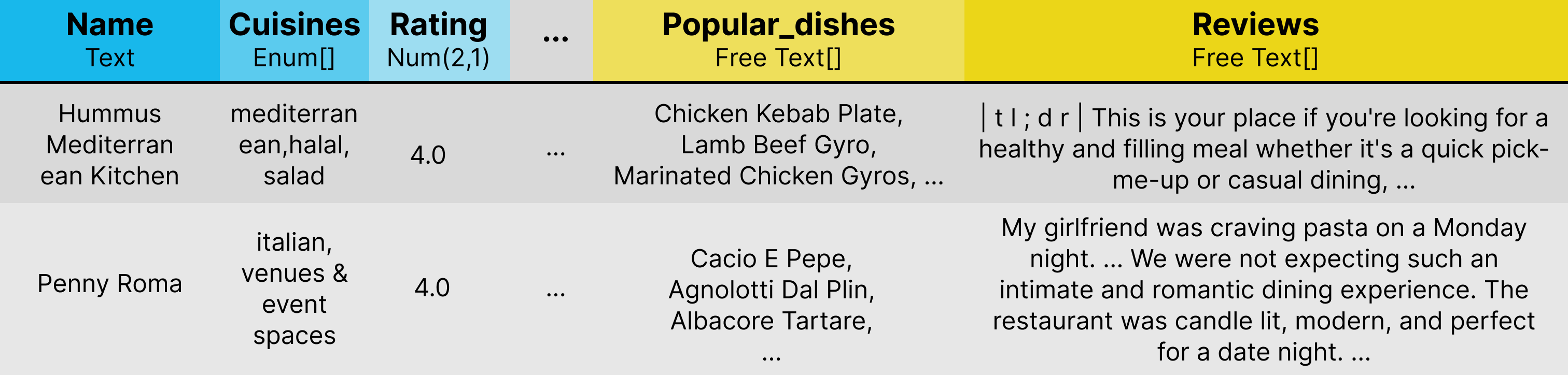
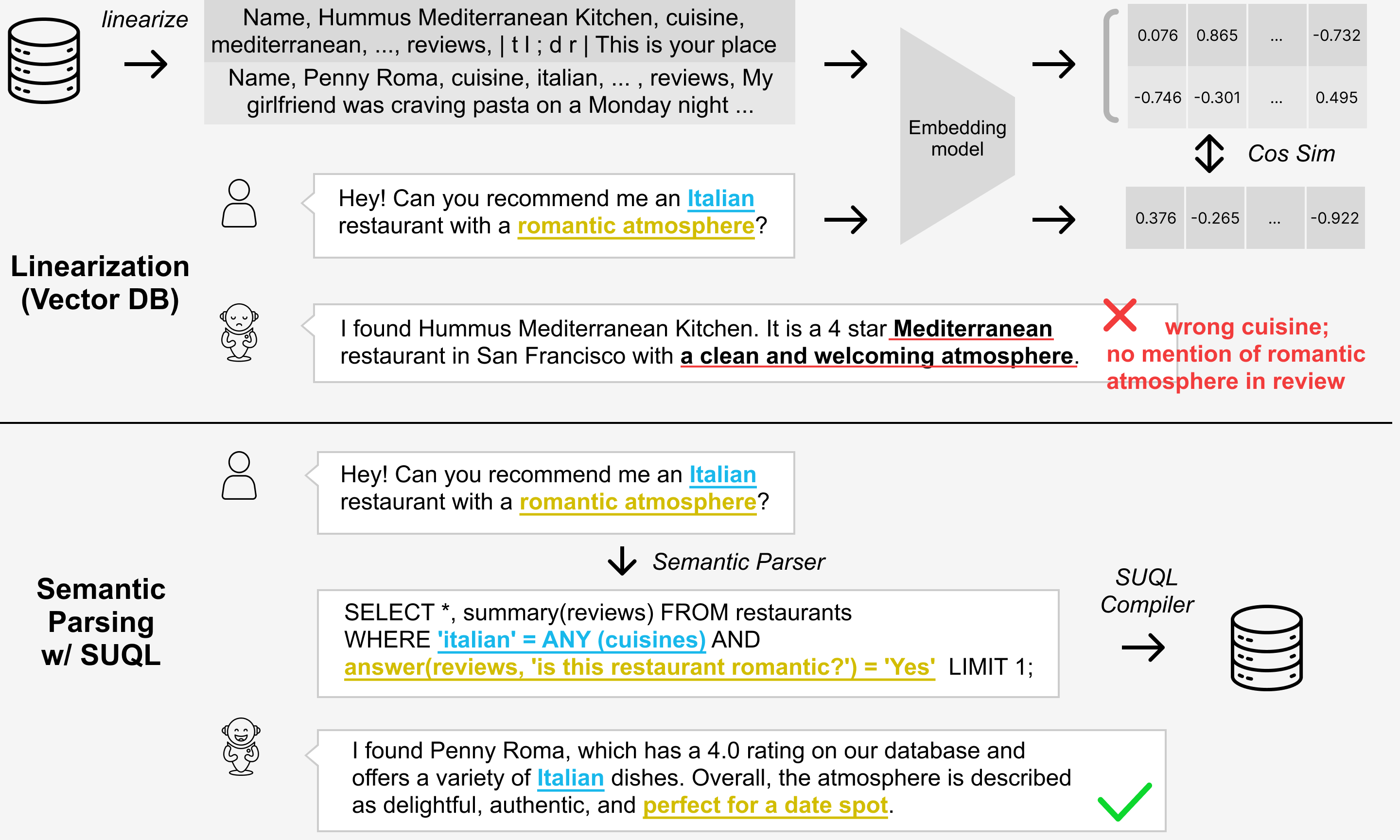
SUQL stands for Structured and Unstructured Query Language. It augments SQL with several important free text primitives for a precise, succinct, and expressive representation. It can be used to build chatbots for relational data sources that contain both structured and unstructured information. Similar to how text-to-SQL has seen great success, SUQL can be uses as the target language for hybrid databases, for instance, for:
One important component of SUQL is the answer function. answer function allows for constraints from free text to be easily combined with structured constraints. Here is one high-level example:
For more details, see our paper at https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.09818.
