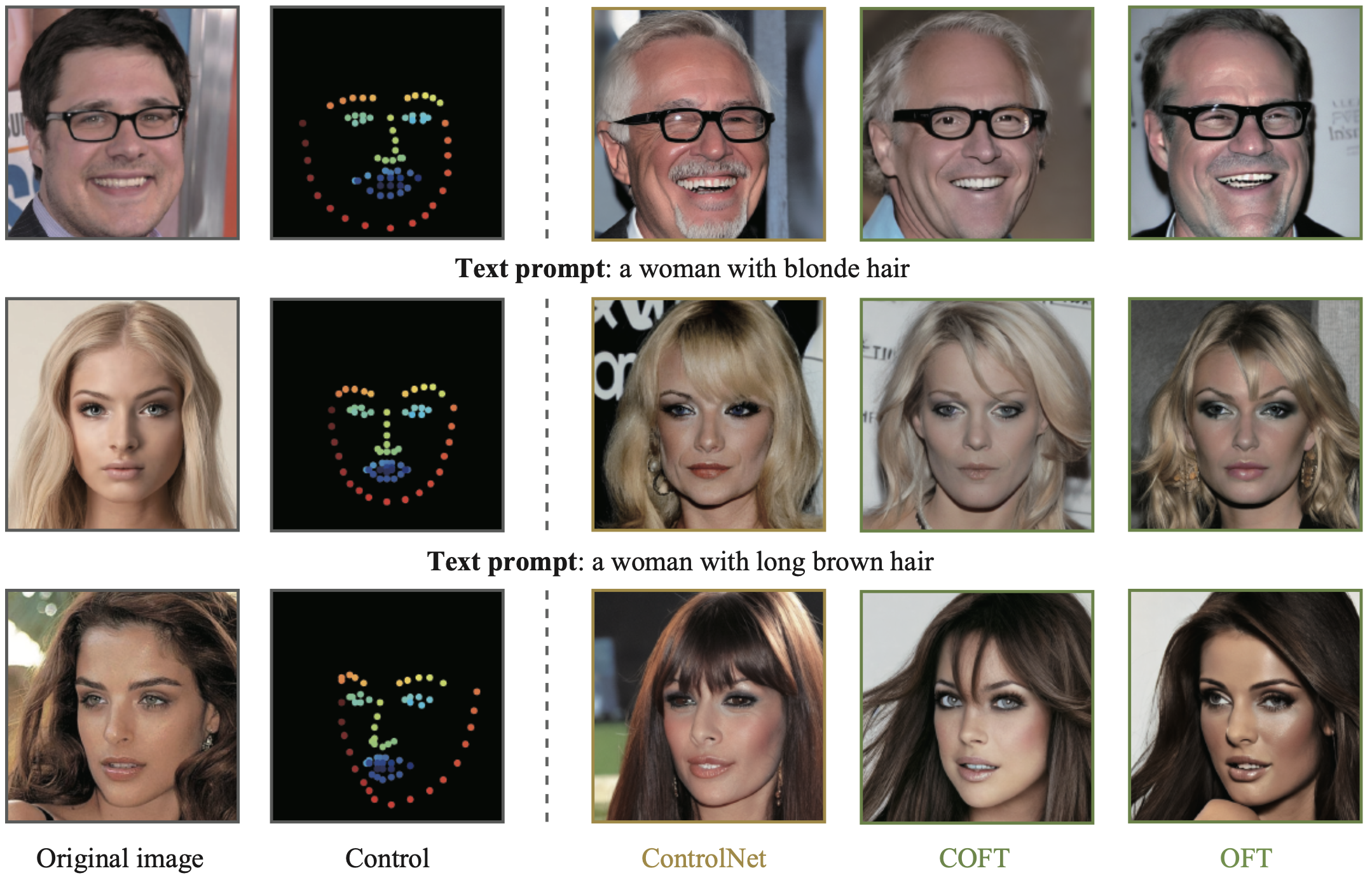
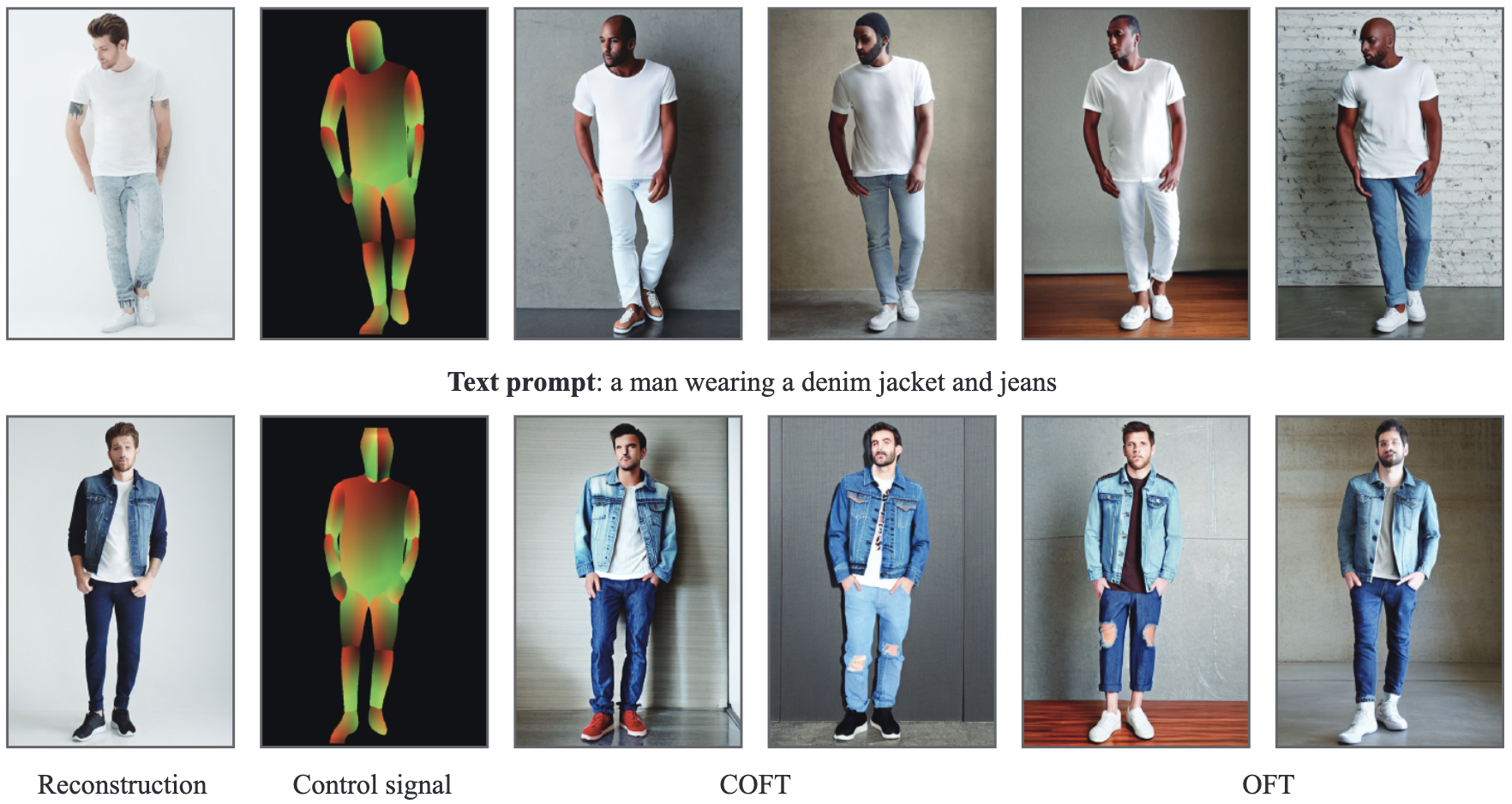
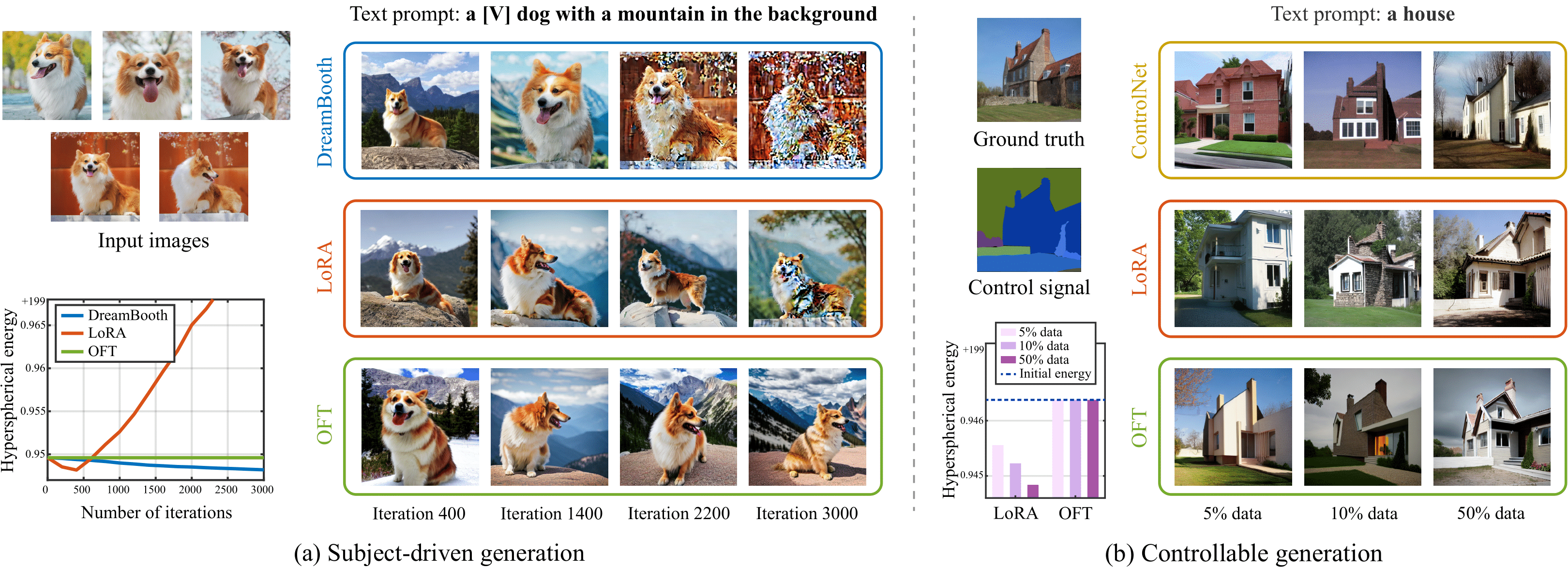
Large text-to-image diffusion models have impressive capabilities in generating photorealistic images from text prompts. How to effectively guide or control these powerful models to perform different downstream tasks becomes an important open problem. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a principled finetuning method -- Orthogonal Finetuning (OFT), for adapting text-to-image diffusion models to downstream tasks. Unlike existing methods, OFT can provably preserve hyperspherical energy which characterizes the pairwise neuron relationship on the unit hypersphere. We find that this property is crucial for preserving the semantic generation ability of text-to-image diffusion models. To improve finetuning stability, we further propose Constrained Orthogonal Finetuning (COFT) which imposes an additional radius constraint to the hypersphere. Specifically, we consider two important finetuning text-to-image tasks: subject-driven generation where the goal is to generate