Fiteft (Fit effective field theory) is a Python package for calculating approximated likelihood function of Standard Model Effective Field Theory (SMEFT) parameters using experimental data. We also provide a method for calculating the best-fit value and confident intervals of SMEFT parameters.
Fiteft is distributed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 3 (see the LICENSE file). This ensures that the source code will be available to users, grants them the freedom to use and modify the program and sets out the conditions under which it can be redistributed.
WARNING: This is the first beta version, which has NOT been well tested. Use it with care and at your own risk.
- Python 3.10 (or 3.X)
- numpy (preferable newest version)
- pandas (preferable newest version)
- re
Optional, for the minimization of the likelihood functions
- scipy (preferable newest version)
We provide a step-by-step intruction via a Google colab notebook. User can run the notebook directly through Google's machine.
- Open the Colab notebook
- Choose
File> Save a copy in Drive. Now you can start run the notebook - Run the setup cell once, then you can run the cells in the example section from top to bottom.
Full instruction is in the example section.
We also provide a ready-to-run, line-by-line jupyter notebook examples/example.ipynb. You can either run it on your machine, or run it via GitHub code space
- Go to the repository page
- Click
Code> Create codespace on master - Open
examples/example.ipynbvia left pannel which will open a jupyter notebook on VScode on GitHub codespace, you then can run the notebook directly on your browser.
You first need to clone the Fiteft project by running this command on your terminal
git clone https://github.com/dunglvht/FiteftIn a Python script, you have to add Fieft to sys.path, import Fiteft, python, pandas, then create a fiteft object
import sys
sys.path.append('<Fiteft_path>')
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import Fiteft
f = Fiteft.fiteft()Note that the default argument of fiteft() is ATLAS-CONF-2020-053, which is the name of the experiment whom data we are using.
Now you can run the fiteft.likelihood() function right away
