Werror"])
ldLibs.addAll(['android', 'log'])
// stl = "gnustl_static"
debuggable = true
}
android.buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled = false
proguardFiles.add(file('proguard-rules.txt'))
}
}
android.sources {
main {
jni {
dependencies {
// library "libc" linkage "shared"
library "binderlib" linkage "shared" buildType "debug"
library "libcutils" linkage "shared" buildType "debug"
library "libutils" linkage "shared" buildType "debug"
}
}
}
}
android.productFlavors {
// for detailed abiFilter descriptions, refer to "Supported ABIs" @
// https://developer.android.com/ndk/guides/abis.html#sa
create("arm") {
ndk.abiFilters.add("armeabi")
}
create("all")
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.2.1'
}
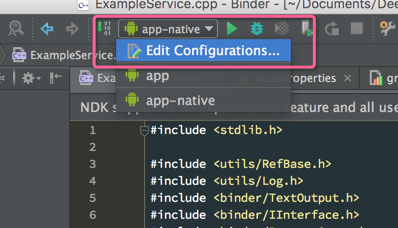
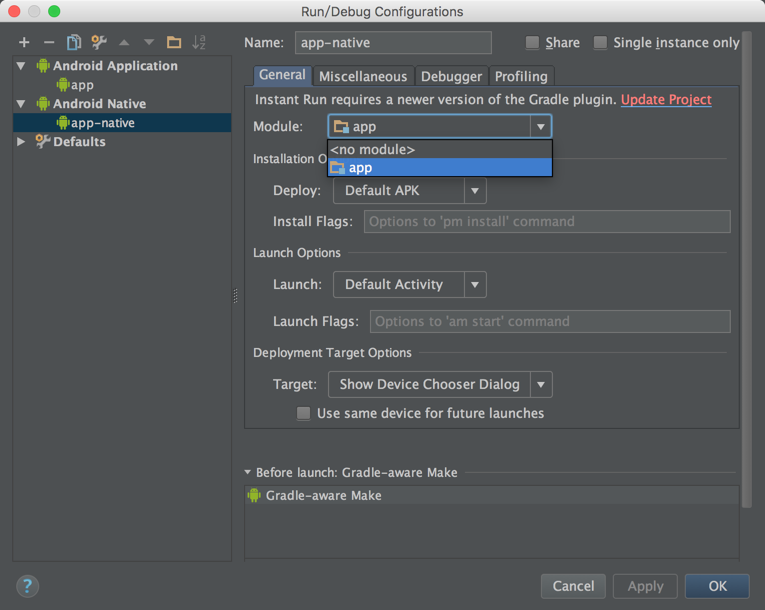
然后添加一个 Android Native 的Configuration
Module这里选择 APP
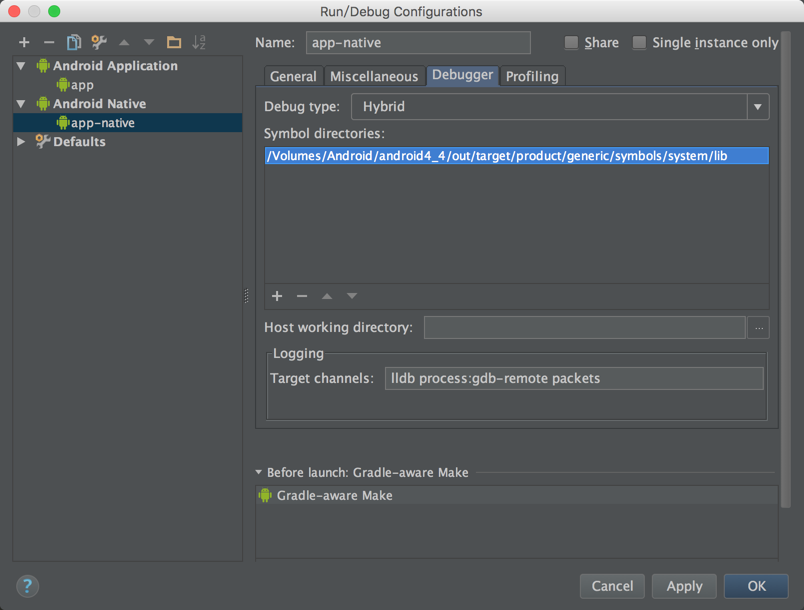
然后在Debugger 里,添加Symbol 文件夹(不确定是否有用)
需要注意的是这个例子需要在自己编译好的系统下运行,因为我们使用的so文件在调试的时候需要根据symbol的地址查找源码,否则就会出现地址找不到的情况.
我没有真机进行调试这里只演示模拟器的调试.
