The Eclipse Leda core utilities are some some optional utilities and scripts for the runtime. They are considered convenient tools for development and testing purposes. They are pre-installed to the Leda Quickstart images.
List of utilities:
- sdv-device-info: Show and update device information
- sdv-health: Show SDV software components health status
- kanto-auto-deployer: Automatically deploys containers on boot
- kantui: A text user interface for kanto-cm to manage containers (start, stop, logs)
- sdv-motd: Message-of-the-Day shown after login prompt
- can-forward: Forwarding a CAN-bus network interface into a containerized Vehicle Application
- sdv-ctr-exec: Execute arbitrary commands in existing containers
- sdv-kanto-ctl: Manage the Kanto Container Management configuration via CLI
- kantocm_zeroconf: A system service to publish running containers with zeroconf
Synposis: ./sdv-device-info [options] [command]
Full help:
Usage: ./sdv-device-info [options] [command]
Update SDV device configuration information in configuration files.
Example: ./sdv-device-info -v env"
Commands:
show : Display configuration (default command)
help : This message
version : Display the SDV software stack versions
env : Format output for use in scripts
Options:
--ansi | -a : Don't use colored output.
--norestart | -n : Do not automatically restart services
--verbose | -v : Enable verbose mode.
--help | -h : This message.
Display the current device configuration, such as Device ID.
Synposis: ./sdv-device-info show
To use device information on other scripts, it may be useful to source the device information variables into the current environment variable context:
Synposis: source ./sdv-device-info env
Example:
$ source ./sdv-device-info env
$ echo $DEVICE_ID
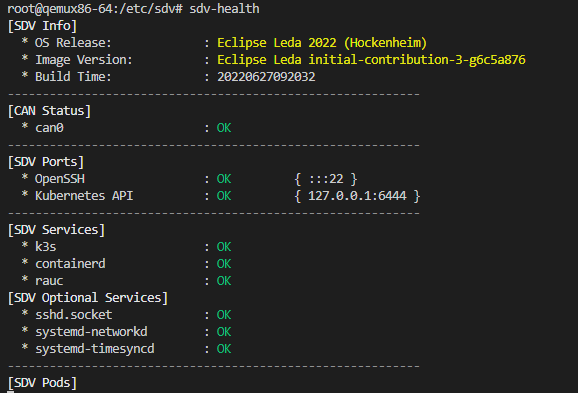
exampledevice1The ./sdv-health utility display a status overview of some important dependencies and device configurations for the SDV stack.
The sdv health utility can be configured using the sdv.conf configuration file.
Example output:
Usage:
Usage: ./can-forward {-h} {-p PID} {-c container} <hw_can>
hw_can Host CAN hw interface to forward. Default: can0
-c container Attemmpt to get netns PID from a running container: (docker, ctr). Default: seat_service
-p PID Use provided PID for transferring vxcan interface (e.g.: docker inspect -f '{{ .State.Pid }}' container)
-h Prints this messageExample:
ps -C seat_service -o pid=
./can-forward -p 1234 can0Note: can-forward does currently not support looking up PID of Kubernetes pods.
Automatically deploys containers to the Kanto Container Management based on deployment descriptors from a given path. All deployment descriptors in the manifests folder will be deployed (created and started) on startup of the service.
Usage:
root@qemux86-64:~# kanto-auto-deployer --help
USAGE:
kanto-auto-deployer [PATH TO MANIFESTS FOLDER]Example:
# Use container manifests from current working directory
/var/containers/manifests_dev/ $ kanto-auto-deployer
Reading manifests from [.]
Already exists [cloudconnector]
Already exists [otelcollector]
Already exists [seatservice-example]
# Use container manifests from specified directory
~ $ kanto-auto-deployer /var/containers/manifests_dev/
Reading manifests from [/data/var/containers/manifests_dev/]
Already exists [cloudconnector]
Already exists [otelcollector]
Already exists [seatservice-example]Systemd service unit is located in /lib/systemd/system/kanto-auto-deployer.service:
[Unit]
Description=Kanto Auto Deployer
After=network-online.target container-management.service
Wants=network-online.target container-management.service
Requires=container-management.service
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[Service]
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5s
ExecStart=/usr/bin/kanto-auto-deployer /var/containers/manifestsExample output:
root@qemux86-64:/lib/systemd/system# systemctl status kanto-auto-deployer.service
* kanto-auto-deployer.service - Kanto Auto Deployer
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/kanto-auto-deployer.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Fri 2022-12-09 09:41:42 UTC; 7min ago
Process: 472 ExecStart=/usr/bin/kanto-auto-deployer /var/containers/manifests (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 472 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Dec 09 09:41:33 qemux86-64 systemd[1]: Started Kanto Auto Deployer.
Dec 09 09:41:33 qemux86-64 kanto-auto-deployer[472]: Creating [databroker]
Dec 09 09:41:41 qemux86-64 kanto-auto-deployer[472]: Created [databroker]
Dec 09 09:41:41 qemux86-64 kanto-auto-deployer[472]: Starting [databroker]
Dec 09 09:41:42 qemux86-64 kanto-auto-deployer[472]: Started [databroker]
Dec 09 09:41:42 qemux86-64 systemd[1]: kanto-auto-deployer.service: Deactivated successfully.Usage:
kantuiKeyboard commands:
- Arrow keys
UpandDownto select a container - Arrow keys
LeftandRightto select a column Enterto change the sort ordering of the currently selected columnSto start the selected container which is currently not runningPto stop the selected containerRto remove a containerLto show the log output of a containerQto quit kantui
Note: The mouse can be used to select ui items.
