Run ComfyUI in a cloud-first AI-Dock container.
Note
These images do not bundle models or third-party configurations. You should use a provisioning script to automatically configure your container. You can find examples in config/provisioning.
All AI-Dock containers share a common base which is designed to make running on cloud services such as vast.ai and runpod.io as straightforward and user friendly as possible.
Common features and options are documented in the base wiki but any additional features unique to this image will be detailed below.
The :latest tag points to :latest-cuda and will relate to a stable and tested version. There may be more recent builds
Tags follow these patterns:
:cuda-[x.x.x-base|runtime]-[ubuntu-version]
:rocm-[x.x.x-runtime]-[ubuntu-version]
:cpu-[ubuntu-version]
Browse here for an image suitable for your target environment.
Supported Platforms: NVIDIA CUDA, AMD ROCm, CPU
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
AUTO_UPDATE |
Update ComfyUI on startup (default false) |
COMFYUI_BRANCH |
ComfyUI branch/commit hash for auto update (default master) |
COMFYUI_FLAGS |
Startup flags. eg. --gpu-only --highvram |
COMFYUI_PORT_HOST |
ComfyUI interface port (default 8188) |
COMFYUI_URL |
Override $DIRECT_ADDRESS:port with URL for ComfyUI |
See the base environment variables here for more configuration options.
| Environment | Packages |
|---|---|
comfyui |
ComfyUI and dependencies |
