Advanced Lane Finding Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Compute the camera calibration matrix and distortion coefficients given a set of chessboard images.
- Apply a distortion correction to raw images.
- Use color transforms, gradients, etc., to create a thresholded binary image.
- Apply a perspective transform to rectify binary image ("birds-eye view").
- Detect lane pixels and fit to find the lane boundary.
- Determine the curvature of the lane and vehicle position with respect to center.
- Warp the detected lane boundaries back onto the original image.
- Output visual display of the lane boundaries and numerical estimation of lane curvature and vehicle position.
1. Briefly state how you computed the camera matrix and distortion coefficients. Provide an example of a distortion corrected calibration image.
The code for this step is contained in the camera_calibration() function of the IPython notebook located in "./Advanced-Lane-Lines.ipynb".
I start by preparing "object points", which will be the (x, y, z) coordinates of the chessboard corners in the world. Here I am assuming the chessboard is fixed on the (x, y) plane at z=0, such that the object points are the same for each calibration image. Thus, objp is just a replicated array of coordinates, and objpoints will be appended with a copy of it every time I successfully detect all chessboard corners in a test image. imgpoints will be appended with the (x, y) pixel position of each of the corners in the image plane with each successful chessboard detection.
I then used the output objpoints and imgpoints to compute the camera calibration and distortion coefficients using the cv2.calibrateCamera() function. I applied this distortion correction to the test image using the cv2.undistort() function and obtained this result:
| Original Chessboard | Undistorted Chessboard |
|---|---|
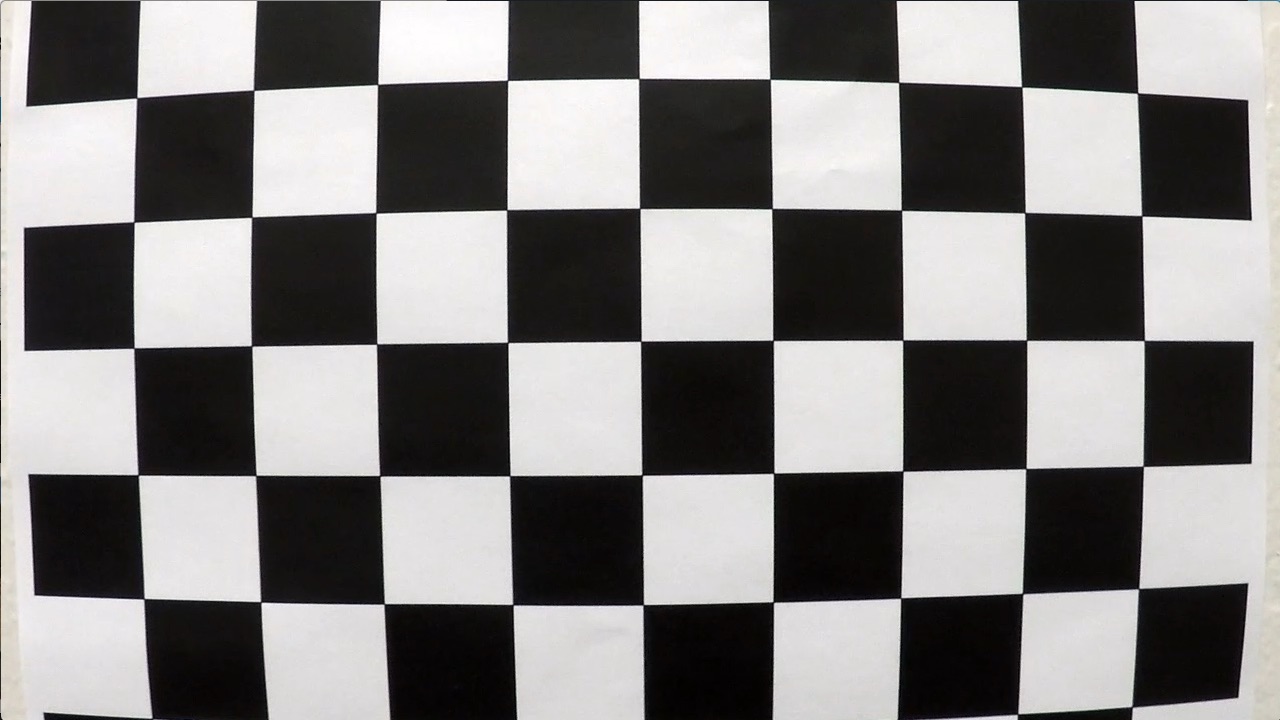 |
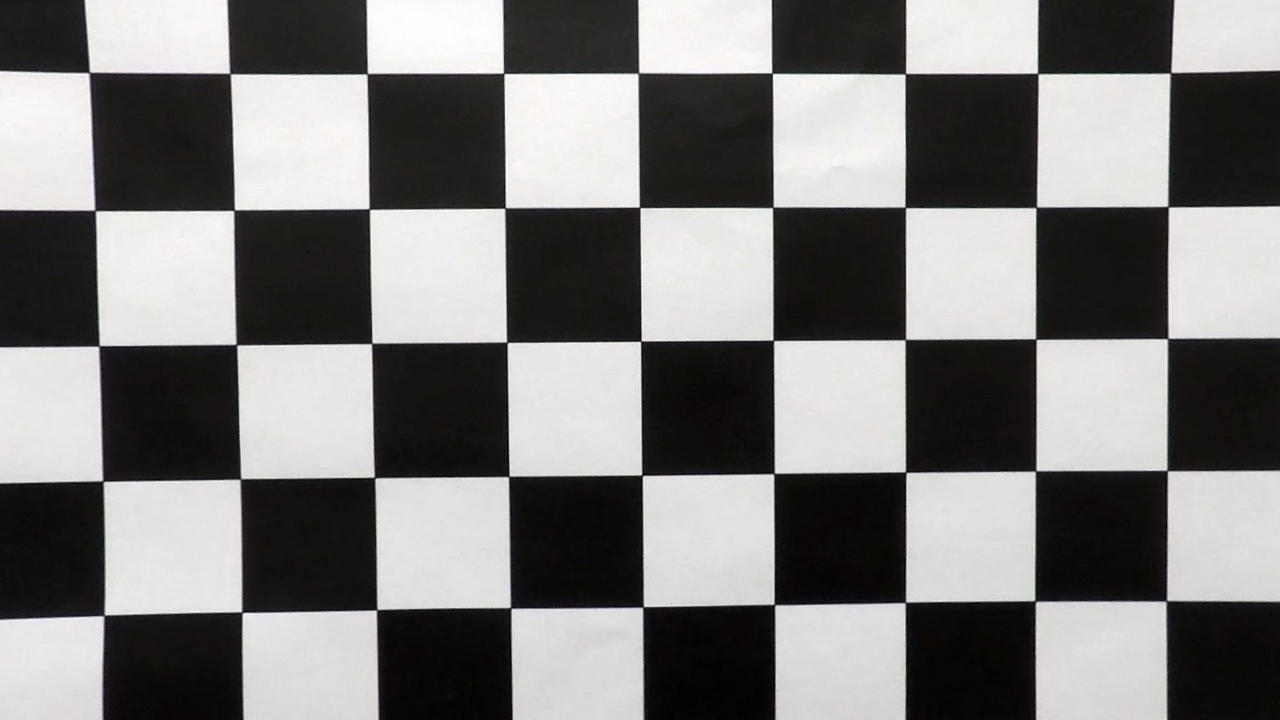 |
The code for this step is contained in the undistort() function of the IPython notebook.
To demonstrate this step, I applied the cv2.undistort(), as same as last step, to one of the test images like this one:
| Original Image | Undistorted Image |
|---|---|
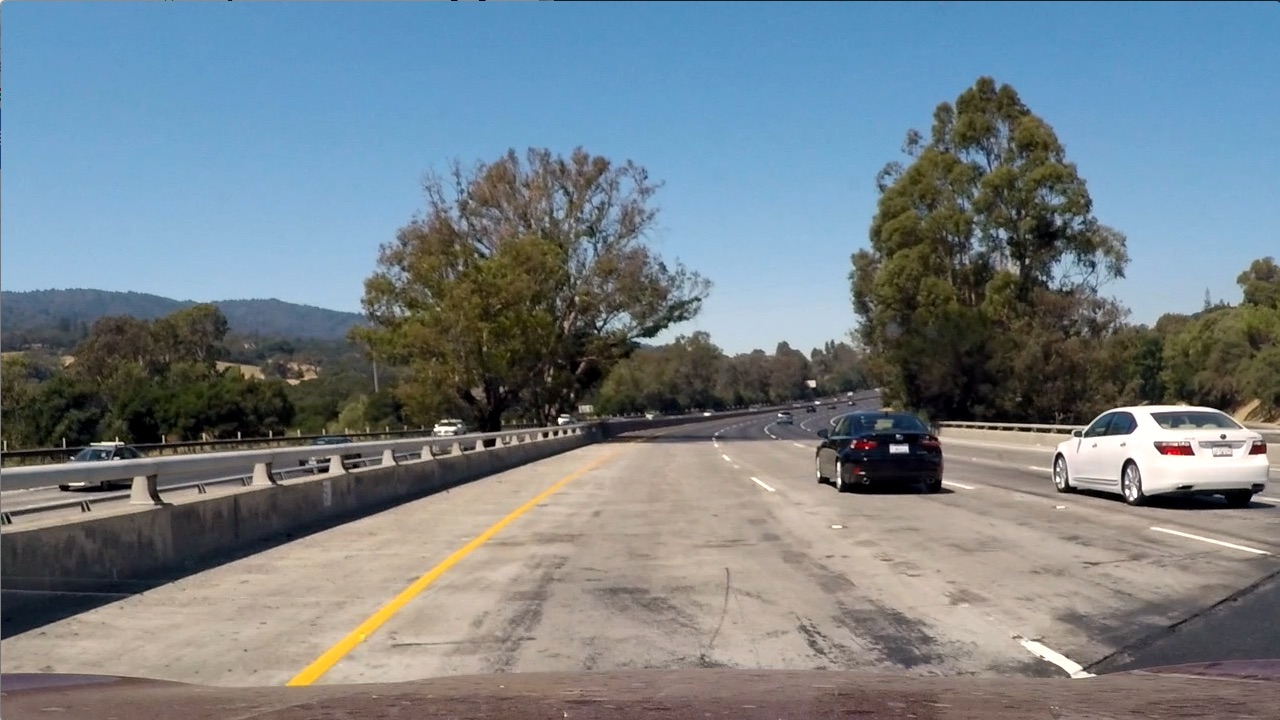 |
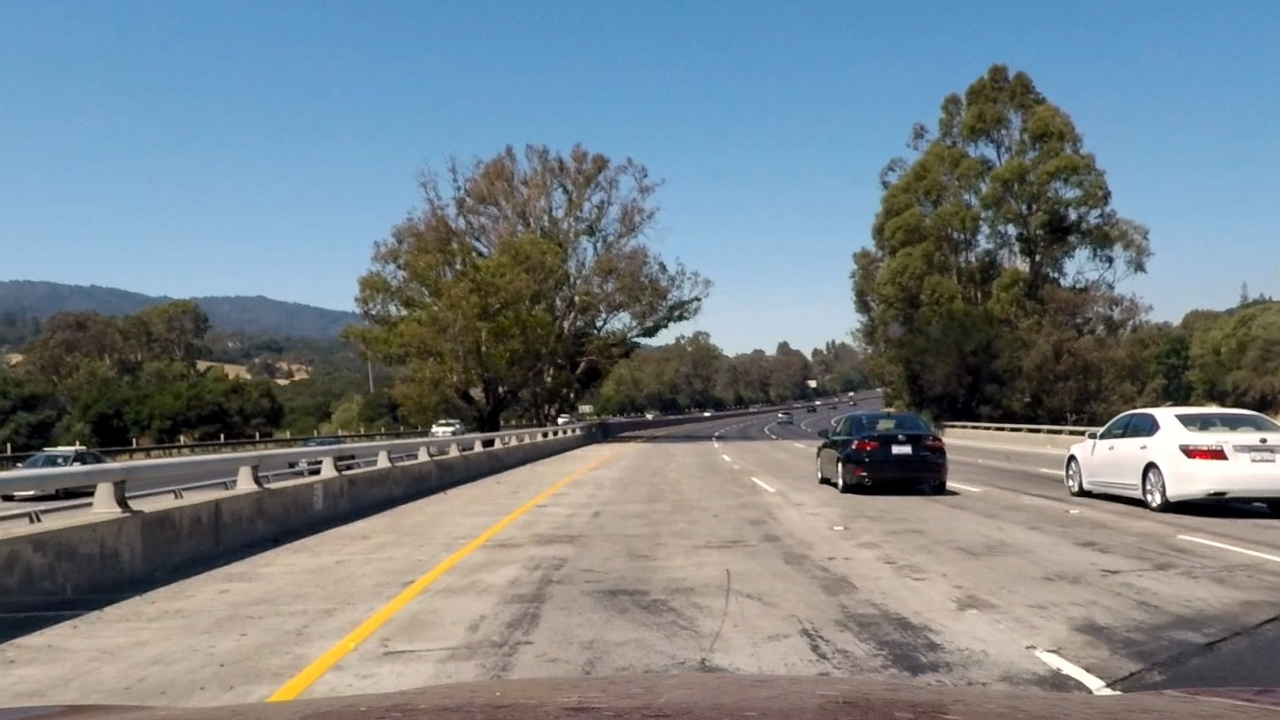 |
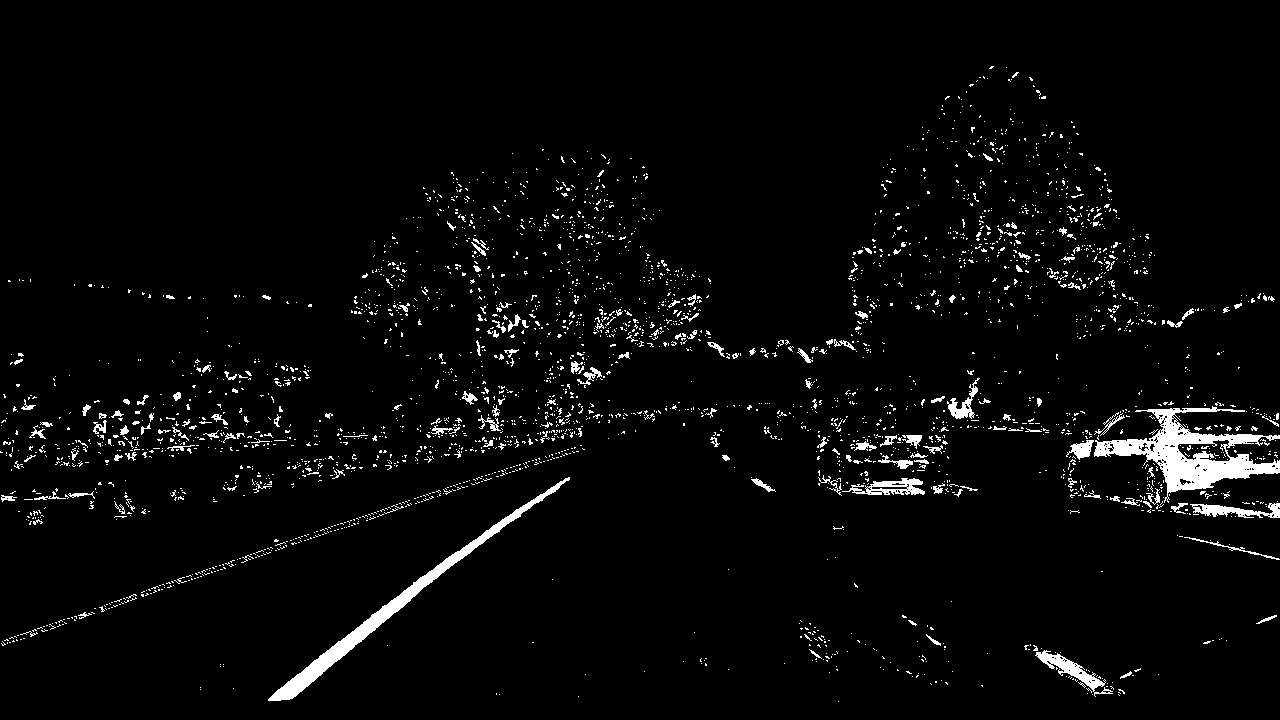
2. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you used color transforms, gradients or other methods to create a thresholded binary image. Provide an example of a binary image result.
