kubectl trace is a kubectl plugin that allows you to schedule the execution
of bpftrace programs in your Kubernetes cluster.
See the release page for the full list of pre-built assets.
The commands here show amd64 versions, 386 versions are available in the releases page.
Linux
curl -LO https://github.com/iovisor/kubectl-trace/releases/download/v0.1.0-rc.1/kubectl-trace_0.1.0-rc.1_linux_amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvf kubectl-trace.tar.gz
mv kubectl-trace /usr/local/bin/kubectl-traceOSX
curl -L -o kubectl-trace.tar.gz https://github.com/iovisor/kubectl-trace/releases/download/v0.1.0-rc.1/kubectl-trace_0.1.0-rc.1_darwin_amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvf kubectl-trace.tar.gz
mv kubectl-trace /usr/local/bin/kubectl-traceWindows
In PowerShell v5+
$url = "https://github.com/iovisor/kubectl-trace/releases/download/v0.1.0-rc.1/kubectl-trace_0.1.0-rc.1_windows_amd64.zip"
$output = "$PSScriptRoot\kubectl-trace.zip"
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $url -OutFile $output
Expand-Archive "$PSScriptRoot\kubectl-trace.zip" -DestinationPath "$PSScriptRoot\kubectl-trace"go get -u github.com/iovisor/kubectl-trace/cmd/kubectl-trace
This will download and compile kubectl-trace so that you can use it as a kubectl plugin with kubectl trace
You can't find the package for your distro of choice? You are very welcome and encouraged to create it and then open an issue to inform us for review.
The official PKGBUILD is on AUR.
If you use yay to manage AUR packages you can do:
yay -S kubectl-trace-git
See architecture.md
You don't need to setup anything on your cluster before using it, please don't use it already on a production system, just because this isn't yet 100% ready.
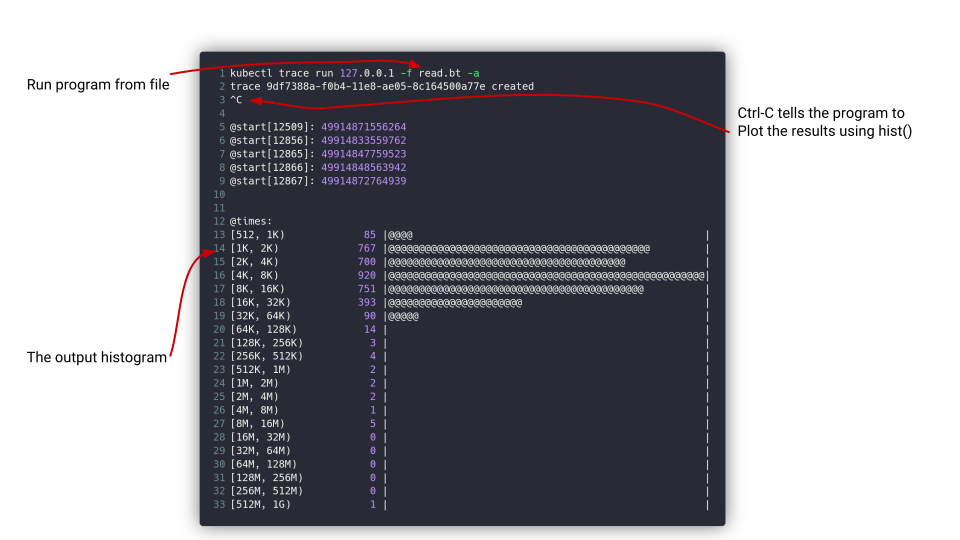
In this case we are running a program that probes a tracepoint
on the node ip-180-12-0-152.ec2.internal.
kubectl trace run ip-180-12-0-152.ec2.internal -e "tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_* { @[probe] = count(); }"
Here we run a program named read.bt against the node ip-180-12-0-152.ec2.internal
kubectl trace run ip-180-12-0-152.ec2.internal -f read.bt
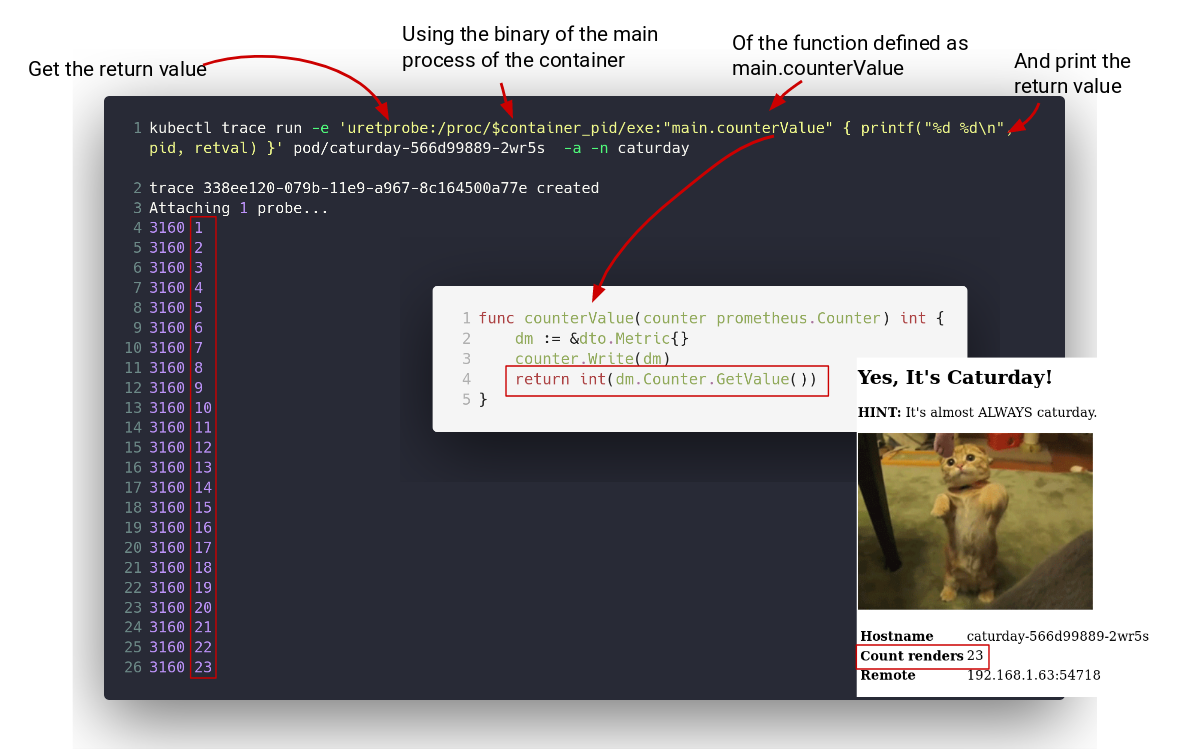
That pod has a Go program in it that is at /caturday, that program has a function called main.counterValue in it that returns an integer
every time it is called.