>>> f.likelihood(pd.DataFrame(np.ones((2,2)), columns = ['c(3)Hq','c[1]Hl(3)-ll0']))
array([[[1803.67453384]],
[[1803.67453384]]])or a shorter version, fiteft.l() function
>>> f.l(np.array([1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0]))
array([[[1803.67453384]]])Detailed usage is provided via jupyter notebooks.
Full description of the file structures, functions is detailed in doc/manual.pdf file.
Full description of the physics will be soon provided after I finished defending my thesis.
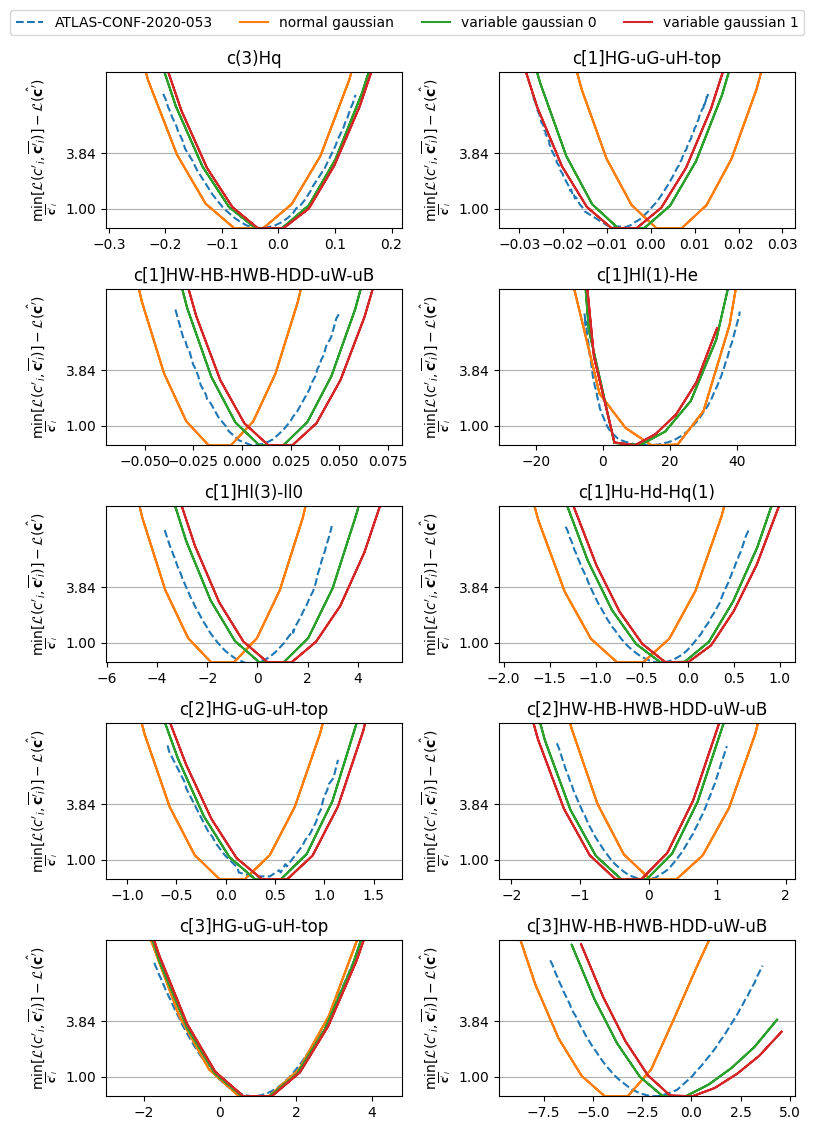
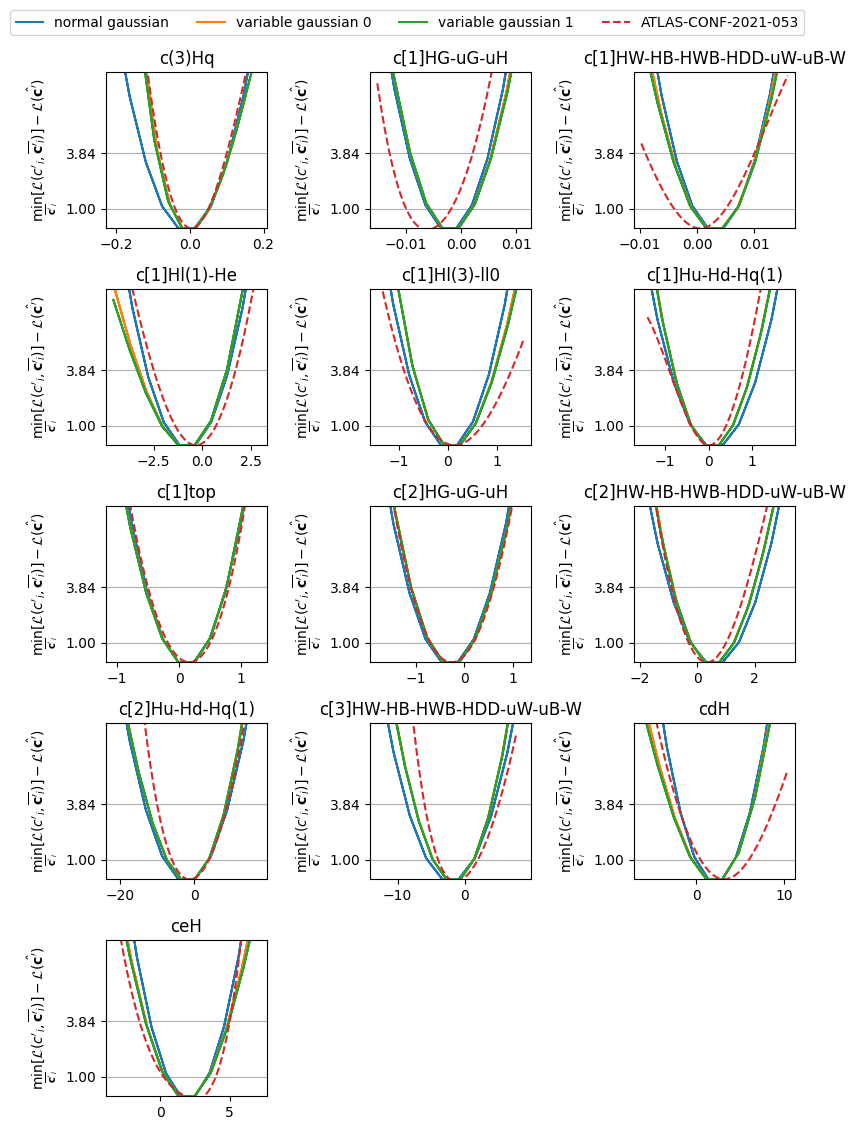
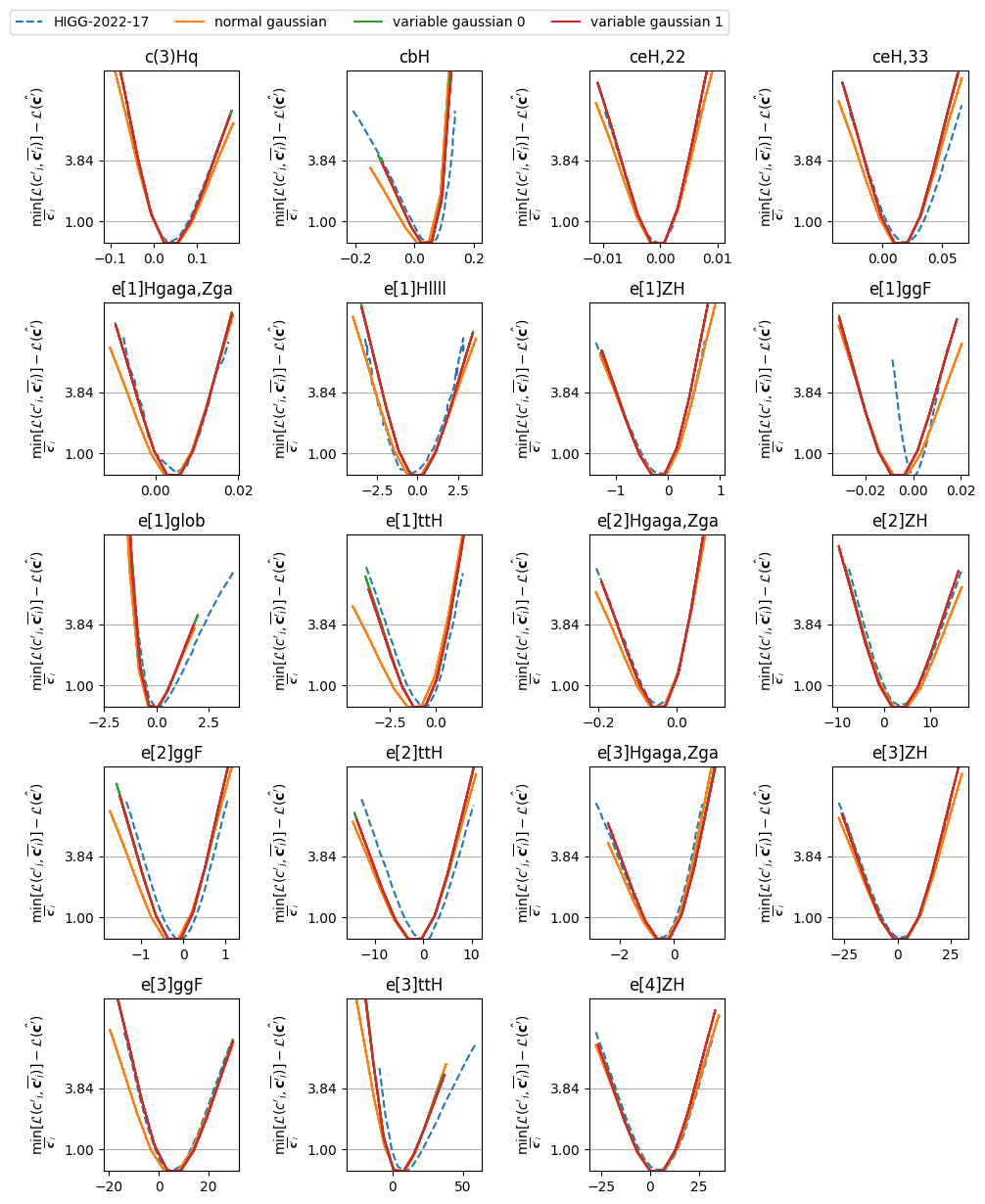
We present our fit results in three definition of the likelihood function and compare them with some of the most recent SMEFT results from the ATLAS experiment: ATLAS-CONF-2020-053, ATLAS-CONF-2021-053, and HIGG-2022-17
The code used to produce these results is in the validation.ipynb file, or if you prefer Python script, validation/{experiment_name}/validate.py file. The calculation process will takes about 3-10 minutes on Github codespace, or 10-30 minutes on Google colab notebook.