Dylan DELORME LUNA - PEI
Jules MANIGNE-MALAN - PEI
Marie MELONI - PEI
Alexandre HALBOUT - Energie
Mateo BOURDAIN - Energie
Ali MROUE - SI
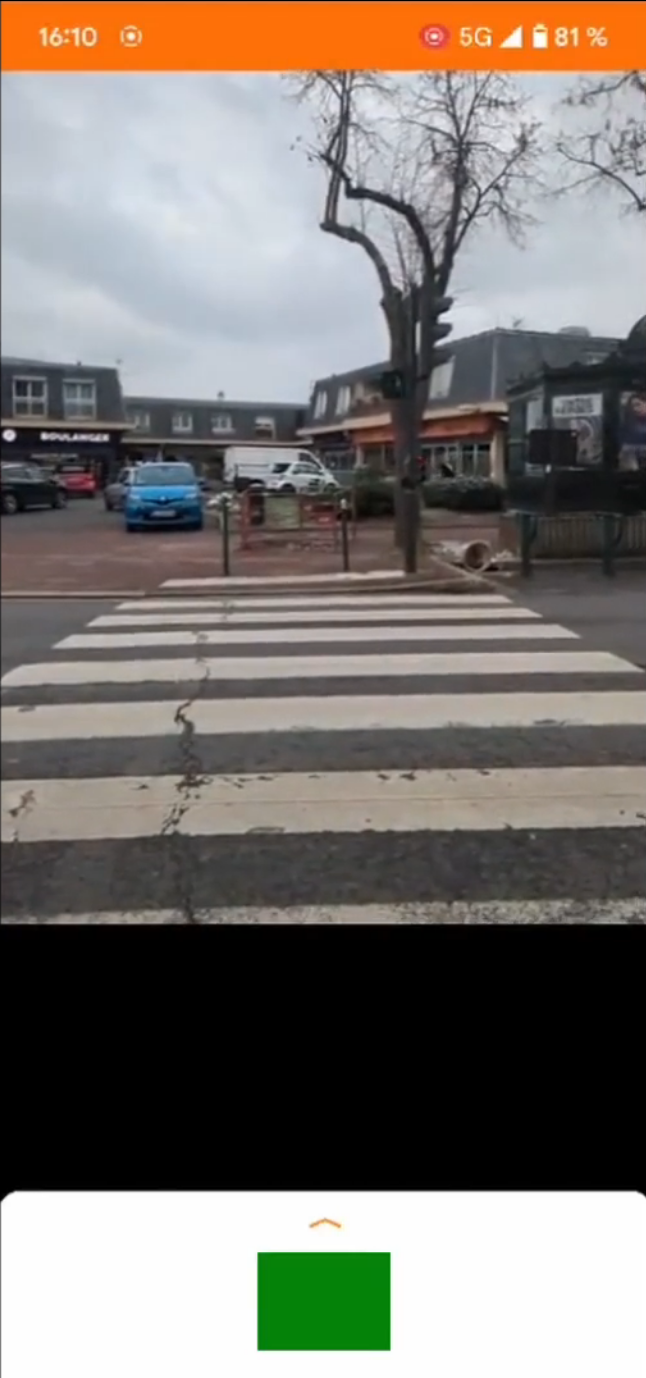
Le projet consiste à développer un outil technique, sous la forme d’une application téléphone android ou ios, qui permettrait avant tout de percevoir des changements d’affichage au niveau des feux piétons dans les agglomérations. Chaque utilisateur, potentiel, dans notre cas les déficients visuels ( DV - Personnes présentant des troubles aigus en terme de vision, caractérisés par des troubles de couleur ou encore une déficience visuelle motrice quasi totale ), pourraient, à l’aide de notre outil, se ballader librement dans les zones urbaines et recevoir des indications sur l’état de chaque passage piéton observé.
Les instructions suivantes permettent d'expliquer comment monter cette application depuis son propre PC.
Une partie des instructions proviennent de la documentation officielle de Tensor Flow Lite, le logiciel permettant de détecter les objets.
