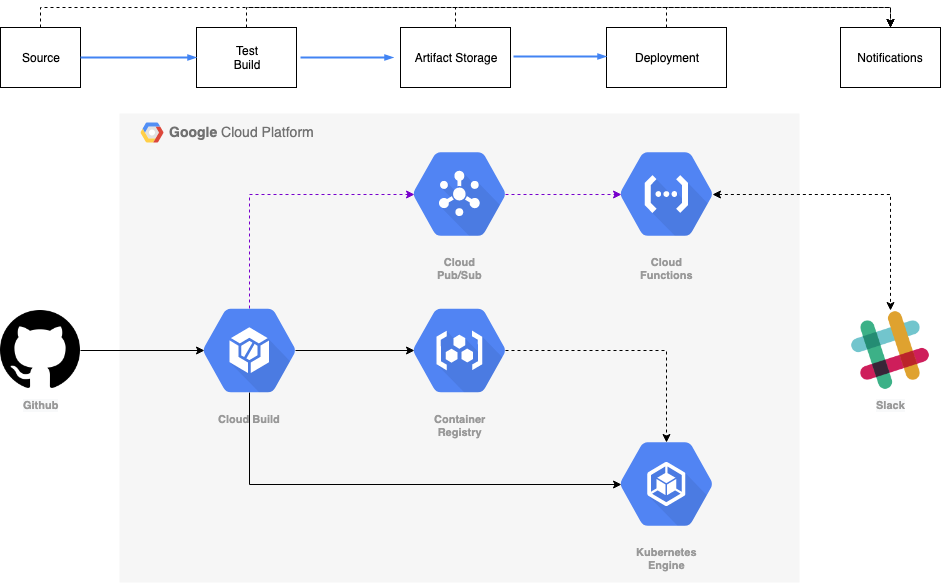
This repository contains code for the sample application and the cloud functions used during the demo of the Cloud Native CI/CD talk given by Vishal Parpia at the Google Cloud Summit Singapore ‘19.
The /app folder contains the sample NodeJs application along with the CloudBuild yaml, Docker files and Kubernetes yaml. The application has some unit tests and integration tests defined which are checked during the build process.
The /functions folder contains the code for the Cloud Functions to listen to Cloudbuild updates and Slack approval events.
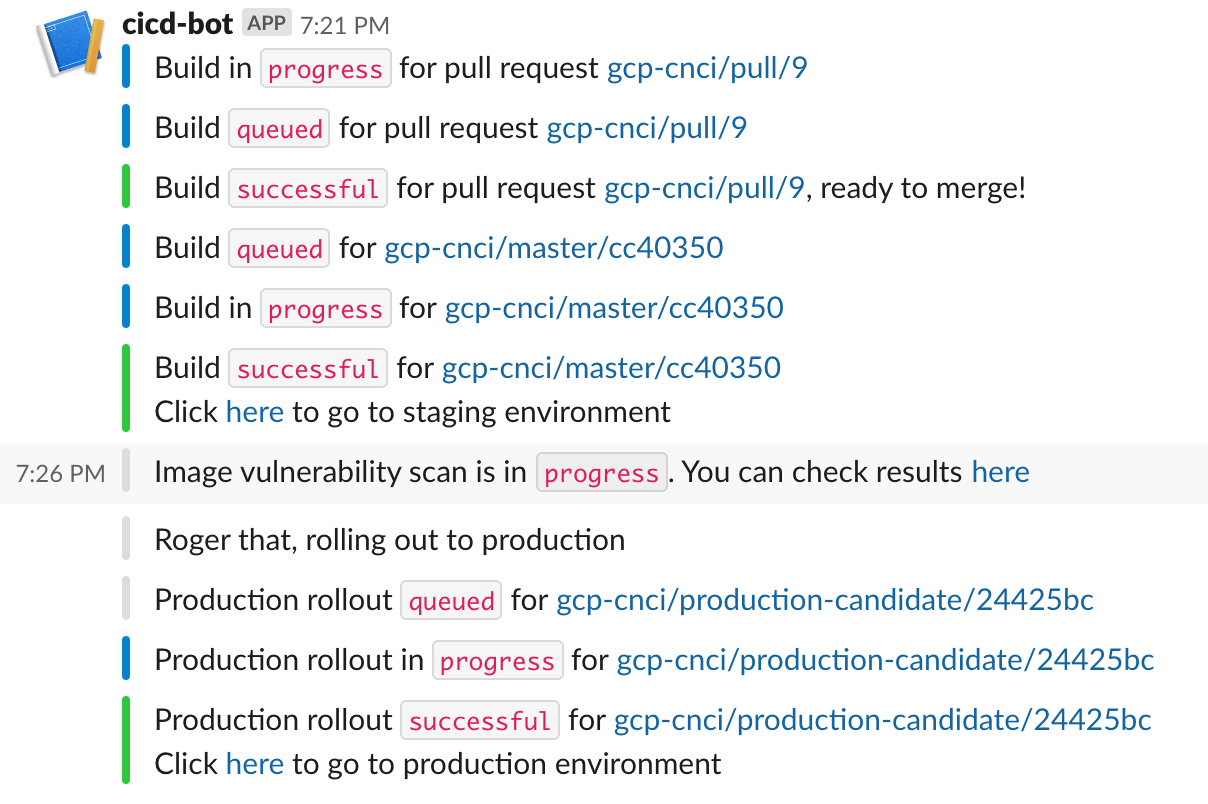
The source for the application to be deployed is this GitHub repository. When a pull request is raised to the master branch it triggers CloudBuild to build and test code based on the PR. If it is successful then the user can merge the PR into the master branch.