I used a combination of color and gradient thresholds to generate a binary image (thresholding steps at threshold() function). Here's an example of my output for this step.
| Operation | Undistorted Image | X Gradient | Y Gradient | Magnitude Gradient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result |  |
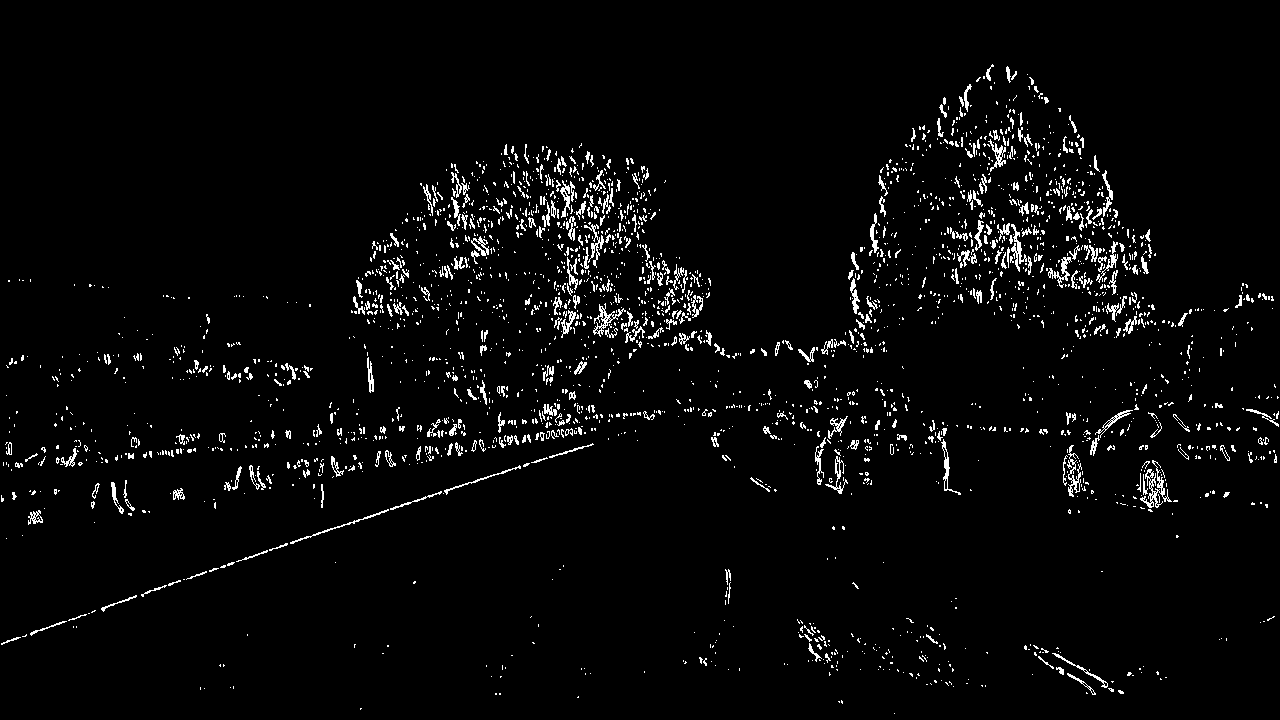 |
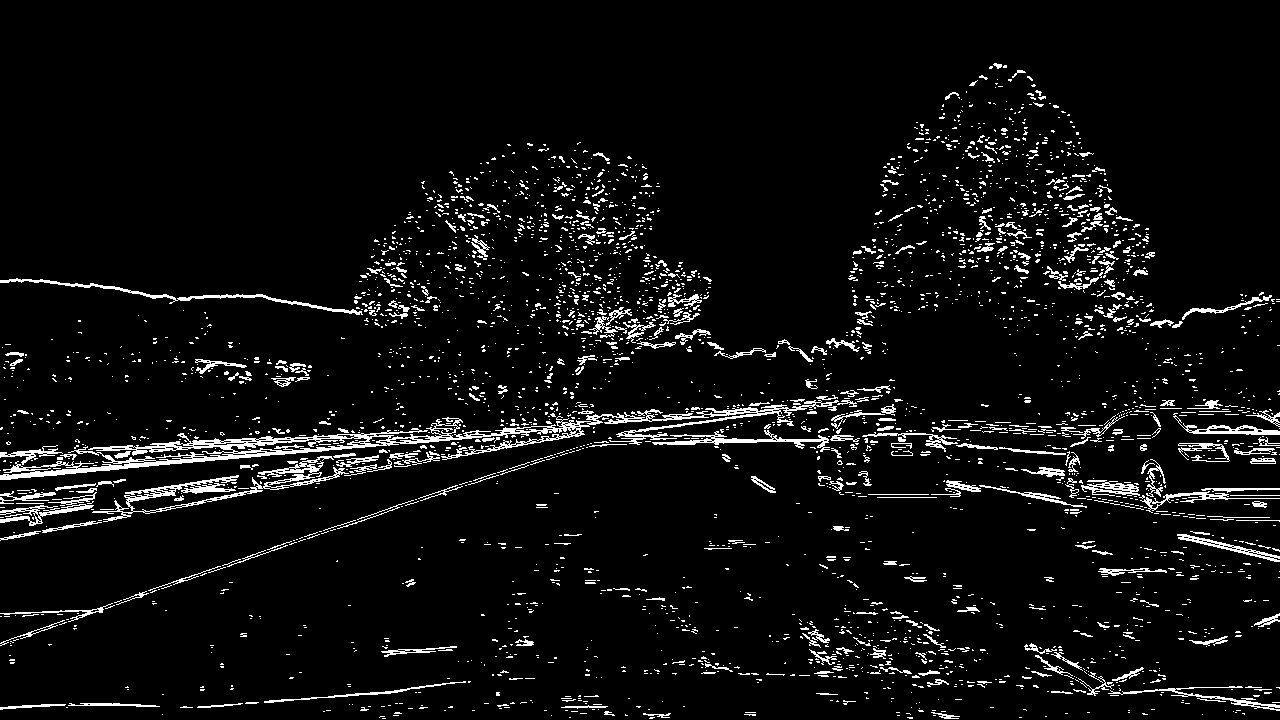 |
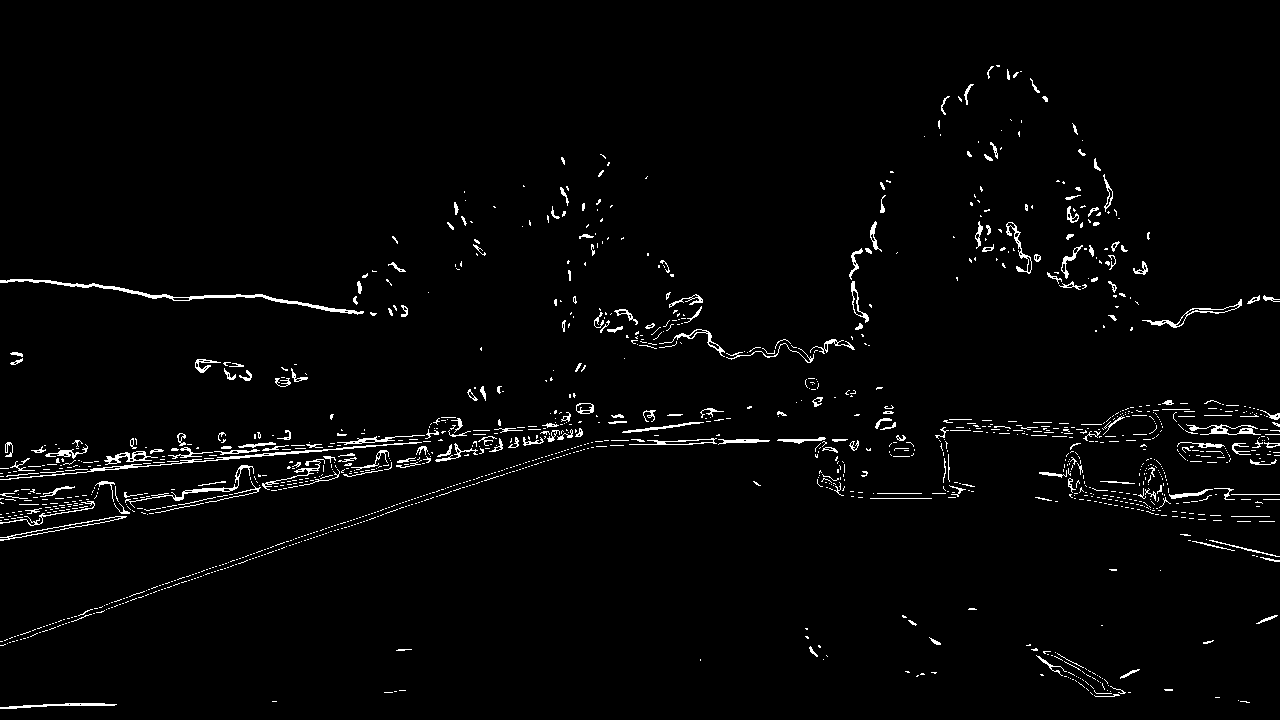 |
| Operation | Direction Gradient | S Channel | Thresholded Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Result |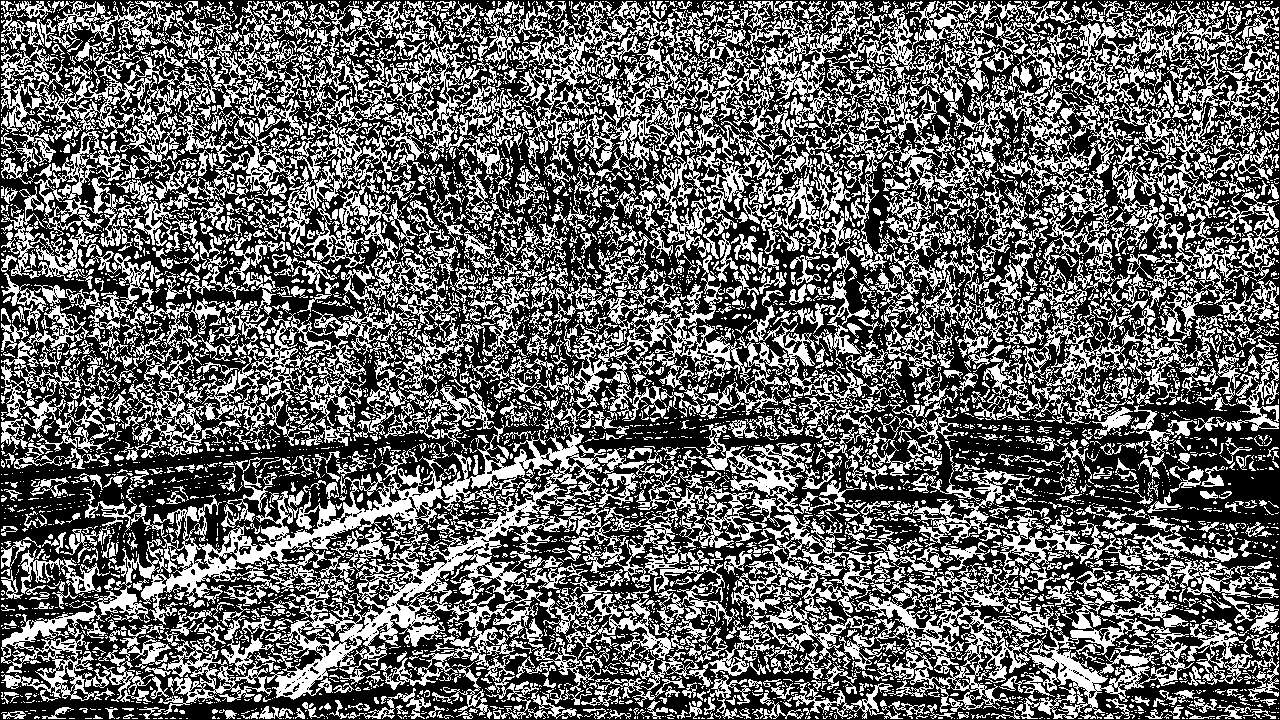  |
