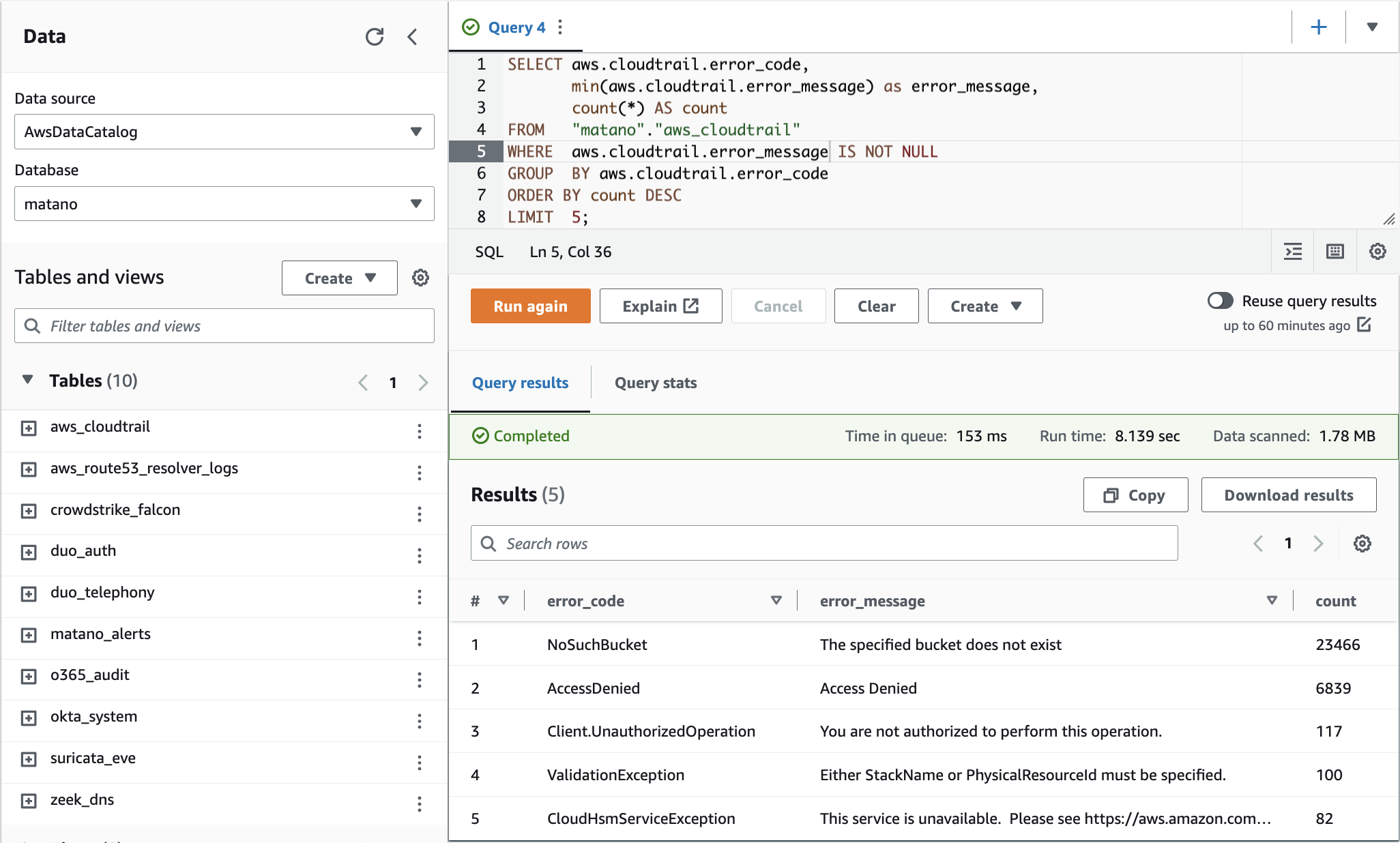
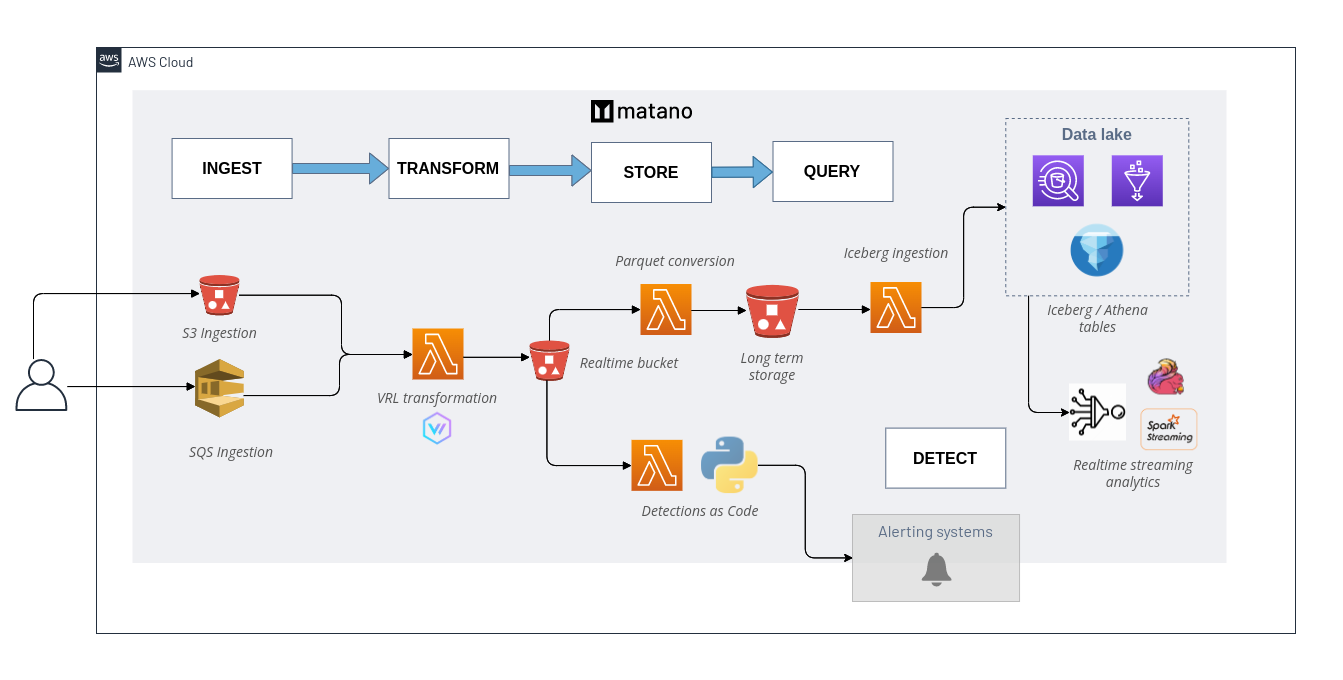
Matano Open Source Security data lake is an open source cloud-native security data lake, built for security teams on AWS.
Note
Matano offers a commercial managed Cloud SIEM for a complete enterprise Security Operations platform. Learn more.
- Security Data Lake: Normalize unstructured security logs into a structured realtime data lake in your AWS account.
- Collect All Your Logs: Integrates out of the box with 50+ sources for security logs and can easily be extended with custom sources.
- Detection-as-Code: Use Python to build realtime detections as code. Support for automatic import of Sigma detections to Matano.
- Log Transformation Pipeline: Supports custom VRL (Vector Remap Language) scripting to parse, enrich, normalize and transform your logs as they are ingested without managing any servers.
- No Vendor Lock-In: Uses an open table format (Apache Iceberg) and open schema standards (ECS), to give you full ownership of your security data in a vendor-neutral format.
- Bring Your Own Analytics: Query your security lake directly from any Iceberg-compatible engine (AWS Athena, Snowflake, Spark, Trino etc.) without having to copy data around.
- Serverless: Fully serverless and designed specifically for AWS and focuses on enabling high scale, low cost, and zero-ops.
- Reduce SIEM costs.
- Augment your SIEM with a security data lake for additional context during investigations.
- Write detections-as-code using Python to detect suspicious behavior & create contextualized alerts.
- ECS-compatible serverless alternative to ELK / Elastic Security stack.
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Route53
- AWS VPC Flow
- AWS Config
- AWS ELB
- Amazon S3 Server Access
- Amazon S3 Inventory Reports
- Amazon Inspector
- Amazon WAF
- Cloudflare
- Crowdstrike
- Duo
- Okta
- GitHub
- Google Workspace
- Office 365
- Snyk
- Suricata
- Zeek
- Custom 🔧
- Amazon Athena (default)
- Snowflake (preview)
- Spark
- Trino
- BigQuery Omni (BigLake)
- Dremio
View the complete installation instructions
Install the matano CLI to deploy Matano into your AWS account, and manage your deployment.