Merging the PR triggers another CloudBuild to perform unit tests, build the Docker image, push the image to Google Container Repository, deploy it to Kubernetes pods for the staging environment and then perform integration tests.
Notifications at each stage are sent to a Slack channel.
The user can now decide if he wants to roll out the build to production, this can be done by clicking on YES or NO action buttons which will be showing in the Slack channel to approve the rollout. If the rollout is approved then another CloudBuild trigger is executed which deploys it to Kubernetes pods for the production environment.
- Generate an SSH key using
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C “a@b.com” - Add the public part of key generated above in Repository’s Deploy Keys (Settings -> Deploy Keys -> Add Key)
- Encrypt the private part of key using Google KMS
-
Create a keyring
gcloud kms keyrings create {keyring_name} --location=global -
Create key
gcloud kms keys create {key_name} --location=global --keyring={keyring_name} --purpose=encryption -
Whitelist cloudbuild service account to decrypt the above key. This can be done as:
In GCP Console: IAM -> Cryptographic keys -> {keyring_name} -> {key_name} -> Show Info Panel -> Add Member -> Give Decrypter permission to cloudbuild service account
-
Encrypt your private key
gcloud kms encrypt --plaintext-file={private_key_path} --ciphertext-file={enc_key_path} --location=global --keyring={keyring_name} --key={key_name} -
Replace the encrypted key at path
app/repo-key-encryptedwith your key -
Create
production-candidatebranch. Replace the encrypted key generated and production kubernetes.yaml file and push it to repo. -
Create
productionbranch and push it (can be empty). Production configs are stored hereNote: production-candidate and production branches should ideally be in different repository as it holds production configuration. The key added to production-candidate branch is for the repo holding production config.
-
Create two clusters, one for staging environment and other for production. Not down cluster names and deployment zones
-
Cloudbuild -> Triggers -> Connect Repository -> check GitHub App by Google -> Authenticate -> Select your repository -> Skip creating triggers for now Create Triggers
-
Create Trigger for Push on master branch. With following details
Type: Branch Regex: master Cloudbuild config path: app/cloudbuild-master.yml Substitution Vars: _APP_DIR: app _GITHUB_REPO_ENC_KEY_PATH: app/repo-key-encrypted/id_rsa_repo_key.enc _GITHUB_REPO_KEY: {key_name} _GITHUB_REPO_KMS_KEYRING: {keyring_name} _GITHUB_REPO_USERNAME: cldcvr _IMAGE_ID: gcp-cnci-example-app _PRODUCTION_CANDIDATE_BRANCH: production-candidate _PRODUCTION_KUBERENETES_TEMPLATE_FILE_NAME: kubernetes.yaml.tpl _PRODUCTION_KUBERNETES_CONFIG_FILE_NAME: kubernetes.yaml _STAGING_DEPLOY_CLUSTER: {STAGING_GKE_CLUSTER_NAME} _STAGING_DEPLOY_ZONE: {STAGING_GKE_CLUSTER_ZONE} _STAGING_KUBERENETES_TEMPLATE_FILE_NAME: staging-kubernetes.yaml.tpl _STAGING_KUBERNETES_CONFIG_FILE_NAME: staging-kubernetes.yaml -
Create Trigger for PR on master with details:
Type: Pull Request Regex: master Cloudbuild config: app/cloudbuild-master-pr.yml Substitution Vars: _APP_DIR: app -
Create Trigger for push on production-candidate with details
Type: Branch Regex: random_string. Note: Put random non existent branch. We will be firing this trigger manually. Note down the trigger name. Cloudbuild config: cloudbuild-delivery.yml Substitution vars: _GITHUB_REPO_ENC_KEY_PATH: repo-key-encrypted/id_rsa_repo_key.enc _GITHUB_REPO_KEY: {prod_config_repo_key_name} _GITHUB_REPO_KMS_KEYRING: {prod_config_repo_keyring_name} _GITHUB_REPO_USERNAME: cldcvr _PRODUCTION_BRANCH: production _PRODUCTION_DEPLOY_CLUSTER: {PRODUCTION_GKE_CLUSTER_NAME} _PRODUCTION_DEPLOY_ZONE: {PRODUCTION_GKE_CLUSTER_ZONE} _PRODUCTION_KUBERNETES_CONFIG_FILE_NAME: kubernetes.yaml
You can get the bot user token using OAuth2 or from your slack app dashboard (if you are using bot for your own workspace). For more information see: https://api.slack.com/docs/oauth#bots
-
Replace trigger name in
functions/repos.jswith your production trigger name. -
Deploy Functions
- Slack Approval Events Listener
cd functions gcloud functions deploy gcpCiCdApprovalAction --runtime nodejs10 --trigger-http --set-env-vars SLACK_BOT_TOKEN='{BOT_TOKEN}' --set-env-vars GCLOUD_PROJECT='{PROJECT_ID}' --service-account={CLOUDFUNCTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT}- CloudBuild Event Listener
cd functions gcloud functions deploy gcpCiCdSlackEvents --runtime nodejs10 --trigger-topic cloud-builds --set-env-vars SLACK_BOT_TOKEN='{BOT_TOKEN}' --set-env-vars GCLOUD_PROJECT='cloudcover-sandbox' --service-account={CLOUDFUNCTION_SERVICE_ACCOUNT}