- Aravinth Panch
- Gunarakulan Gunaretnam
- Abhitharani Jeyachandran
- Viththiyakaran Nadarajah
- Jayanthan Amalanathan
- Shanjeevan Amalanathan
-
Download and install Visual Studio Code
-
Install VS Code extensions for development process
- Live Server
- Prettier
- Code Runner
- ESLint
- Live Share
-
Download and install Git
-
Set up GPG key
-
Step 01:
- Open gitbash
-
Step 02:
- gpg --full-generate-key
-
Step 03:
- gpg --armor --export "Your public key without quotes"
-
Step 04:
- Copy and paste the public key in the SSH and GPG keys section of GitHub settings
-
Step 05:
- git config --global commit.gpgsign true
-
Step 07:
- Run Windows PowerShell as Administrator: Set-Content -Path ~.gnupg\gpg-agent.conf -Value "default-cache-ttl 86400$([System.Environment]::NewLine)max-cache-ttl 157680000"
-
Step 08:
- In gitbash run the following commands to ensure the new parameters have been loaded:
- gpgconf.exe --reload gpg-agent
- gpgconf.exe --list-options gpg-agent
- In gitbash run the following commands to ensure the new parameters have been loaded:
-
-
Branches
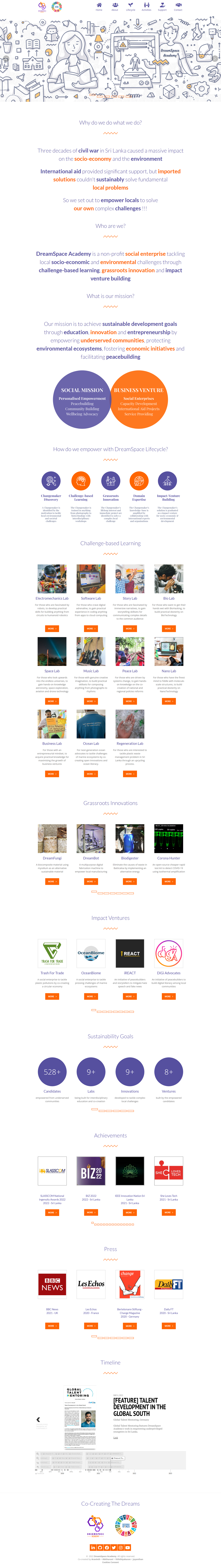
- master: This is the main branch of the project. https://dreamspace.academy/pages/1-0-index.php
- dev: Implement new features and debug. The development processes are done inside this branch. https://dev.dreamspace.academy/pages/1-0-index.php
-
Git commands
-
Step 01: Clone the repository
-
Step 02: Change the working branch to dev branch
- git checkout -b dev origin/dev
-
Step 03: Check for untracked files, directories and modifications
- git status
-
Step 04: Add files that are not tracked by git
- vim .gitignore
-
Step 05: Track untracked files, directories and modifications
- git add .
-
Step 06:
- git commit -m "feat: add commit message"
-
Step 07:
- git push origin dev
-
Step 08:
- git checkout master
-
Step 09:
- git merge dev
-
-
Git commit guidelines
-
Conventional commits. https://medium.com/neudesic-innovation/conventional-commits-a-better-way-78d6785c2e08
-
feat: The commit implements a new feature for the application.
-
fix: The commit fixes a defect in the application.
-
chore: The commit includes a technical or preventative maintenance task that is necessary for managing the product or the repository, but it is not tied to any specific feature or user story.
-
docs: The commit adds, updates, or revises documentation that is stored in the repository.
-
perf: The commit improves the performance of algorithms or general execution time of the product, but does not fundamentally change an existing feature.
-
change: The commit changes the implementation of an existing feature.
-
ci: The commit makes changes to continuous integration or continuous delivery scripts or configuration files.
-
test: The commit enhances, adds to, revised, or otherwise changes the suite of automated tests for the product.
-
security: The commit improves the security of the product or resolves a security issue that has been reported.
-
style: The commit updates or reformats the style of the source code, but does not otherwise change the product implementation.
-
deprecate: The commit deprecates existing functionality, but does not remove it from the product.
-
refactor: The commit refactors existing code in the product, but does not alter or change existing behavior in the product.
-
revert: The commit reverts one or more commits that were previously included in the product, but were accidentally merged or serious issues were discovered that required their removal from the main branch.
-
-