This micromamba environment will be activated on shell login.
See the base micromamba environments here.
The following services will be launched alongside the default services provided by the base image.
The service will launch on port 8188 unless you have specified an override with COMFYUI_PORT_HOST.
ComfyUI will be updated to the latest version on container start. You can pin the version to a branch or commit hash by setting the COMFYUI_BRANCH variable.
You can set startup flags by using variable COMFYUI_FLAGS.
To manage this service you can use supervisorctl [start|stop|restart] comfyui.
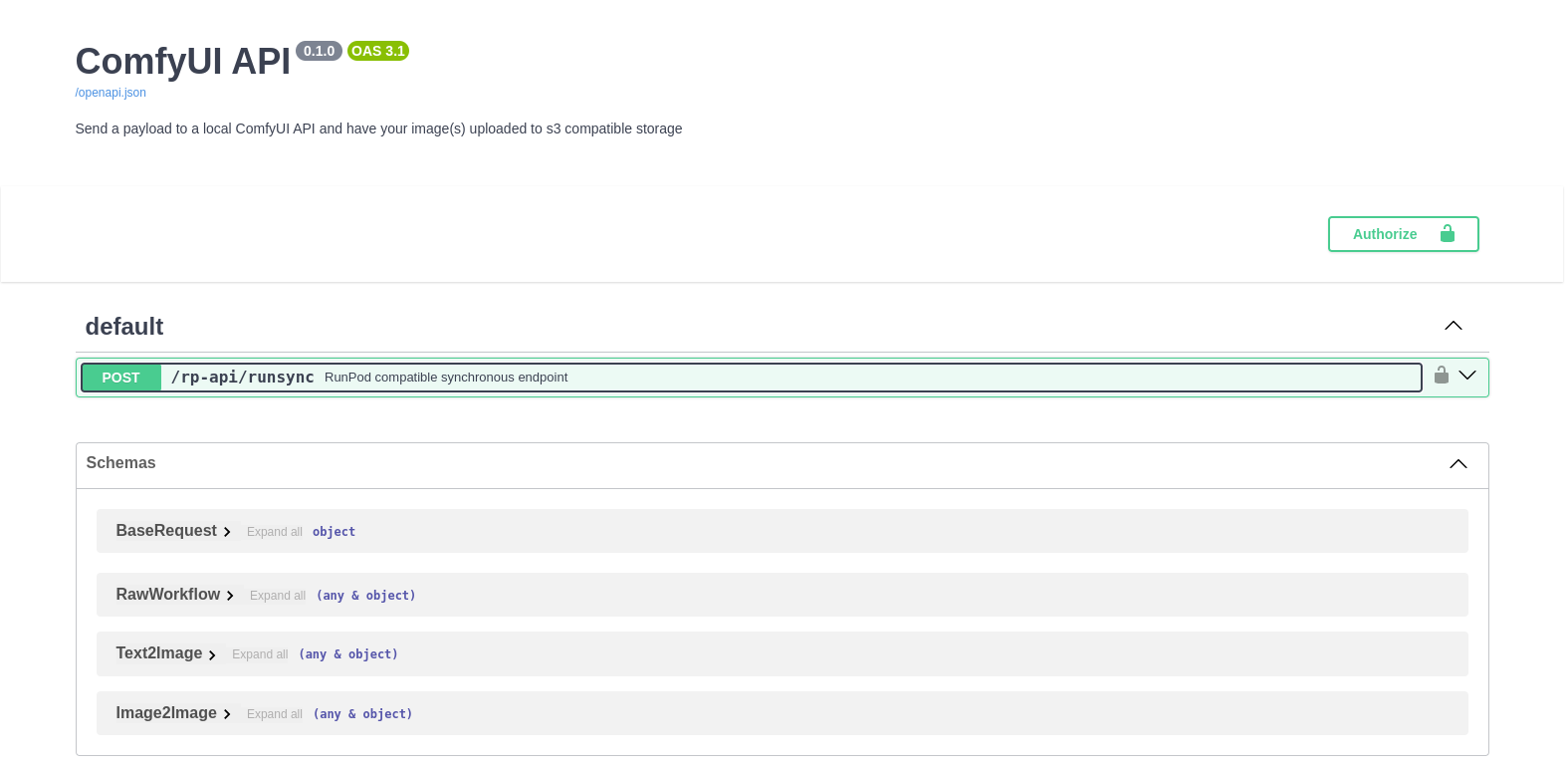
This service is available on port 8188 and is used to test the RunPod serverless API.
You can access the api directly at /rp-api/runsync or you can use the Swager/openAPI playground at /rp-api.
There are several example payloads included in this repository.
This API is available on all platforms - But the container can ony run in serverless mode on RunPod infrastructure.
To learn more about the serverless API see the serverless section
Note
All services are password protected by default. See the security and environment variables documentation for more information.
Vast.ai
Runpod.io
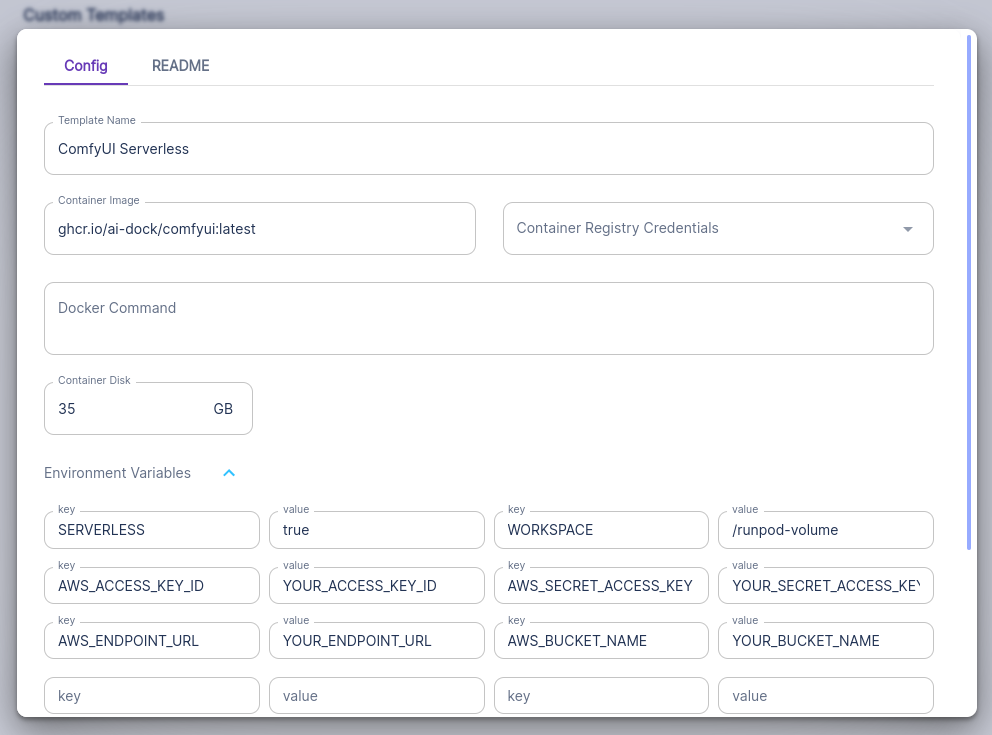
The container can be used as a RunPod serverless worker. To enable serverless mode you must run the container with environment variables SERVERLESS=true and WORKSPACE=/runpod-volume.
