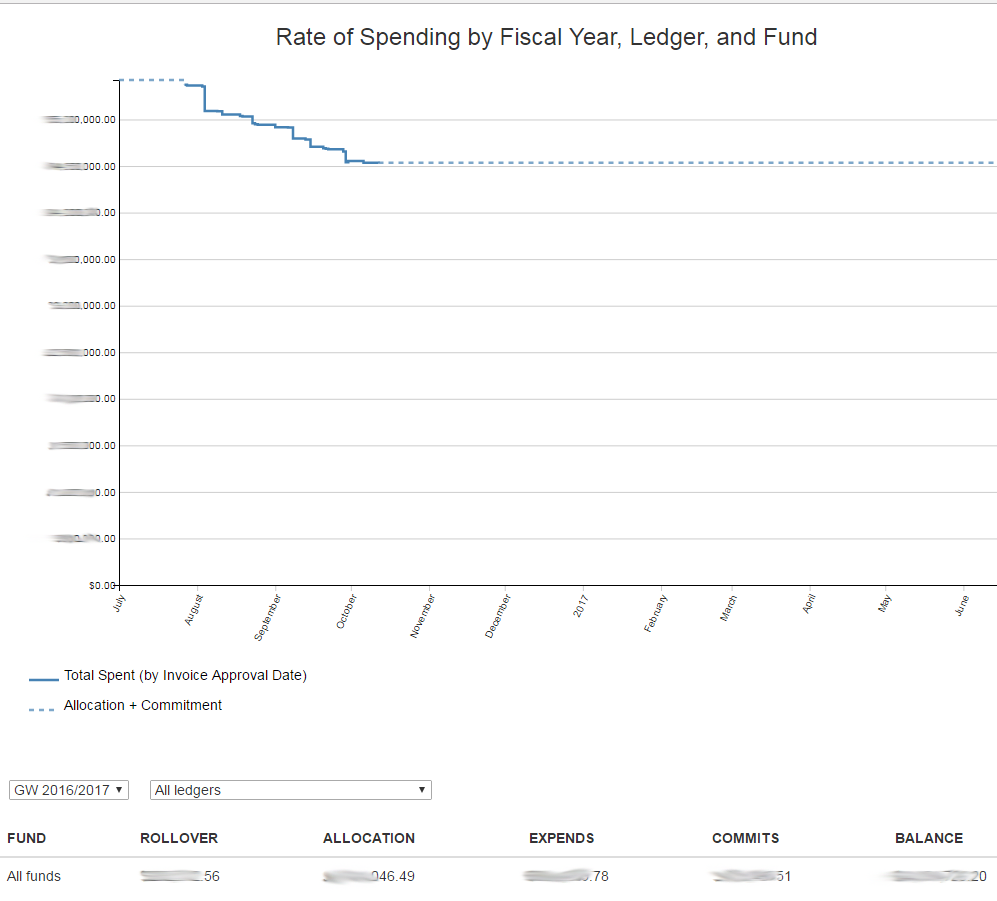
A lightweight web app for viewing Voyager acquisitions data. Optimized for the Chrome browser. (May not work in IE.) A timeseries chart shows the rate of spending over time at either the ledger or the fund level. A table shows allocations, expenditures, and commitments across funds. Clicking on a fund row displays a modal table of line-item purchases.
A Python/SQL script loads Voyager data into a local database for simplified, fast lookup. A web server, written in Javascript, serves data to a web page written with D3.js, which displays the data dynamically. The server script updates the local database daily, though this can be easily re-configured.
- Python 3.4 or greater
- Node.js 4.4.7 or greater
- PostgreSQL database server, 9.4 or greater
- Oracle Instant Client (version appropriate to your version of Voyager)
Installation has been tested on a Linux server (ubuntu 14.04 LTS) and a Windows 7 desktop machine (with admin privileges).
-
Create a new postgreSQL database and create/associate a user with this database.
-
For platform-specific installation instructions, see https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Detailed_installation_guides
-
On creating new users in postgreSQL, see the documentation here: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.5/static/app-createuser.html
-
In the psql shell, run this command to grant the user privileges to read, write, and create tables on the new database:
GRANT ALL ON DATABASE [database name] TO [user name];
Or see the documentation here: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.5/static/sql-grant.html
-
-
Install Node.js: https://nodejs.org/en/
-
Install Python 3: https://www.python.org/downloads/
-
Install the Oracle Instant Client packages (necessary to communicate with the Voyager database).
-
Select the packages appropriate to the version of Oracle that corresponds to your version of Voyager (as described in the Voyager documentation). Instant Client packages can be found here: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/features/instant-client/index-097480.html
-
Download and install both the Basic and ODBC packages.
-
-
Install the voyager-dashboard.
-
(Optional but recommended) Create a Python 3 virtual environment for this project: https://virtualenv.pypa.io/en/stable/
-
Clone/download the files and folders in this repository into a new local folder (e.g., "dashboard").
-
From the dashboard folder, run the Node package manager (at the command line) to install the dependencies.
home/dashboard/npm install-
If using virtualenv (step #1), activate the environment.
-
From the dashboard folder, install the Python dependencies. (Note: you may need to run pip3 if you have both Python 2 and Python 3 installed on your machine and are not using virtualenv.)
home/dashboard/pip install -r requirements.txt-
Modify the following lines in dashboard/cd-db-update.py to reflect your system setup:
#!/home/ENV/bin/python**(path to the Python interpreter in your virtualenv or for your system)log_dir = '/home/your_directory/your_log_directory/'(path to a directory within your dashboard directory that will hold the SQL error log files)engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine(('postgresql://username:password@localhost:portnum/db_name'))(credentials for the local postrgreSQL database created in Step 1)dsn = cx_Oracle.makedsn('**DSN for the Voyager database**')See http://cx-oracle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/module.html#cx_Oracle.makedsnconnection = cx_Oracle.connect('**username**', '**password**', dsn)Credentials for Oracle Voyager accessIn addition, lines 63-65, 156-57, and 204-206 -- in the Voyager SQL queries -- should be modified for your local institution and needs. (Additional changes to the SQL may be necessary, depending on your configuration of Voyager.)
-
Modify the following lines in dashboard/public/queries.json:
"connection": {"host": "localhost", "port": "**your_postgres_port_number**", "database": "**your_postgres_db_name**", "user": "**username**", "password": "**password**" } -
Modify the following lines in dashboard/server.js:
var pyOptions = { mode: 'text', pythonPath: 'home/ENV/bin/python', scriptPath: './' }; -
Run cd-db-update.py to do the initial load from Voyager into the postgreSQL database:
dashboard/python cd-db-update.py -
Start the Node server:
dashboard/node server.js -
Open a browser and go to localhost:3000/index.html
-
(Optional) To make the dashboard accessible over HTTP to other users, there are at least two options:
-
Change the following line in server.js to point to a port that is open for HTTP traffic:
server = app.listen(3000);(3000 is the port number) -
Set up a third-party web server (like Apache) to listen on an open port and redirect traffic to the port specified by server.js (e.g., 3000). With Apache 2.x, you can use mod_proxy: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/current/mod/mod_proxy.html
-
-