The framework proposals a unified API for vendors to provide solutions to various aspects of performing the principles of chaos engineering in a Cloud Native environment, its built-in modules will heavily testify reliability, availability and resilience for distriuted system, especially for messaging and eventing. Currently, the community supported the following platforms:
- Apache RocketMQ
- Apache Kafka
- Redis -- ongoing
Take RocketMQ for example:
- Prepare one control node and some cluster nodes and ensure that the control node can use SSH to log into a bunch of db nodes
- Edit driver-rocketmq/rocketmq.yaml to set the host name of cluster nodes, client config, broker config.
- Install openmessaging-chaos in control node:
mvn clean install - Run the test in the control node:
bin/chaos.sh --driver driver-rocketmq/rocketmq.yaml --install - After the test, you will get yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-driver-chaos-result-file and yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-driver-latency-point-graph.png (Gnuplot must be installed).
In one shell, we start the some cluster nodes and the controller using docker compose.
cd docker
./up.sh --devIn another shell, use docker exec -it chaos-control bash to enter the controller, then
mvn clean install
bin/chaos.sh --driver driver-rocketmq/rocketmq.yaml --installUsage: messaging-chaos [options]
Options:
-c, --concurrency
The number of clients. eg: 5
Default: 4
* -d, --driver
Driver. eg.: driver-rocketmq/rocketmq.yaml
-f, --fault
Fault type to be injected. eg: noop, minor-kill, major-kill,
random-kill, fixed-kill, random-partition, fixed-partition,
partition-majorities-ring, bridge, random-loss, minor-suspend,
major-suspend, random-suspend, fixed-suspend
Default: noop
-i, --fault-interval
Fault injection interval. eg: 30
Default: 30
-n, --fault-nodes
The nodes need to be fault injection. The nodes are separated by
semicolons. eg: 'n1;n2;n3' Note: this parameter must be used with
fixed-xxx faults such as fixed-kill, fixed-partition, fixed-suspend.
-h, --help
Help message
--install
Whether to install program. It will download the installation package on
each cluster node. When you first use OpenMessaging-Chaos to test a
distributed system, it should be true.
Default: false
-t, --limit-time
Chaos execution time in seconds (excluding check time and recovery
time). eg: 60
Default: 60
-m, --model
Test model. Currently only queue model is supported.
Default: queue
--order
Check the partition order of messaging platform. Just for mq model.
Default: false
--pull
Driver use pull consumer, default is push consumer. Just for mq model.
Default: false
-r, --rate
Approximate number of requests per second. eg: 20
Default: 20
--recovery
Calculate failure recovery time.
Default: false
--rto
Calculate failure recovery time in fault.
Default: false
-u, --username
User name for ssh remote login. eg: admin
Default: root
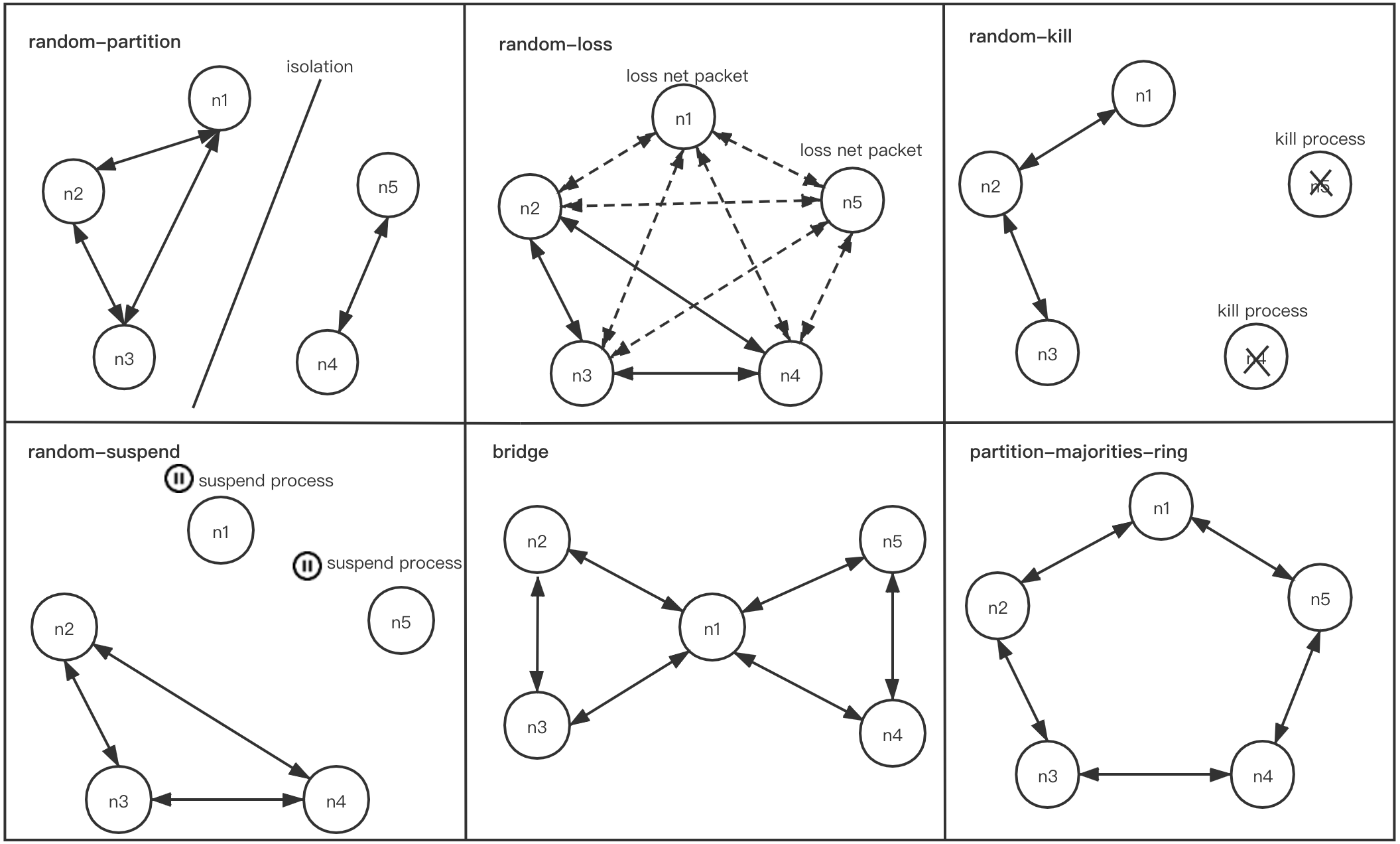
The following fault types are currently supported:
- random-partition (fixed-partition): isolates random(fixed) nodes from the rest of the network.
- random-loss: randomly selected nodes lose network packets.
- random-kill (minor-kill, major-kill, fixed-kill): kill random(minor, major, fixed) processes and restart them.
- random-suspend (minor-suspend, major-suspend, fixed-suspend): pause random(minor, major, fixed) nodes with SIGSTOP/SIGCONT.
- bridge: a grudge which cuts the network in half, but preserves a node in the middle which has uninterrupted bidirectional connectivity to both components (note: number of nodes must be greater than 3).
- partition-majorities-ring: every node can see a majority, but no node sees the same majority as any other. Randomly orders nodes into a ring (note: number of nodes must be equal to 5).