The handlers will accept a job, process it and upload your images to s3 compatible storage.
You may either set your s3 credentials as environment variables or you can pass them to the worker in the payload.
You should set AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, AWS_ENDPOINT_URL and AWS_BUCKET_NAME.
If passed in the payload these variables should be in lowercase.
Incorrect or unset s3 credentials will not resut in job failure. You can still retrieve your images from the network volume.
When used in serverless mode, the container will skip provisioning and will not update ComfyUI or the nodes on start so you must either ensure everyting you need is built into the image (see Building the Image) or first run the container with a network volume in GPU Cloud to get everything set up before launching your workers.
After launching a serverless worker, any instances of the container launched on the network volume in GPU cloud will also skip auto-updating. All updates must be done manually.
The API is documented in openapi format. You can test it in a running container on the ComfyUI port at /rp-api/docs - See ComfyUI RP API for more information.
The API can use multiple handlers which you may define in the payload. Three handlers have been included for your convenience
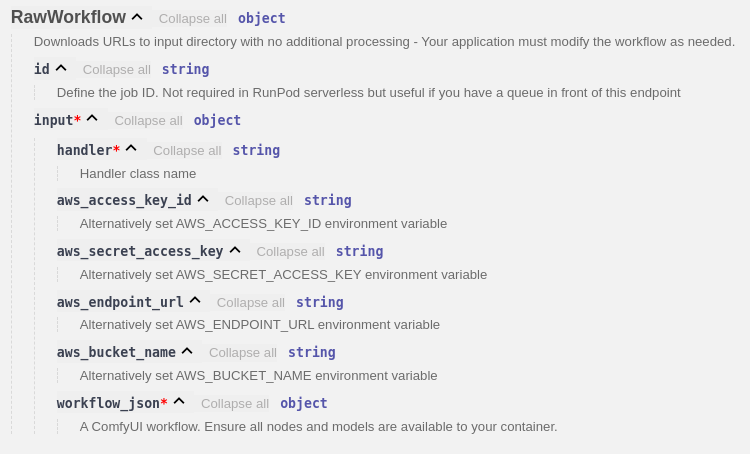
This handler should be passed a full ComfyUI workflow in the payload. It will detect any URL's and download the files into the input directory before replacing the URL value with the local path of the resource. This is very useful when working with image to image and controlnets.
This is the most flexible of all handlers.
This is a basic handler that is bound to a static workflow file (/opt/serverless/workflows/text2image.json).
You can define several overrides to modify the workflow before processing.
This is a basic handler that is bound to a static workflow file (/opt/serverless/workflows/image2image.json).
You can define several overrides to modify the workflow before processing.
These handlers demonstrate how you can create a simple endpoint which will require very little frontend work to implement.
You can find example payloads for these handlers here
The author (@robballantyne) may be compensated if you sign up to services linked in this document. Testing multiple variants of GPU images in many different environments is both costly and time-consuming; This helps to offset costs