subject-specific images given a few images of a subject and a text prompt, and controllable generation where the goal is to enable the model to take in additional control signals. We empirically show that our OFT framework outperforms existing methods in generation quality and convergence speed.
Stay tuned, more information and code coming soon.
- 2023.6.23: initial commit. Code for running controllable generation (ControlNet-like tasks) and subject-driven generation (Dreambooth-like tasks).
- Code for running controllable generation (ControlNet-like tasks)
- Code for running subject-driven generation (Dreambooth-like tasks)
- Refine readme
- Fast version of OFT
- More examplar applications
Run the scripts in the 'scripts' folder to automatically download the preprocessed data required for oft-control or oft-db.
Note: When using the downloading script, it is necessary to agree to the terms of their licenses and properly cite them in your work.
oft-controlfor Controllable Generation: e.g., for running the densepose-to-image experiment, run the script:
bash scripts/dataset_setup_control_deepfashion.shoft-dbfor Subject-driven Generation: download and store the dreambooth, run:
bash scripts/dataset_setup_db_dreambooth.shAfter downloading and placing the data, your directory structure should look like this:
data
├── ADE20K
│ ├── train
│ │ ├── color
│ │ ├── segm
│ │ └── prompt_train_blip.json
│ └── val
│ │ ├── color
│ │ ├── segm
│ │ └── prompt_val_blip.json
└── COCO
│ ├── train
│ │ ├── color
│ │ ├── depth
│ ...
...
├── dreambooth
│ ├── backpack
│ ├── backpack_dog
│ ...
-
To download the required model for this project, visit the following link: v1-5-pruned.ckpt
-
Store the downloaded model weights in the
modelsdirectory.
Follow these steps to set up the project environment:
- Clone the oft repository. We'll call the directory that you cloned oft as $OFT_ROOT.
git clone https://github.com/Zeju1997/oft.git- Construct the virtual environment:
conda env create -f environment.ymlThere are only two hyperparameters that one need to adjusted, we noticed that generally with more number of blocks the fine-tuning results become worse. Block sharing is by default false, but might work if the control is very simple.