Linux
curl -OL https://github.com/matanolabs/matano/releases/download/nightly/matano-linux-x64.sh
chmod +x matano-linux-x64.sh
sudo ./matano-linux-x64.shmacOS
curl -OL https://github.com/matanolabs/matano/releases/download/nightly/matano-macos-x64.sh
chmod +x matano-macos-x64.sh
sudo ./matano-macos-x64.shRead the complete docs on getting started
To get started, run the matano init command.
- Make sure you have AWS credentials in your environment (or in an AWS CLI profile).
- The interactive CLI wizard will walk you through getting started by generating an initial Matano directory for you, initializing your AWS account, and deploying into your AWS account.
- Initial deployment takes a few minutes.
Once initialized, your Matano directory is used to control & manage all resources in your project e.g. log sources, detections, and other configuration. It is structured as follows:
➜ example-matano-dir git:(main) tree
├── detections
│ └── aws_root_credentials
│ ├── detect.py
│ └── detection.yml
├── log_sources
│ ├── cloudtrail
│ │ ├── log_source.yml
│ │ └── tables
│ │ └── default.yml
│ └── zeek
│ ├── log_source.yml
│ └── tables
│ └── dns.yml
├── matano.config.yml
└── matano.context.jsonWhen onboarding a new log source or authoring a detection, run matano deploy from anywhere in your project to deploy the changes to your account.
Read the complete docs on configuring custom log sources
Vector Remap Language (VRL), allows you to easily onboard custom log sources and encourages you to normalize fields according to the Elastic Common Schema (ECS) to enable enhanced pivoting and bulk search for IOCs across your security data lake.
Users can define custom VRL programs to parse and transform unstructured logs as they are being ingested through one of the supported mechanisms for a log source (e.g. S3, SQS).
VRL is an expression-oriented language designed for transforming observability data (e.g. logs) in a safe and performant manner. It features a simple syntax and a rich set of built-in functions tailored specifically to observability use cases.
Let's have a look at a simple example. Imagine that you're working with HTTP log events that look like this:
{
"line": "{\"status\":200,\"srcIpAddress\":\"1.1.1.1\",\"message\":\"SUCCESS\",\"username\":\"ub40fan4life\"}"
}You want to apply these changes to each event:
- Parse the raw
linestring into JSON, and explode the fields to the top level - Rename
srcIpAddressto thesource.ipECS field - Remove the
usernamefield - Convert the
messageto lowercase
Adding this VRL program to your log source as a transform step would accomplish all of that:
transform: |
. = object!(parse_json!(string!(.json.line)))
.source.ip = del(.srcIpAddress)
del(.username)
.message = downcase(string!(.message))
schema:
ecs_field_names:
- source.ip
- http.statusThe resulting event 🎉:
{
"message": "success",
"status": 200,
"source": {
"ip": "1.1.1.1"
}
}Read the complete docs on detections
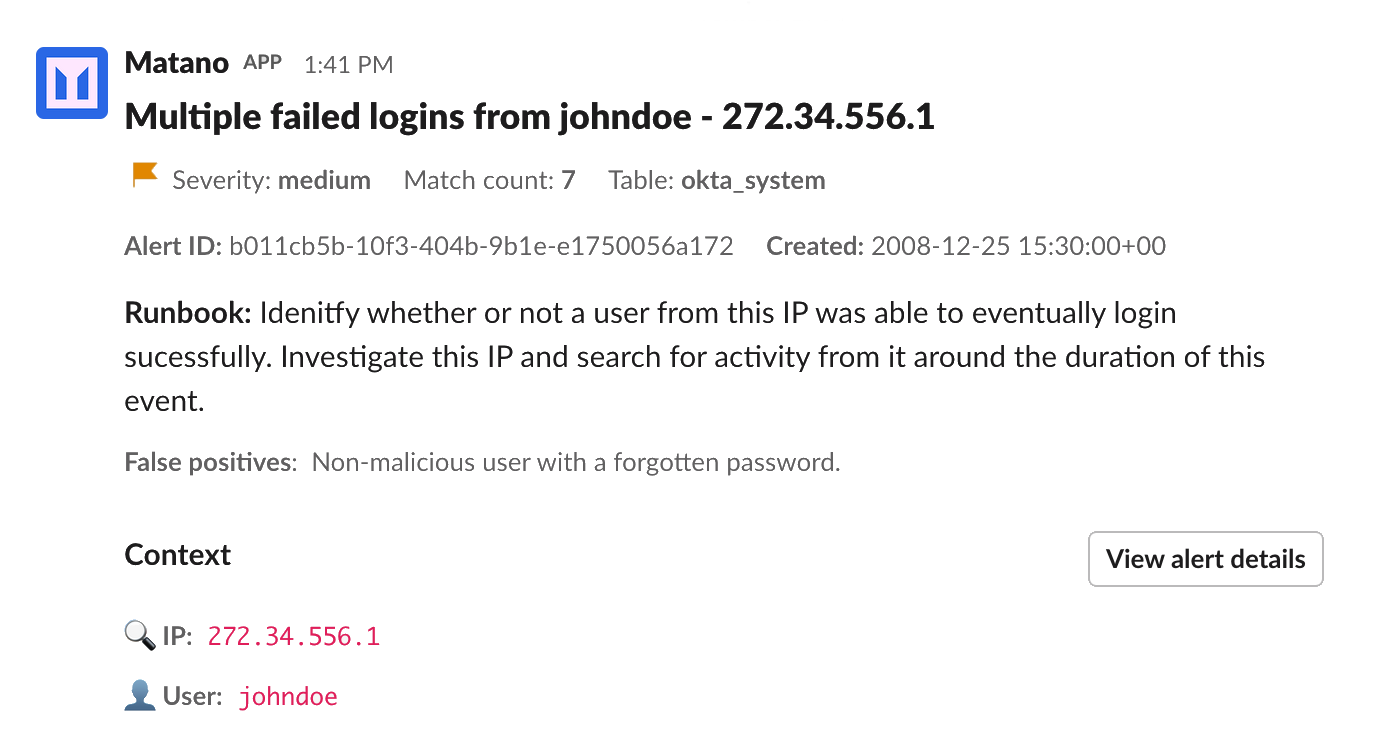