- Cette courte vidéo présente la problématique ainsi que notre solution.
3 modèles CANAI pre-entraînés sont déjà installés et prêts a l'utilisation. Par défaut, le plus performant est séléctionné.
-
Android Studio 3.2 (installed on a Linux, Mac or Windows machine)
-
Android device in developer mode with USB debugging enabled
-
USB cable (to connect Android device to your computer)
Clone the CANAI example GitHub repository to your computer to get the demo application.
git clone https://github.com/dydelu/PFECanai
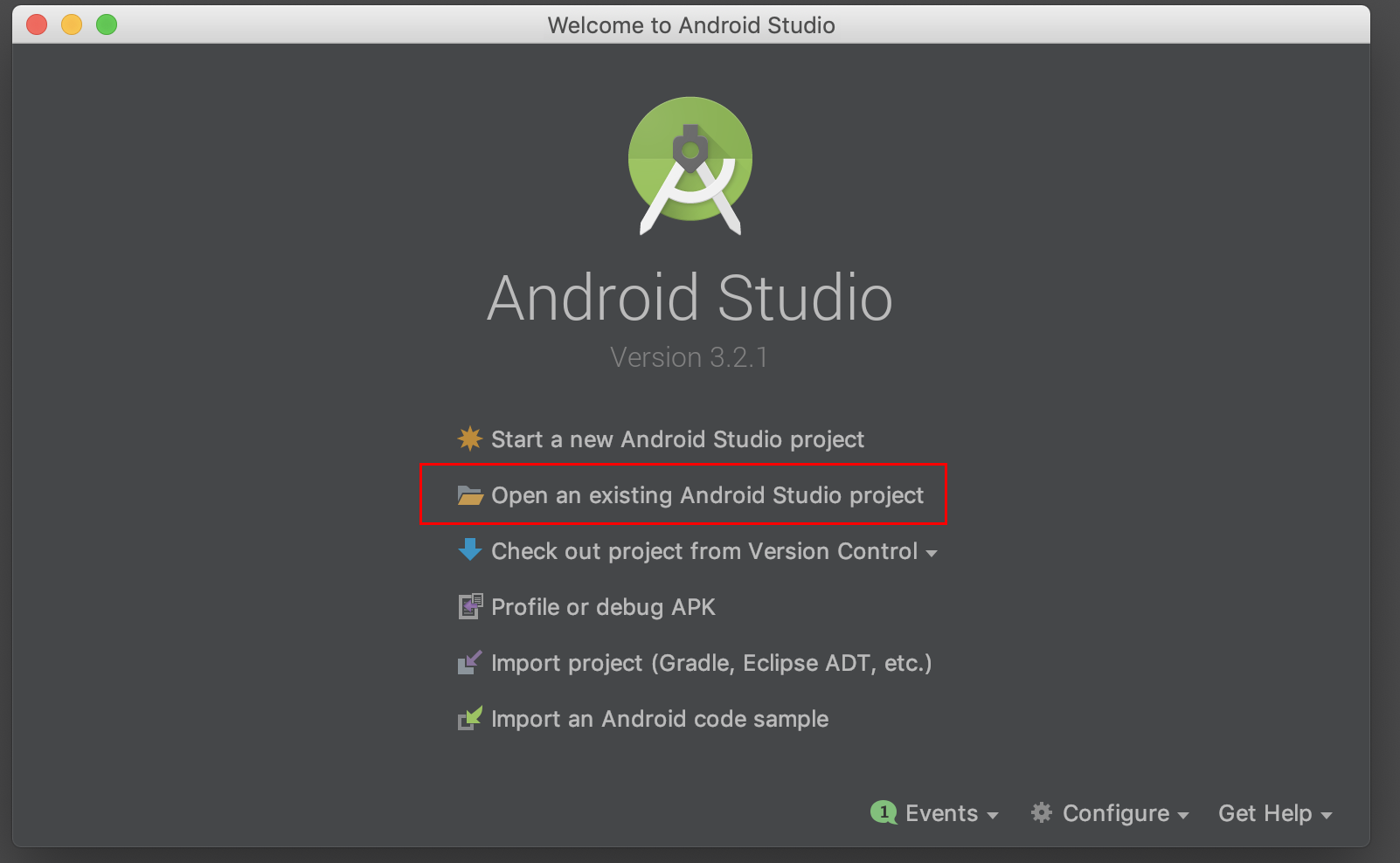
Open the TensorFlow source code in Android Studio. To do this, open Android
Studio and select Open an existing project, setting the folder to
examples/lite/examples/image_classification/android
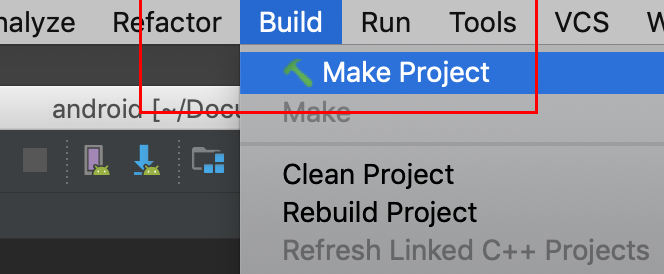
Select Build -> Make Project and check that the project builds successfully.
