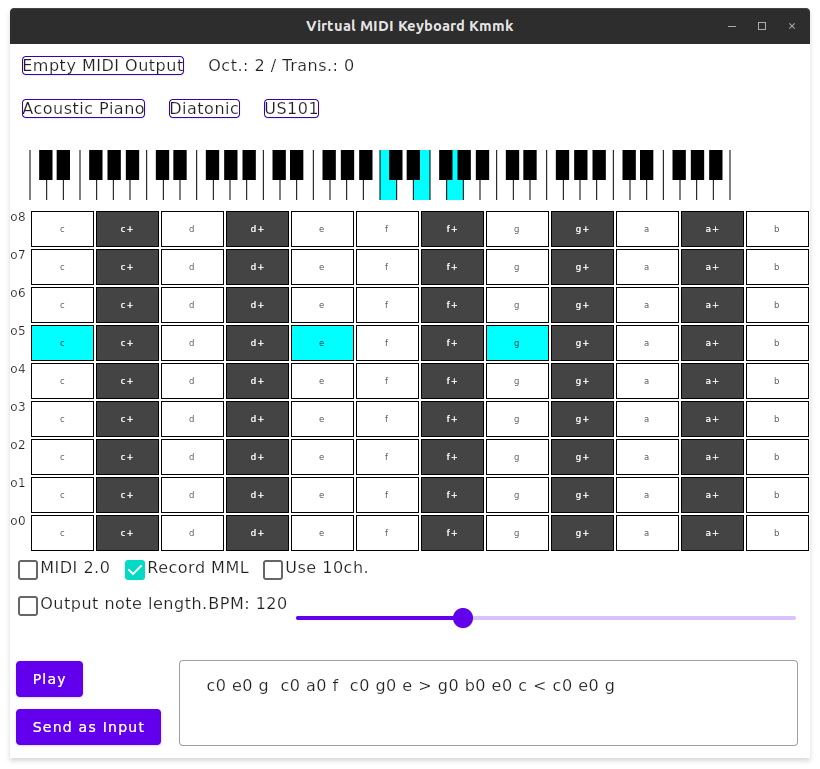
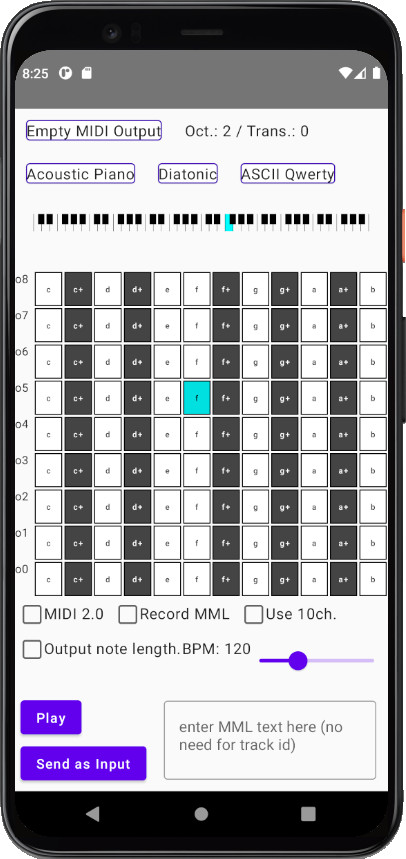
Kmmk is a virtual MIDI keyboard application based on ktmidi.
Here are the basics: it receives either keyboard inputs, mouse clicks or touch inputs, among whatever the underlying platform accepts. Then it sends note on/off operations etc. to the target MIDI output device.
Kmmk makes use of Kotlin Multiplatform and Jetpack Compose, and should run on Android and desktop i.e. Linux, Mac and most likely Windows (not verified).
Kmmk has various features.
(Linux and Mac only) when kmmk is launched, it creates a virtual MIDI input port for itself so that any MIDI apps (e.g. DAWs) can use it as a virtual MIDI keyboard.
It supports two PC keyset layouts:
- Diatonic: like piano. When there is no semitone e.g.
e-sharporb-sharpthen the corresponding key is left blank. - Chromatic: every key has an assigned note. That means, the key right next to
eis notfbutf+becausefis placed on right-upper next toe.
By default the keyboard is laid out as ASCII QWERTY sequence. We also provide some other keyboard layouts that extend the key ranges beyond QWERTY.
SHIFT+UP increases octave, SHIFT+DOWN decreases it. SHIFT+LEFT decreases transpose, SHIFT+RIGHT increases it.
You can also choose "channel 10" which usually means a drum channel. For channel 10, it will show drum set names instead of instruments.
When you type "notes" then they will be recorded at the text entry box, as simple MML (Music Macro Language), implemented as in mugene-ng.
The recorded MML can be compiled as a MIDI sequence and then sent to the target MIDI output device, just like MIDI players do.
Since ktmidi supports MIDI 2.0, we leverage the feature in this application. It does not really connect bidirectionally, but sends MIDI-CI Set New Protocol message to the recipient, so unless the recipient refuses to connect unless any further testing (e.g. using MIDI-CI Test New Protocol messages), it would optimisitically work. There is no known host applications that support MIDI 2.0 devices anyways.
Unless you check "MIDI 2.0" option, it will send MIDI 1.0 messages.
Those features can be powerful when they are combined together. For example, you can code some drum patterns as in MML, then play it and send the MIDI seqneunce to your DAW via the kmmk virtual MIDI input.
The key events cannot be received until kmmk receives pointer event on the button pad, which is not doable on buttons but only doable on the rightmost text labels. It is annoying, but focus events are not designed well yet.
The button pad can be hidden by toggle button ([+] Text), but to keep receiving key events until you click on [*] button for the same reason.
Android emulators from Google (i.e. the ones you download as part of Android Studio) do not appropriately handle key events and you won't be able to keep key-on states. Hopefully not on Android devices (otherwise the entire API does not make sense), but not sure.
kmmk is distributed under the MIT License.