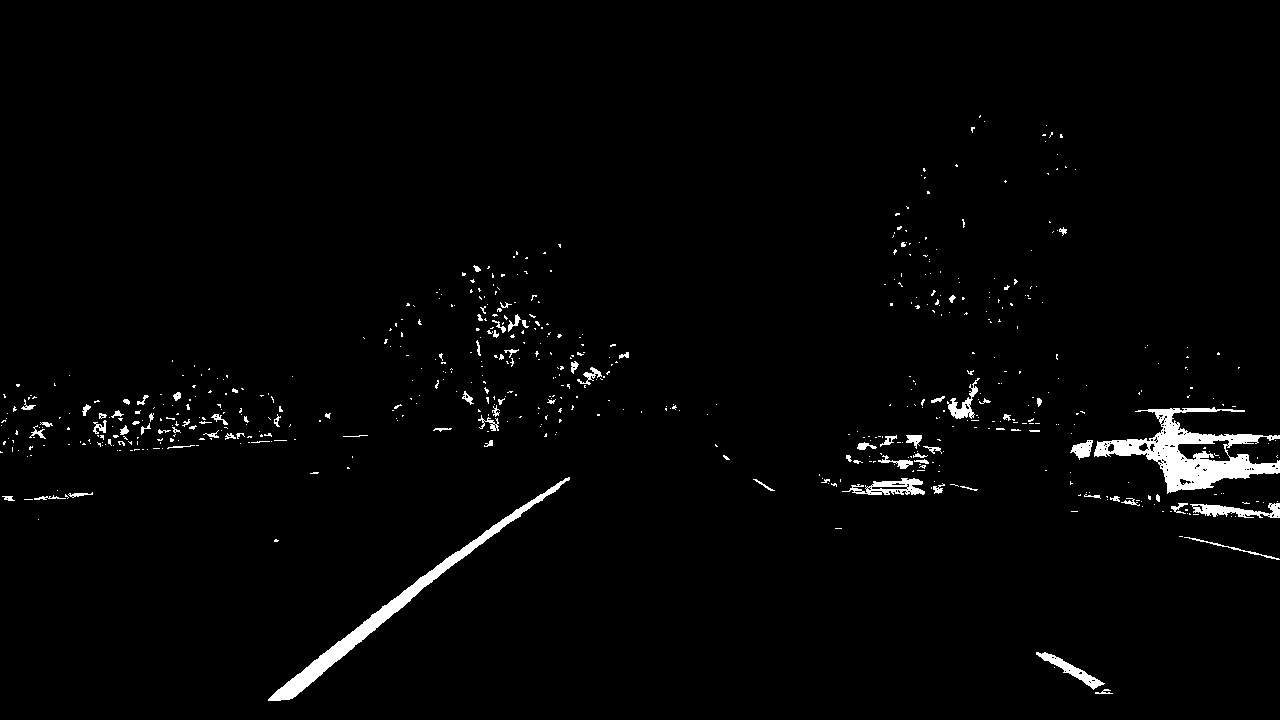 |
 |
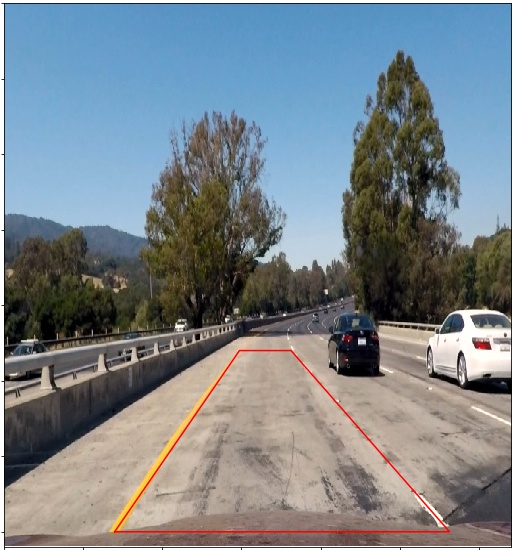
3. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you performed a perspective transform and provide an example of a transformed image.
The code for my perspective transform includes a function called perspective(). The perspective() function takes as inputs an image (thresh), as well as source (src) and destination (dst) points. I chose the hardcode the source and destination points in the following manner:
src = np.float32(
[[280, 700], # Bottom left
[595, 460], # Top left
[725, 460], # Top right