Use detections to define rules that can alert on threats in your security logs. A detection is a Python program that is invoked with data from a log source in realtime and can create an alert.
def detect(record):
return (
record.deepget("event.action") == "CreateInstanceExportTask"
and record.deepget("event.provider") == "ec2.amazonaws.com"
and record.deepget("event.outcome") == "failure"
)def detect(r):
return (
"authentication" in r.deepget("event.category", [])
and r.deepget("event.outcome") == "failure"
)
def title(r):
return f"Multiple failed logins from {r.deepget('user.full_name')} - {r.deepget('source.ip')}"
def dedupe(r):
return r.deepget("source.ip")---
tables:
- aws_cloudtrail
- okta_system
- o365_audit
alert:
severity: medium
threshold: 5
deduplication_window_minutes: 15
destinations:
- slack_my_teamfrom detection import remotecache
# a cache of user -> ip[]
user_to_ips = remotecache("user_ip")
def detect(record):
if (
record.deepget("event.action") == "ConsoleLogin" and
record.deepget("event.outcome") == "success"
):
# A unique key on the user name
user = record.deepget("user.name")
existing_ips = user_to_ips[user] or []
updated_ips = user_to_ips.add_to_string_set(
user,
record.deepget("source.ip")
)
# Alert on new IPs
new_ips = set(updated_ips) - set(existing_ips)
if existing_ips and new_ips:
return TrueRead the complete docs on alerting
All alerts are automatically stored in a Matano table named matano_alerts. The alerts and rule matches are normalized to ECS and contain context about the original event that triggered the rule match, along with the alert and rule data.
Example Queries
Summarize alerts in the last week that are activated (exceeded the threshold)
select
matano.alert.id as alert_id,
matano.alert.rule.name as rule_name,
max(matano.alert.title) as title,
count(*) as match_count,
min(matano.alert.first_matched_at) as first_matched_at,
max(ts) as last_matched_at,
array_distinct(flatten(array_agg(related.ip))) as related_ip,
array_distinct(flatten(array_agg(related.user))) as related_user,
array_distinct(flatten(array_agg(related.hosts))) as related_hosts,
array_distinct(flatten(array_agg(related.hash))) as related_hash
from
matano_alerts
where
matano.alert.first_matched_at > (current_timestamp - interval '7' day)
and matano.alert.activated = true
group by
matano.alert.rule.name,
matano.alert.id
order by
last_matched_at descYou can deliver alerts to external systems. You can use the alerting SNS topic to deliver alerts to Email, Slack, and other services.
For general help on usage, please refer to the official documentation. For additional help, feel free to use one of these channels to ask a question:
- Discord (Come join the family, and hang out with the team and community)
- Forum (For deeper conversations about features, the project, or problems)
- GitHub (Bug reports, Contributions)
- Twitter (Get news hot off the press)
Thanks go to these wonderful people (emoji key):
This project follows the all-contributors specification. Contributions of any kind are welcome!