在已经经过编译的系统源码目录下运行以下命令
> $ . build/envsetup.sh ⬡ 5.7.0
build/envsetup.sh:537: command not found: complete
WARNING: Only bash is supported, use of other shell would lead to erroneous results
including device/asus/deb/vendorsetup.sh
including device/asus/flo/vendorsetup.sh
including device/asus/grouper/vendorsetup.sh
including device/asus/tilapia/vendorsetup.sh
including device/generic/armv7-a-neon/vendorsetup.sh
including device/generic/mips/vendorsetup.sh
including device/generic/x86/vendorsetup.sh
including device/lge/hammerhead/vendorsetup.sh
including device/lge/mako/vendorsetup.sh
including device/samsung/manta/vendorsetup.sh
> $ lunch ⬡ 5.7.0
You're building on Darwin
Lunch menu... pick a combo:
1. aosp_arm-eng
2. aosp_x86-eng
3. aosp_mips-eng
4. vbox_x86-eng
5. aosp_deb-userdebug
6. aosp_flo-userdebug
7. aosp_grouper-userdebug
8. aosp_tilapia-userdebug
9. mini_armv7a_neon-userdebug
10. mini_mips-userdebug
11. mini_x86-userdebug
12. aosp_hammerhead-userdebug
13. aosp_mako-userdebug
14. aosp_manta-userdebug
Which would you like? [aosp_arm-eng]
============================================
PLATFORM_VERSION_CODENAME=REL
PLATFORM_VERSION=4.4.1
TARGET_PRODUCT=aosp_arm
TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT=eng
TARGET_BUILD_TYPE=release
TARGET_BUILD_APPS=
TARGET_ARCH=arm
TARGET_ARCH_VARIANT=armv7-a
TARGET_CPU_VARIANT=generic
HOST_ARCH=x86
HOST_OS=darwin
HOST_OS_EXTRA=Darwin-15.4.0-x86_64-i386-64bit
HOST_BUILD_TYPE=release
BUILD_ID=KOT49E
OUT_DIR=out
============================================
> $ emulator ⬡ 5.7.0
emulator: WARNING: system partition size adjusted to match image file (550 MB > 200 MB)
这样就可以将模拟器启动起来
然后就可以在Android Studio里运行例子了.
上面所有步骤配置好以后,则可以调试应用了
- 选择
Attach debug to Android process
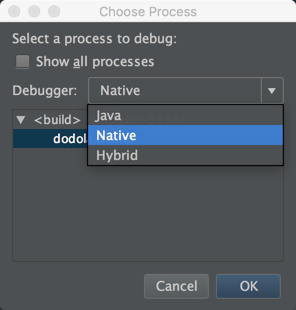
- 在弹出的对话框里选择
Native选项
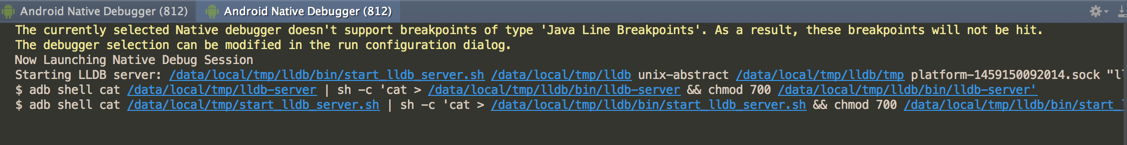
- 点击ok以后,debug的控制台会输出LLDB的调用命令
哈,这样我们在调试的时候就可以深入到binder内部看一下它的流程了
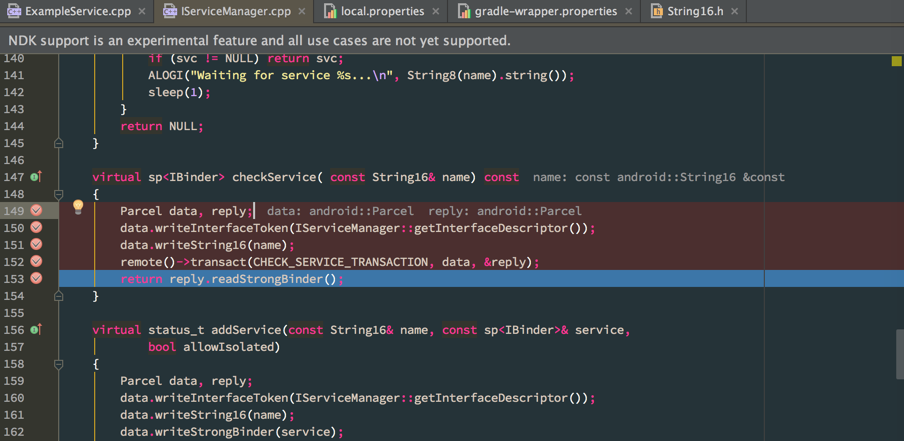
下面这个图是断点到IServiceManager.cpp的情况,以及变量的结构
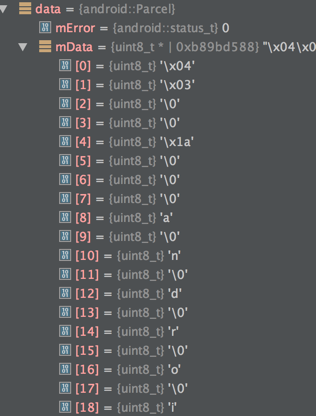
下面这个图是mData里的结构(以前只能靠YY)