An Acorn Atom emulator.
(This is actually forked from my Atari 2600 emulator.) This is work in progress. You can play pretty much any Acorn Atom game that doesn't use a 6522 VIA chip but it's not all documented yet.
You'll need some ROMs.
You can get them from here.
Unpack them so the roms appear in acorn_roms in the top directory.
We'll be needing Atom_Kernel.rom, Atom_Basic.rom and Atom_FloatingPoint.rom in particular.
To run you'll need to install stack from here
Then use:
stack build
stack exec alcator
The code uses glfw. You may need to install homebrew and then run
brew install glfw3
This Acorn Atom is configured with 40K RAM and 24K of ROM. It doesn't have a 6522 VIA.
If the keyboard seems unreliable, then the emulator is working properly. The original Atom had no keyboard based interrupts and so no keyboard buffer. If it polled at the wrong moment it could easily miss your key press.
Key mappings:
| Emulator | Atom |
|---|---|
| left-alt | debugger |
| right-alt | REPT |
| ` | quit |
| up | up |
| shift-up | down |
| shift-right | left |
| right | right |
| page down | copy |
| shift-2 | " |
| shift-= | + |
| shift-6 | & |
| shift-7 | ' |
| shift-8 | ( |
| shift-9 | ) |
| shift-- | = |
| = | : |
| shift-= | * |
| shift-=; | + |
| ' | @ |
I'll try to improve the key mapping but that does mean some faking of the state of the shift key and that could have weird side-effects.
Command line options
-w <dir> - work from given directory
-d - start in debugger
-c <cmd> - run specified debugger command
For example -c '<"game.state"' will load
the previously saved state into RAM.
On startup a utility in utility.bin is loaded to #9800, just above screen memory. Use LINK #9800 to install it. This will now give access to *LOAD "file" and *RUN "file" that will read (and/or execute) files in .atm format.
For example, if Level 9 Snowball is stored in software/L9/SNOWBALL/SNOWBALL you can start it with
LINK #9800
*RUN "software/L9/SNOWBALL/VDUBLO"
*RUN "software/L9/SNOWBALL/SNOWBALL"
and to run Bug-Byte Pinball use
LINK #9800
*LOAD "software/BB/PINBALL"
RUN
You can rebuild utility.bin using sh make_os but you'll need ca65 installed.
A good trick is to use LINK #9800 and *LOAD to load a game and then use left-alt and the > command to save it before starting.
(Note: it's possible some applications will want memory above #9800 and cause a conflict. Eg. games often load at #8200.)
Hit left-alt to go into debugger.
Command syntax:
{<statement>;<statement>...} - block
Put multiple commands in a block, eg. r100{s;l} will step and list the current instruction 100 times.
c - continue
Return to playing game
g - dump graphics state
Eg. r10{s;g} will step through 10 instructions dumping graphics state each step.
s - single instruction step
Eg. r100000s will step 100000 instructions
r<expr><statement> - repeat statement
Eg. r(2*y){s;l} will step and list instructions a number of times given by double the Y register.
(You can leave out the 'r' if the expression can be unambiguously read as an expression.)
x<string> - execute command
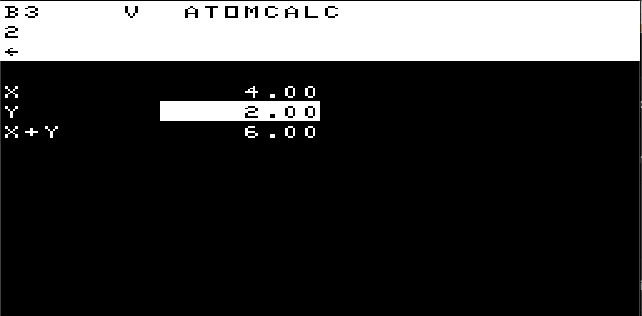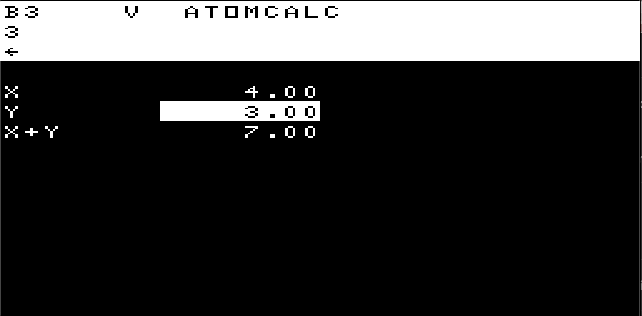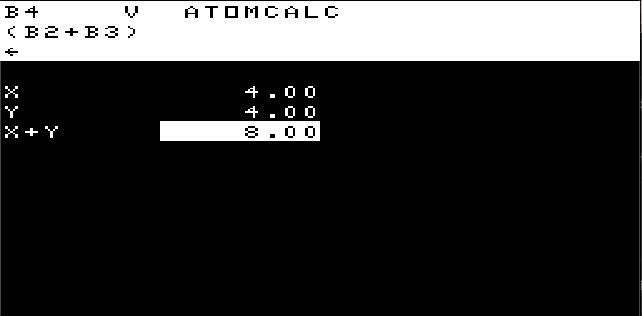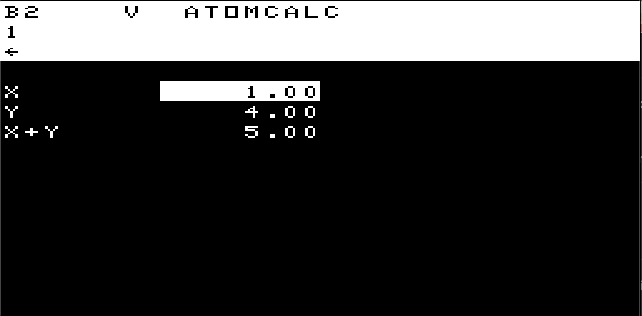
Executes command in string. Eg. x"p1" will print 1.
l<expr>
l<expr>expr> - list disassembly
Disassemble from given expression with optional number of instructions.
Eg. l(pc+2)10 lists 10 instructions starting at PC+2.
p<expr> - print
Print expression. Eg. p?0x9c7f prints byte at address 0x9c7f
u<expr><statement> - until
Perform statement until condition met.
Eg. u(row==160){s};u(row>160){s;l} will step until row 160 of screen is reached and will then step, disassembling each instruction, until row 160 is finished.
Eg. u(y>x){l;s} will step until Y register is larger than X.
><filename> - save
Saves current state of Atom into a file.
<<filename> - load
Loads current state of Atom from a file.
<var>=<expr>
Set value of variable.
Eg. U=1;V=2;pU+V will print 3.
Expression syntax
t - current clock value
col - current column
row - current row
Note the names of flags come from names of branch instructions:
eq - Z flag
ne - negated Z flag
mi - N flag
pl - negated N flag
cs - C flag
cc - negated c flag
a, x, y, s - registers
==, !=, >, <, >=, <=, +, -, <<, >>, *, / ~, &, | all do obvious thing
?<expr> - read byte from address
!<expr> - read 2 byte word from address
Complex examples
u(pc==0x5828){s;l} - keep executing until address 5828
u(?pc==0x20){s;l} - keep executing until first JSR
p(!(0x101+s)+1) - print return address on top of stack