- Number of blocks: r
- eps-deviation (only with the constrained variant COFT): eps
- Block-sharing: block_share
| r = 2 | r = 4 | r = 8 | r = 16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trainable Params | 29.5 M | 16.3 M | 9.7 M | 6.4 M |
| mIoU ↑ | 27.18 | 27.06 | 24.09 | 21.0 |
| mAcc ↑ | 39.39 | 40.09 | 36.95 | 32.55 |
| aAcc ↑ | 65.24 | 62.96 | 60.25 | 55.5 |
- Create the model with additional OFT parameters:
python oft-control/tool_add_control_oft.py \
--input_path=./models/v1-5-pruned.ckpt \
--output_path=./models/control_sd15_ini_oft.ckpt \
--eps=1e-3 \
--r=4 \
--coft- Specify the control signal and dataset. Train the model specify the same hyperparameters as above:
python oft-control/train.py \
--eps=1e-3 \
--r=4 \
--coft- Because OFT does not affect the neuron norm, the neuron magnitude might be sub-optimal. Run the following script for performing magnitude post-stage fitting after training an oft to improve on the magnitude.
python oft-control/train_with_norm.py - After finetuning with OFT, run inference to generate images based on control signal. Because the inference takes some time, to perform large scale evaluation, we split the dataset into different sub-datasets and run inference on multiple gpus:
python oft-control/test_oft_parallel.py \
--img_ID=1 \
--eps=1e-3 \
--r=4 \
--coft- To evaluate OFT results on the three tasks listed in the paper (landmark-to-image (L2I), canny-to-image (C2I) and segmentation map-to-image (S2I)), run the following scripts on the generated images.
python oft-control/eval_landmark.pypython oft-control/eval_canny.pyNote, for evaluating the segmentation map-to-image (S2I) task, please install the Segformer repository. Run the following testing command on both the original and generated images.
python tools/test.py local_configs/segformer/B4/segformer.b4.512x512.ade.160k.py ./weights/segformer.b4.512x512.ade.160k.pth- Similar to the example for diffusers-dreambooth, you can run the finetuning using oft with the following command. The three paramters that need to be adjusted are the same as above:
- Number of blocks: r
- eps-deviation (only with the constrained variant COFT): eps
- Block-sharing: block_share Within the 'oft-db' folder, run the training script to run the result on the dreambooth dataset. Dreambooth dataset consists of 30 subjects, with 25 validation prompts each ($i: 0-749):
cd oft-db
./train_dreambooth_oft.sh $i- We also provide the evaluation scripts:
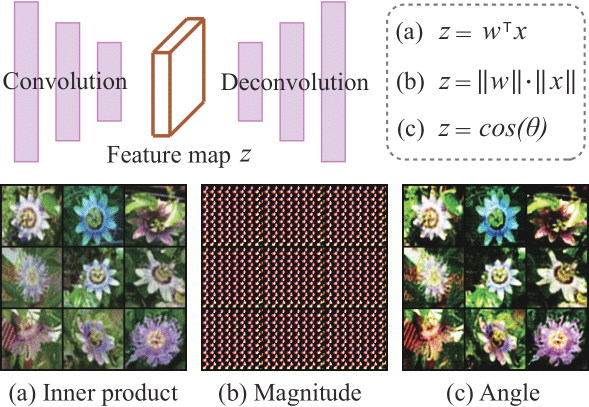
python eval_ablation.py- A toy experiment to demonstrate the importance of angular information. Train a simple convolutional autoencoder on some dataset, as an example, the author trained one on the 102flowers dataset:
python examples/toy_exp_ae.py@InProceedings{Qiu2023OFT,
title={Controlling Text-to-Image Diffusion by Orthogonal Finetuning},
author={Qiu, Zeju and Liu, Weiyang and Feng, Haiwen and Xue, Yuxuan and Feng, Yao and Liu, Zhen and Zhang, Dan and Weller, Adrian and Schölkopf, Bernhard},
booktitle={NeurIPS},
year={2023}
}This project builds upon the work of several other repositories. We would like to express our gratitude to the following projects for their contributions:
- lora: Low-rank Adaptation for Fast Text-to-Image Diffusion Fine-tuning.
- ControlNet: Official implementation of Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models.
- Diffusers: A library for state-of-the-art pretrained diffusion models.
- OPT: Official implementation of Orthogonal Over-Parameterized Training.