android_long_task is a flutter plugin to run dart code in an android foreground service with simplicity
Does it work on IOS as well?
What About IOS?
Is there a plugin to run long running tasks in IOS background?
Answer : No & No & No. this is an IOS limitation and you must consider this before creating your app and change your design or requirements if necessary
TLDR basically you should know that you must write the code you want to run in your ForegroundService in a different main function called serviceMain if you want to know exactly why read the rest.
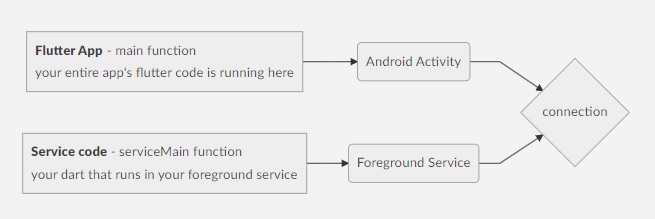
This is why : a flutter app that runs on android runs in an Activity. and an Activity is an android OS component where all android apps run in. in order for Android OS components to run their code they must run in a system Process. so activities run in a Process.
Service is another Android OS component that runs code in the background without showing anything to the user. because Android OS since version 8 will not allow Services to run for long. we have a special type of Service which is Foreground Service. it is a type of Service in Android OS that will not be killed by Android OS and must show a notification to the user as long as it runs. the purpose of Foreground Service is to run your code as long as you want outside the application.
Note: the reason Google added this limitation to Android OS is because too many Services running in the background will slow down the device and consumes too much battery. so since Android 8 Services cannot run for long. but sometimes Some apps need to run some processes in the background for long or all the time. android allows this through Foreground Services. a Background Service can become a Foreground Service if it shows a UI element to the user indicating that a it is running. this UI element must be a notification.
Here comes the YOU MUST KNOW PART :
Android Activities and Services do not run in the same process. that is the reason why when user closes your app and your app's process gets killed by the system, your code in foreground service will still run. because your flutter app code runs in an Activity which has a separate process from your Foreground Service. This behavior also means that the code that runs in Activities and Foreground Services are running in different Environments (Processes). because of this the dart code you run in your activity runs differently from the dart code you run in your service. that is why we have basically 2 functions that runs dart code one is the main function which runs your app. the other is serviceMain function which runs your dart code in your service. in simpler terms just imagine you are running a second app along side your app, but the second app only shows a notification
Foreground Service has a notification icon. this icon must be named ic_launcher.png and exist in this directory android\app\src\main\res\mipmap
if you're using flutter_launcher_icons to generate your app launcher icons, you don't need to do any changes
just add plugin to your pubspec.yaml
there is no need to for adding native code or making changes in your AndroidManifest.xml file
dependencies:
android_long_task: ^last_versioncreate a service data class to specify the data that is shared between your app dart-code and your service dart-code. in this class you will add the shared data you need and also specify the ForegroundService notification's title and description
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:android_long_task/android_long_task.dart';
class SharedUploadData extends ServiceData {
int progress = 0;
@override
String get notificationTitle => 'uploading';
@override
String get notificationDescription => 'progress -> $progress';
String toJson() {
var map = {
'progress': progress,
};
return jsonEncode(map);
}
static AppServiceData fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return AppServiceData()..progress = json['progress'] as int;
}
}create a serviceMain() function in your lib/main.dart file. this is where you define the dart code that is going to run in your ForegroundService. make sure to annotate it with @pragma('vm:entry-point') otherwise it won't run in release mode
//this entire function runs in your ForegroundService
@pragma('vm:entry-point')
serviceMain() async {
//make sure you add this
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
//if your use dependency injection you initialize them here
//what ever dart objects you created in your app main function is not accessible here
//set a callback and define the code you want to execute when your ForegroundService runs
ServiceClient.setExecutionCallback((initialData) async {
//you set initialData when you are calling AppClient.execute()
//from your flutter application code and receive it here
var serviceData = AppServiceData.fromJson(initialData);
//runs your code here
serviceData.progress = 20;
await ServiceClient.update(serviceData);
//run some more code
serviceData.progress = 100;
await ServiceClient.endExecution(serviceData);
await ServiceClient.stopService();
});
}What is ServiceClient
service client is basically an interface to your ForegroundService. it providers methods like
-
update(sharedData)which is used to update the shared data between your app's dart-code and your service's dart-code. -
endExecution(sharedData)will end the execution of the call that was invoked from application side and started the service.AppClient.execute()is the function that should be called from application side when you want to start the service. the shared data argument you give toServiceClient.endExecution(sharedData)function will be return type ofAppClient.execute()that was called from application side. -
stopService()which stops the service. note that you don't have to stop the ForegroundService if that is what you need. -
setExecutionCallback(callback)which sets the callback that runs in your service when you callAppClient.execute()from application side
Note : ServiceClient should only be used in the code that runs in serviceMain() function
now you can call AppClient.execute() from your app dart-code to start ForegroundService and run the serviceMain() function in it.
import 'package:android_long_task/android_long_task.dart';
//you can listen for shared data updates
AppClient.updates.listen((json) {
var serviceDataUpdate = AppServiceData.fromJson(json);
//your code
});
var resultJson = await AppClient.execute(initialSharedData);
var serviceDataResult = AppServiceData.fromJson(resultJson);
AppClientis the interface that allows you to communicate with ForegroundService from application side dart-code.AppClientmethods must only be called from the application sideAppClient.execute()has a returned type of your shared-data in json which is the result of your background task and will be set fromserviceMainby callingServiceClient.endExecution(serviceData)and if you don't call it at allAppClient.execute()in above code will be finished and won't return anything- you could also use
AppClient.getData()to get the last data. if the ForegroundService is running it will return the last changes. if ForegroundService is stopped the initial data will be returned. if you have not calledAppClient.execute()at allnullwill be returned
- add options to customize ForegroundService Notification more
- add ability to start ForegroundService when Device Restarts/Turns On