You will need Android SDK configured in the settings. You'll need at least SDK
version 23. The build.gradle file will prompt you to download any missing
libraries.
This Image Classification Android reference app demonstrates two implementation
solutions,
lib_task_api
that leverages the out-of-box API from the
TensorFlow Lite Task Library,
and
lib_support
that creates the custom inference pipleline using the
TensorFlow Lite Support Library.
You can change the build variant to whichever one you want to build and run—just
go to Build > Select Build Variant and select one from the drop-down menu. See
configure product flavors in Android Studio
for more details.
The file download.gradle directs gradle to download the two models used in the
example, placing them into assets.
`build.gradle` is configured to use TensorFlow Lite's nightly build.
If you see a build error related to compatibility with Tensorflow Lite's Java API (for example, `method X is undefined for type Interpreter`), there has likely been a backwards compatible change to the API. You will need to run `git pull` in the examples repo to obtain a version that is compatible with the nightly build.
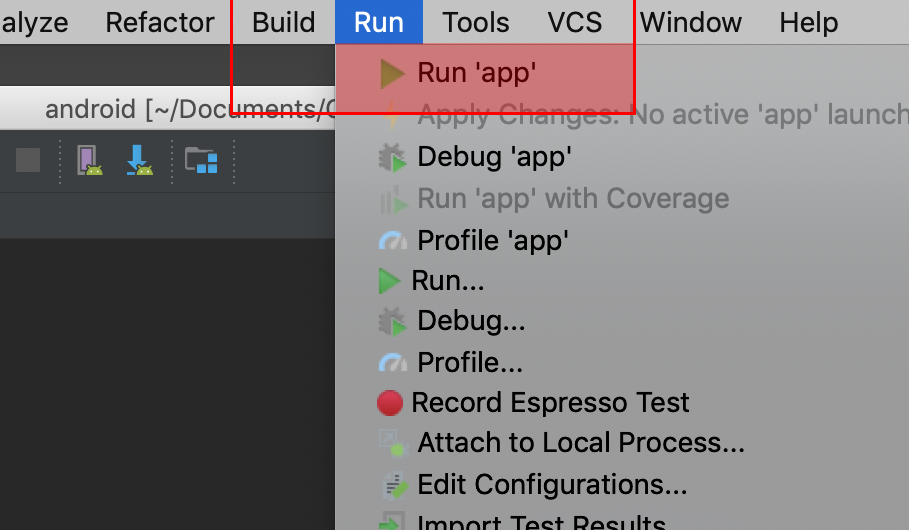
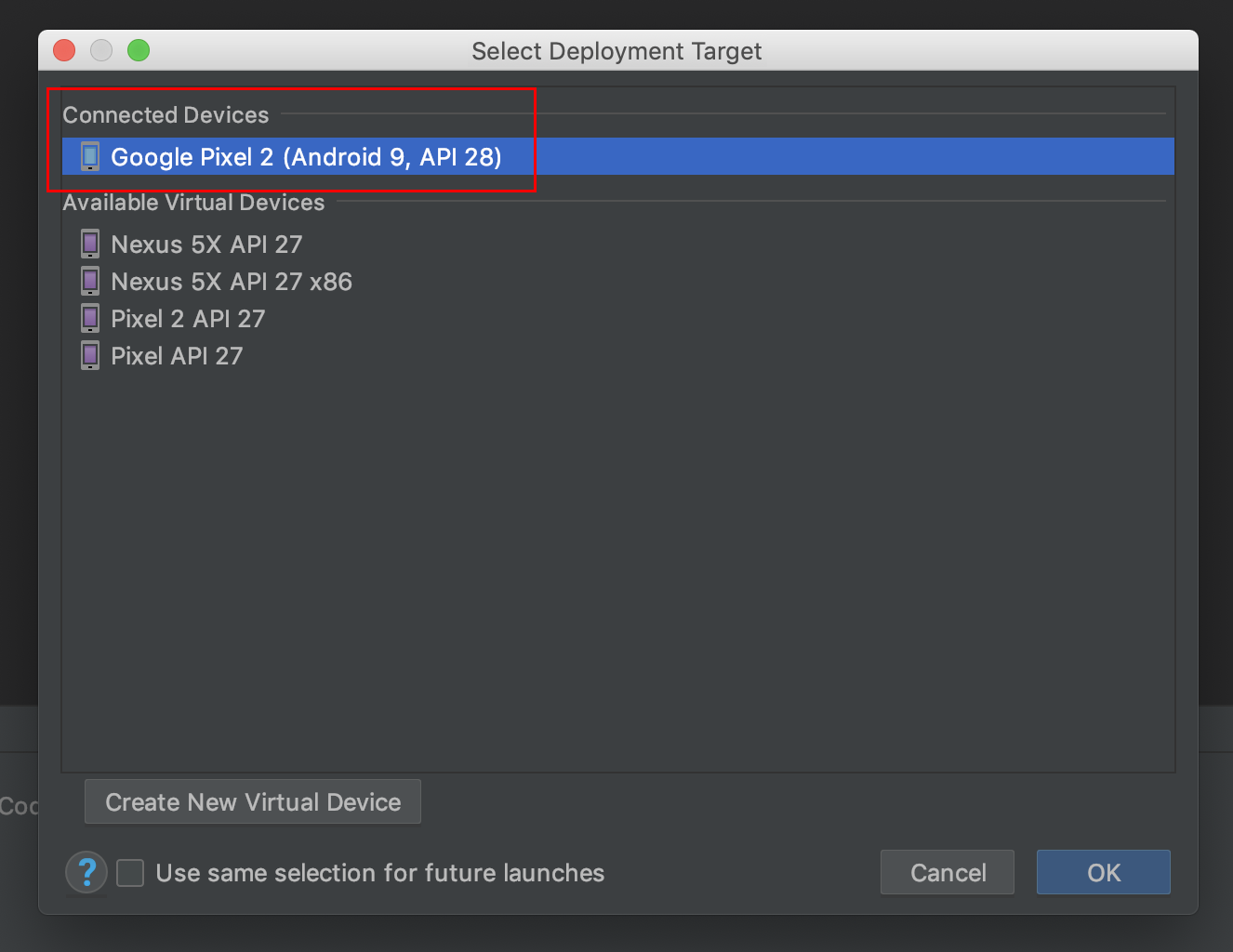
Connect the Android device to the computer and be sure to approve any ADB
permission prompts that appear on your phone. Select Run -> Run app. Select
the deployment target in the connected devices to the device on which the app
will be installed. This will install the app on the device.
To test the app, open the app called VClassify on your device. When you run
the app the first time, the app will request permission to access the camera.
Re-installing the app may require you to uninstall the previous installations.
Do not delete the assets folder content. If you explicitly deleted the files,
choose Build -> Rebuild to re-download the deleted model files into the assets
folder.