The purpose of this program is to load an uretprobe on the /caturday binary so that every time the main.counterValue function is called
we get the return value out.
Since kubectl trace for pods is just an helper to resolve the context of a container's Pod, you will always be in the root namespaces
but in this case you will have a variable $container_pid containing the pid of the root process in that container on the root pid namespace.
What you do then is that you get the /caturday binary via /proc/$container_pid/exe, like this:
kubectl trace run -e 'uretprobe:/proc/$container_pid/exe:"main.counterValue" { printf("%d\n", retval) }' pod/caturday-566d99889-8glv9 -a -n caturday
In general, you run kprobes/kretprobes, tracepoints, software, hardware and profile events against nodes using the node/node-name syntax or just use the
node name, node is the default.
When you want to actually probe an userspace program with an uprobe/uretprobe or use an user-level static tracepoint (usdt) your best
bet is to run it against a pod using the pod/pod-name syntax.
It's always important to remember that running a program against a pod, as of now, is just a facilitator to find the process id for the binary you want to probe on the root process namespace.
You could do the same thing when running in a Node by knowing the pid of your process yourself after entering in the node via another medium, e.g: ssh.
So, running against a pod doesn't mean that your bpftrace program will be contained in that pod but just that it will pass to your program some
knowledge of the context of a container, in this case only the root process id is supported via the $container_pid variable.
By default kubectl trace will use the default service account in the target namespace (that is also default), to schedule the pods needed for your bpftrace program.
If you need to pass a service account you can use the --serviceaccount flag.
kubectl trace run --serviceaccount=kubectltrace ip-180-12-0-152.ec2.internal -f read.btIf your cluster has pod security policies you will need to make so that kubectl trace can
use a service account that can run privileged containers.
That service account, then will need to be in a group that uses the proper privileged PodSecurityPolicy.
First, create the service account that you will use with kubectl trace,
you can use a different namespace other than default, just remember to pass that namespace to the run command when you will use kubectl trace:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: kubectltrace
namespace: defaultNow that we have a kubectltrace service account let's create a Pod Security Policy:
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
name: kubectltrace
spec:
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
privileged: true
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
volumes:
- '*'
allowedCapabilities:
- '*'
hostPID: true
hostIPC: true
hostNetwork: true
hostPorts:
- min: 1
max: 65536Ok, this PodSecurityPolicy will allow users assigned to it to run privileged containers,
kubectl trace needs that because of the extended privileges eBPF programs need to run with
to trace your kernel and programs running in it.
Now with a ClusterRoleBinding you bind the ClusterRole with the ServiceAccount, so that
they can work together with the PodSecurityPolicy we just created.
You can change the namespace: default here if you created the service account in a namespace other than default.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: kubectltrace-psp
rules:
- apiGroups:
- policy
resources:
- podsecuritypolicies
resourceNames:
- kubectltrace
verbs:
- use
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: kubectltrace-psp
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kubectltrace
namespace: default
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: kubectltrace-pspOK! Now that we are all set we can just run the program by specifying the service account we just created and it will use our pod security policy!
kubectl trace run --serviceaccount=kubectltrace ip-180-12-0-152.ec2.internal -f read.btIf you used a different namespace other than default for your service account, you will want to specify the namespace too, like this:
kubectl trace run --namespace=mynamespace --serviceaccount=kubectltrace ip-180-12-0-152.ec2.internal -f read.btNeed more programs? Look here.
🏆 All the MVP goals are done!
To consider this project (ready) the goals are:
- basic program run and attach
- list command to list running traces - command:
kubectl trace get - delete running traces
- run without attach
- attach command to attach only - command:
kubectl trace attach <program> - allow sending signals (probably requires a TTY), so that bpftrace commands can be notified to stop by the user before deletion and give back results
More things after the MVP:
The stuff here had been implemented - YaY
The program is now limited to run programs only on your nodes but the idea is to have the ability to attach only to the user namespace of a pod, like:
kubectl trace run pod/<pod-name> -f read.bt
And even on a specific container
kubectl trace run pod/<pod-name> -c <container> f read.bt
So I would say, the next thing is to run bpftrace programs at a pod scope other than at node scope.
Already pumped up to commit some code? Here are some resources to join the discussions in the IOVisor community and see what you want to work on.
- Mailing List: http://lists.iovisor.org/mailman/listinfo/iovisor-dev
- IRC: #iovisor at irc.oftc.net
- Slack #kubectl-trace in the Kubernetes Slack
- Kubectl Trace Issue Tracker: Github Issues
Special thanks to Ramon Gilabert for the logo.