Installing PostgreSQL database
-
Follow the instruction there to install a postgreSQL database. For instance, if you are installing on Ubuntu, then follow section
PostgreSQL Apt Repositoryat https://www.postgresql.org/download/linux/ubuntu/. -
After that, the SUQL compiler needs to make use of python functions within postgreSQL. This is done via the
postgresql-plpython3language. If you are using Ubuntu, simply runsudo apt-get install postgresql-plpython3-15. -
Then, in your database's command line (incurred via
psql your_database_name), doCREATE EXTENSION plpython3u;. This loads this language into the current db.
-
Install dependencies in
requirements.txt; -
Run
python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm; -
Run
pip install -e .to install SUQL as a library.
The entry point to the SUQL compiler is the following snippet under src/suql/yelp_loop.py:
visitor = SelectVisitor()
root = parse_sql(second_sql)
visitor(root)
second_sql = RawStream()(root)
The SelectVisitor might modify the original sql (second_sql here) and return the caller a new one. It might create a new temporary table named temp_*, from which the modified SQL will be executed on.
Here is a rough breakdown of what you need to do to set up SUQL on your domain:
-
Set up OpenAI API key with
export OPENAI_API_KEY=[your OpenAI API key here] -
Write a semantic parser prompt, and substitute
prompts/parser_sql.promptwith it. Include examples of how to use theanswerfunction. -
Set up an embedding server for the SUQL compiler to query. Go to
sql_free_text_support/embedding_support.py, and modify the lineembedding_store.add("restaurants", "_id", "popular_dishes")andembedding_store.add("restaurants", "_id", "reviews")to match your database with its column names. For instance, the current two lines there are saying that set up an embedding server for therestaurantsdatabase, which has_idcolumn as the unique row identifier, for thepopular_dishesandreviewscolumns (these columns need to be of typeTEXTorTEXT[]). By default, this will be set up on port 8509, which is then called byexecute_free_text_sql. In case you need to use another port, please change both addresses. Note that this embedding server uses a mongodb to cache embedding results. Please follow https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/installation/ for your OS. -
In the command line for your database, copy and paste all content under
custom_functions.sql. This will define theanswerandsummaryfunctions under your PostgreSQL database. -
Set up the backend server for the
answer,summaryfunctions. As you probably noticed, the code incustom_functions.sqlis just making queries to a server. This server can be instantiated by runningpython reviews_server.py. -
There is a classifier to determine whether a user utterance requires database access, at this line:
llm_generate(template_file='prompts/if_db_classification.prompt', ...). This may or may not be applicable to your domain, and if it is, please modify the corresponding prompt. -
A note on PostgreSQL's permission issue. The user-facing parts of this system would only require SELECT privilege (it would be safe to grant only SELECT privilege for GPT-generated queries). This user is named
select_userwith passwordselect_userin this file. You should change the default values foruser,password, anddatabasethere to match your PostgreSQL set up. This user also appears once in this file of the SUQL compiler, so that intermediate tables created can be queried. Please also change it to match your user name. -
Furthermore, various parts of the SUQL compiler require the permission to create a temporary table. You can search for
creator_roleunder this file. You would need to create a user with the privilege to CREATE tables under your database, and changecreator_roleto match that user and password. -
Test with
python yelp_loop.py.
-
if you see error msgs similar to
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/tmp/data-gym-cache/9b5ad71b2ce5302211f9c61530b329a4922fc6a4.2749b823-646b-45d7-9fcf-11414469d900.tmp'. Refer to openai/tiktoken#75. A likely solution is settingTIKTOKEN_CACHE_DIR="". -
A lot of times, Azure/OpenAI's chatGPT deployment's latency is unstable. We have experienced up to 10 minutes of latency for some inputs. These cases are rare (we estimate < 3% of cases), but they do happen from time to time. For those cases, if we cancel the request and re-issue them, then we typically can get a response in normal time. To counter this issue, we have implemented a max-wait-then-reissue functionality in our API calls. Under this file, we have the following block:
if max_wait_time is None:
max_wait_time = 0.005 * total_token + 1
This says that if a call to llm_generate does not set a max_wait_time, then it is dynamically calculated based on this linear function of total_token. This is imperfect, and we are erroring on the side of waiting longer (e.g., for an input with 1000 tokens, this would wait for 6 seconds, which might be too long). You can set a custom wait time, or disable this feature or together by setting attempts = 0.