[1125, 700]]) # Bottom right
dst = np.float32(
[[250, 720], # Bottom left
[250, 0], # Top left
[1065, 0], # Top right
[1065, 720]]) # Bottom right This resulted in the following source and destination points:
| Source | Destination |
|---|---|
| 280, 700 | 250, 720 |
| 595, 460 | 250, 0 |
| 725, 460 | 1065, 0 |
| 1125, 700 | 1065, 720 |
I verified that my perspective transform was working as expected by drawing the src and dst points onto a test image and its warped counterpart to verify that the lines appear parallel in the warped image.
| Undistorted Image | Perspective Transformed Image |
|---|---|
 |
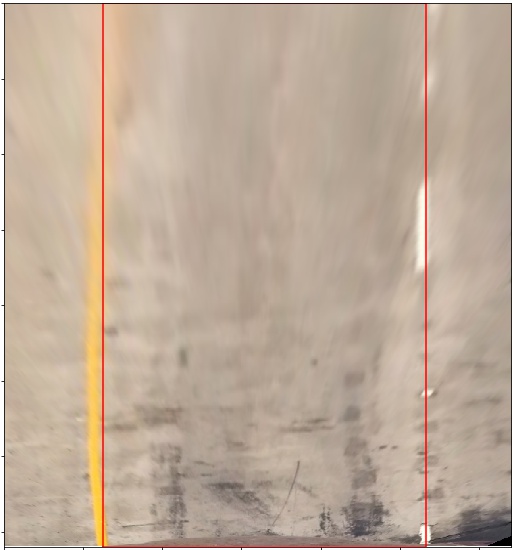 |
| Thresholded Perspective Transformed Image |
|---|
 |
4. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you identified lane-line pixels and fit their positions with a polynomial?
Then I did some other stuff and fit my lane lines with a 2nd order polynomial like this:
| Apply Histogram | Sliding Window Search | Search from Prior |
|---|---|---|
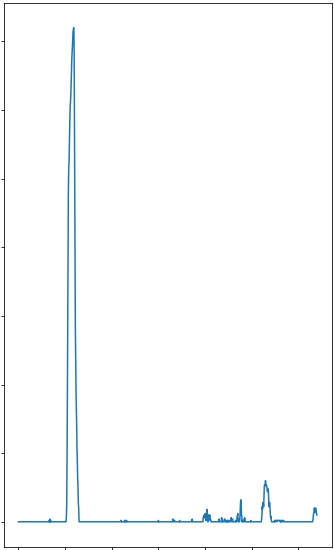 |
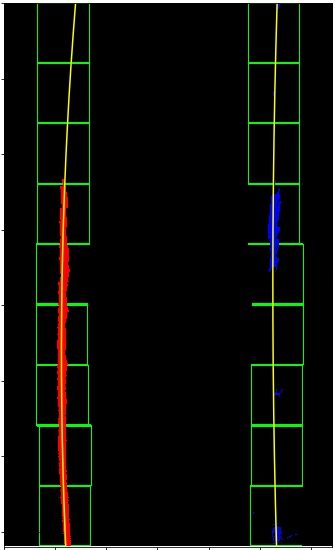 |
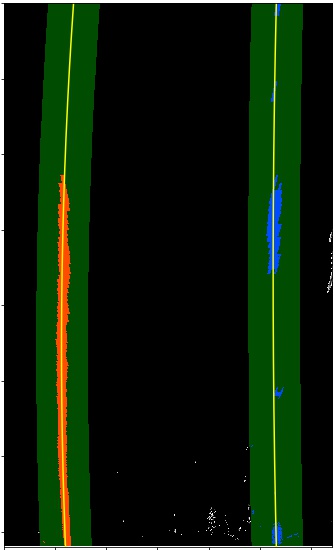 |
The implemented functions are hist(), fit_polynomial(), and search_around_poly().
5. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you calculated the radius of curvature of the lane and the position of the vehicle with respect to center.
I did this in measure_curvature_real() function of the IPython notebook.
6. Provide an example image of your result plotted back down onto the road such that the lane area is identified clearly.
I implemented this step in the function draw_lane() and caption(). Here is an example of my result on a test image:
| Drawed Lane Image | Final output |
|---|---|
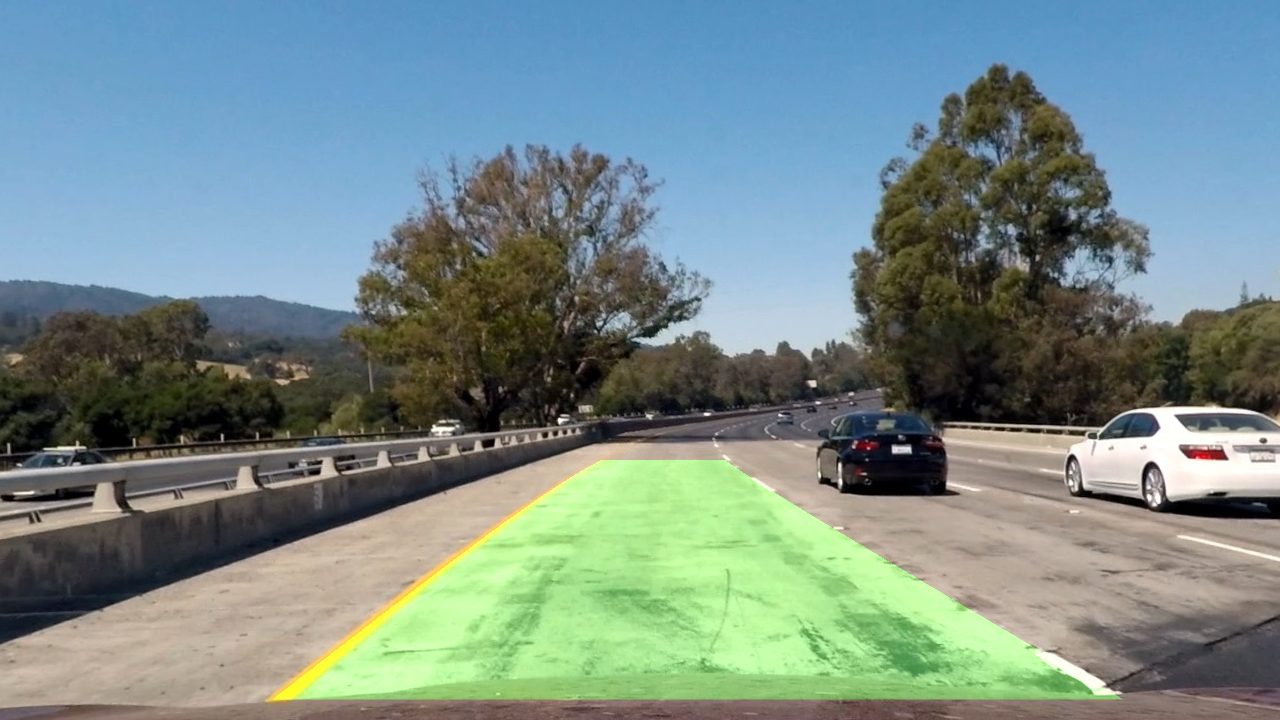 |
 |
1. Provide a link to your final video output. Your pipeline should perform reasonably well on the entire project video (wobbly lines are ok but no catastrophic failures that would cause the car to drive off the road!).
Below is a link to my video result.
1. Briefly discuss any problems / issues you faced in your implementation of this project. Where will your pipeline likely fail? What could you do to make it more robust?
Although I successfully detected the lane of the project_video.mp4. But when I apply my pipeline to challenge_video.mp4 or harder_challenge_video.mp4, it can't detect normally. Below are some portions I may need to improve.
-
Changed lane
Because the polynomial calculation is depended on previous experience. If user change lane, the lane detection algorithm would be fail. So, if user changes lane, I need to re-calculate lane polynomial.
-
Abnormally detected Lane
If the lane have some lane like shadow or cavity, it may affect my lane detection. I need to improve lane detection algorithm.
-
Curvature too large.
If the curvature is too large, my lane detection algorithm may fail to detect lane with the background. I may need to increase the degree of polynomial.
