Get and set macros created by commandline arguments.
Install with npm:
$ npm install --save macro-storeCreate a parser function that works like yargs-parser or minimist and handles creating, using, and removing macros through command line arguments.
var macros = require('macro-store');
var parser = macros('macro-store');
var args = parser(process.argv.slice(2));
//=> { _: ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'], verbose: true, cwd: 'qux', isMacro: 'qux' }The returned args object also contains the store methods to give implementors direct access to setting, getting, and deleting macros in the store.
args.set('foo', ['bar', 'baz', 'bang']);
args.get('foo');
//=> ['bar', 'baz', 'bang']The following examples are using the example file run at the command line with node example.js.
The objects returned may be used in implementing applications however they choose.
Jump to the API documentation for implementation information.
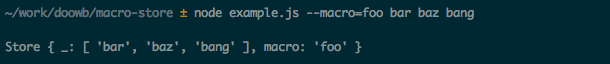
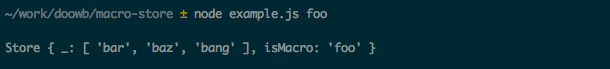
The following shows creating a simple macro called foo.
The following shows using the foo macro, and that the resulting args object contains the expanded value.
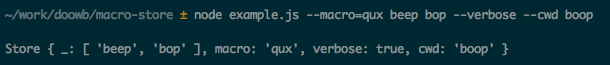
The following shows creating a complex macro called qux that includes options --verbose and --cwd boop.
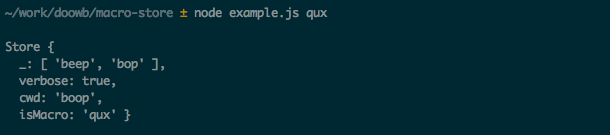
The following shows that using a complex macro is the same as a simple macro, but the args object contains the options verbose: true and cwd: 'boop', which were set when creating the qux macro.
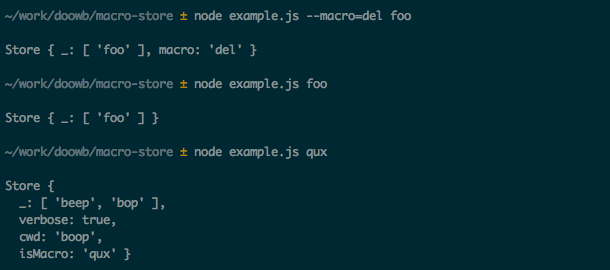
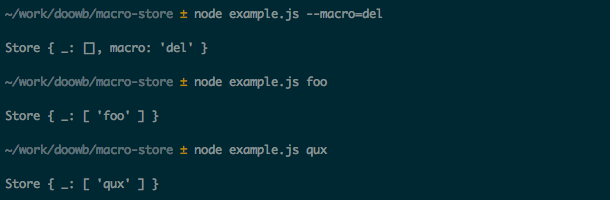
The following shows how to delete the macro foo. This only deletes foo and shows that qux is still set.
The following shows how to delete all macros. This shows that foo and qux have been deleted so the args object will contain the exact values passed in from the command line.
Handle macro processing and storing for an array of arguments.
Set macros by specifying using the --macro or --macro=set option and a list of values.
Remove a macro by specifying --macro=del option and the macro name.
Default is to replace values in the argv array with stored macro values (if found).
Params
name{String}: Custom name of the data-store to use. Defaults to 'macros'.options{Object}: Options to pass to the store to control the name or instance of the data-storeoptions.name{String}: Name of the data-store to use for storing macros. Defaults tomacrosoptions.store{Object}: Instance of data-store to use. Defaults tonew DataStore(options.name)options.parser{Function}: Custom argv parser to use. Defaults to yargs-parserreturns{Function}: argv parser to process macros
Example
// create an argv parser
var parser = macros('custom-macro-store');
// parse the argv
var args = parser(process.argv.slice(2));
// => { _: ['foo'] }
// following input will produce the following results:
//
// Set 'foo' as ['bar', 'baz', 'bang']
// $ app --macro foo bar baz bang
// => { _: [ 'bar', 'baz', 'bang' ], macro: 'foo' }
//
// Use 'foo'
// $ app foo
// => { _: [ 'bar', 'baz', 'bang' ], isMacro: 'foo' }
//
// Remove the 'foo' macro
// $ app --macro --del foo
// => { _: [ 'foo' ], macro: 'del' }Parser function used to parse the argv array and process macros.
Params
argv{Array}: Array of arguments to processoptions{Object}: Additional options to pass to the argv parserreturns{Object}args: object described above
Exposes Store for low level access
Example
var store = new macros.Store('custom-macro-store');Initialize a new Store with the given options.
Params
options{Object}options.name{String}: Name of the json file to use for storing macros. Defaults to 'macros'options.store{Object}: Instance of data-store to use. Allows complete control over where the store is located.
Example
var macroStore = new Store();
//=> '~/data-store/macros.json'
var macroStore = new Store({name: 'abc'});
//=> '~/data-store/abc.json'Set a macro in the store.
Params
key{String}: Name of the macro to set.arr{Array}: Array of strings that the macro will resolve to.returns{Object}this: for chaining
Example
macroStore.set('foo', ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']);Get a macro from the store.
Params
name{String}: Name of macro to get.returns{String|Array}: Array of tasks to get from a stored macro, or the original name when a stored macro does not exist.
Example
var tasks = macroStore.get('foo');
//=> ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']
// returns input name when macro is not in the store
var tasks = macroStore.get('bar');
//=> 'bar'Remove a macro from the store.
Params
name{String|Array}: Name of a macro or array of macros to remove.returns{Object}this: for chaining
Example
macroStore.del('foo');Changelog entries are classified using the following labels (from keep-a-changelog):
added: for new featureschanged: for changes in existing functionalitydeprecated: for once-stable features removed in upcoming releasesremoved: for deprecated features removed in this releasefixed: for any bug fixes
Custom labels used in this changelog:
dependencies: bumps dependencieshousekeeping: code re-organization, minor edits, or other changes that don't fit in one of the other categories.
changed
- refactored parser to return an
argsobject similar to yargs-parser and minimist - handles
--macrooption for creating, getting, and removing macros from theargsobject.
changed
- refactored to export a function that creates a parser function.
- the parser function returns an object with the action taken and the processed arguments.
- data-store: Easily get, set and persist config data. | homepage
- minimist: parse argument options | homepage
- verb-generate-readme: Generate your project's readme with verb. Requires verb v0.9.0 or higher. | homepage
- verb: Documentation generator for GitHub projects. Verb is extremely powerful, easy to use, and is used… more | homepage
- yargs-parser: the mighty option parser used by yargs | homepage
Pull requests and stars are always welcome. For bugs and feature requests, please create an issue.
(This document was generated by verb-generate-readme (a verb generator), please don't edit the readme directly. Any changes to the readme must be made in .verb.md.)
To generate the readme and API documentation with verb:
$ npm install -g verb verb-generate-readme && verbInstall dev dependencies:
$ npm install -d && npm testBrian Woodward
Copyright © 2016, Brian Woodward. Released under the MIT license.
This file was generated by verb, v0.9.0, on August 17, 2016.