Usage:
kantui 0.1.0
A TUI for Kanto CM that allows easier management of deployed containers. Requires root.
USAGE:
kantui [OPTIONS]
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
-s, --socket <SOCKET> Set the path to the kanto-cm UNIX socket [default:
/run/container-management/container-management.sock]
-t, --timeout <TIMEOUT> Time before sending a SIGKILL after a SIGTERM to a container
(seconds) [default: 5]
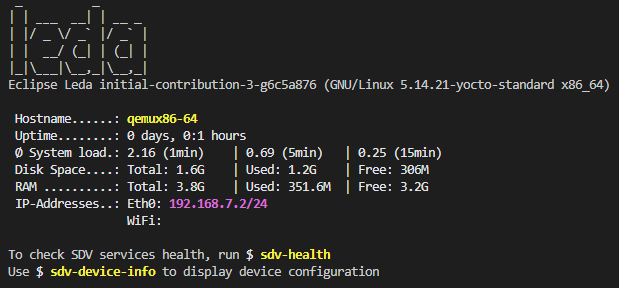
-V, --version Print version informationThe sdv-motd script provides an alternative motd profile, which displays some additional information after login.
Example output:
The sdv-ctr-exec wrapper allows to execute arbitrary user commands in existing containers.
Kanto Container Management cli tool (kanto-cm) only allows to manage the lifecycle of a container,
but does not allow to specify or override the entrypoint or command definitions of an existing container.
The ctr command line tool of containerd allows the execution of additional tasks in a running container.
As a convenient tool, sdv-ctr-exec allows the simple execution of arbitrary commands inside of containers.
This is especially useful for non-service-containers, or containers which have additional binaries (e.g. cli tools) embedded.
Usage:
root@qemux86-64:~# sdv-ctr-exec
/usr/bin/sdv-ctr-exec -h to print this message
Usage:
/usr/bin/sdv-ctr-exec <container-id> <command>
or
/usr/bin/sdv-ctr-exec -n <container-name> <command>Example:
# Note: Both options are equivalent
# Executing a containerized cli tool using ctr
ctr --namespace kanto-cm image pull ghcr.io/eclipse/kuksa.val/kuksa-client:master
ctr --namespace kanto-cm container create --net-host --tty ghcr.io/eclipse/kuksa.val/kuksa-client:master kuksa-client
ctr --namespace kanto-cm tasks start --detach kuksa-client
ctr --namespace kanto-cm tasks exec --tty --exec-id sometask kuksa-client /kuksa-client/bin/kuksa-client --port 30555 --protocol grpc --insecure
# Executing a containerized cli tool using sdv-ctr-exec
# will only work with kuksa-client tags <= 0.3.0
kanto-cm create --i --t --network=host --name=kuksa-client ghcr.io/eclipse/kuksa.val/kuksa-client:0.3.0
kanto-cm start --name=kuksa-client
sdv-ctr-exec -n kuksa-client /kuksa-client/bin/kuksa-client --port 30555 --protocol grpc --insecuresdv-kanto-ctl is a convenience shell utility to manage the Container Manager configuration file.
- Add and remove container registries (for authentication purposes)
- Set primitive values in configuration
- Restart container-management.service on configuration changes
- Automatically back up configuration file
- Display changes to user
Synopsis: ./sdv-kanto-ctl <command> [<options>]
Full help:
$ ./sdv-kanto-ctl --help
Eclipse Kanto Container Manager Configuration Utility
See https://websites.eclipseprojects.io/kanto/docs/references/containers/container-manager-config/
Usage: ./sdv-kanto-ctl <command> {options}
Commands:
add-registry -h <hostname> -u <username> -p <password>
Adds or replaces a container registry authentication configuration
-h or --hostname: Configure the hostname of the container registry (e.g. hub.docker.io, ghcr.io, ...)
-u or --username: Configure the username
-p or --password: Configure the password
remove-registry -h <hostname>
Removes the specified container registry
-h or --hostname: The hostname of the container registry
remove-all-registries
Removes all configured container registries
list-registries
Prints all configured container registries
show-config
Print the container management configuration
set <key> <value>
Set a primitive configuration value. Key in JSON Dot-Notation
Examples: ./sdv-kanto-ctl set containers.registry_configurations.MyRegistry.credentials.password foobar
./sdv-kanto-ctl set things.enable true
Options:
--no-reload : Do not reload the configuration and restart the container-management service automatically
--ansi : Don't use colored output.
--verbose | -v : Enable verbose mode.
--help : This message.The utilities are pre-installed on Eclipse Leda Quickstart distros in the SDV Full Image partition.
To install the shell scripts:
- Install bash
- Copy the scripts to the device, e.g. to
/usr/bin/or to your user's home directory - Ensure executable bit:
chmod a+x sdv-*
To build the binary utilities (e.g. kantui and kanto-auto-deployer)
- Install Rust
- Build the sources with cargo
To install the binary utilities via Debian packages:
- Download the Debian packages from the GitHub Releases page
- Copy the packages to the target device
- Install via
apt-get install <file>
Note: The Debian packages are built specifically for Leda, and may not be compatible with other Linux distros. As long as there are minimum dependencies, they may be installable on recent Debian or Ubuntu releases.
See CONTRIBUTING.md
- Clone the repository into Visual Studio (
F1->Remote-Containers: Clone repository into volume) - Provide the git repository url.
- Install Rust
- Switch to the respective source folder in
src/rust/<component> - Run
cargo test
To run shell tests:
./run-tests.shThe tests use the BATS framework and Docker to perform some rudimentary test scenarios on the shell scripts.
Please see LICENSE