This starter is designed to help you get up and running with EdgeDB and Next.js quickly. It includes a basic setup for authentication, EdgeDB schema, and a UI to get you started. Below you can find the steps to set up the project and start building your app as well as some ideas for extending it further.
This template includes:
- Next.js for React framework
- EdgeDB for database
- EdgeDB Auth for authentication
- Tailwind CSS for utility-first CSS framework
- ESLint for linting
.
├── README.md
├── app
│ ├── auth
│ ├── dashboard
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ ├── globals.css
│ ├── layout.tsx
│ └── page.tsx
├── auth-setup.ts
├── components/
├── src/
├── public/
├── dbschema
│ ├── default.esdl
│ └── migrations
├── edgedb.toml
├── edgedb.ts
├── eslint.config.js
├── next-env.d.ts
├── next.config.js
├── package.json
├── password-auth-setup.ts
├── pnpm-lock.yaml
├── postcss.config.js
├── tailwind.config.ts
└── tsconfig.jsonDirectory structure:
app/- Next.js pages and componentspublic/- static assetscomponents/- React componentssrc/- utility functionsdbschema/- EdgeDB schema and migrationsedgedb.toml- EdgeDB configurationedgedb.ts- EdgeDB clientauth-setup.ts- script to set up EdgeDB Authpassword-auth-setup.ts- script to set up email+password authenticationeslint.config.js- ESLint configurationnext-env.d.ts- Next.js typesnext.config.js- Next.js configurationpackage.json- npm dependenciespnpm-lock.yaml- pnpm lockfilepostcss.config.js- PostCSS configurationtailwind.config.ts- Tailwind CSS configurationtsconfig.json- TypeScript configuration
To get started with this template, you need to:
git clone https://github.com/edgedb/nextjs-edgedb-auth-template.git
cd nextjs-edgedb-auth-template
pnpm iYou can also click the "Use this template" button to create a new repository based on this template.
You can just use npx edgedb, it would do the right thing
to automatically install and run EdgeDB CLI for you.
This README will use npx edgedb <command> style, but if you have
the CLI installed you can use it directly, like this: edgedb <command>.
However, you can install the CLI manually
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.edgedb.com | shFor more installation options, see the EdgeDB installation guide.
To run this project, you need to initialize a new EdgeDB project. Run the following command:
npx edgedb project initThis template includes a script to set up EdgeDB Auth. It defaults to email+password authentication. Run the following command:
pnpm auth:setupThis template includes a script to generate TypeScript types from the EdgeDB schema. Run the following command:
pnpm generate:allpnpm devFollow the instructions in the terminal to open the app in your browser.
To view the database in the EdgeDB UI or make changes to the EdgeDB Auth configuration, run:
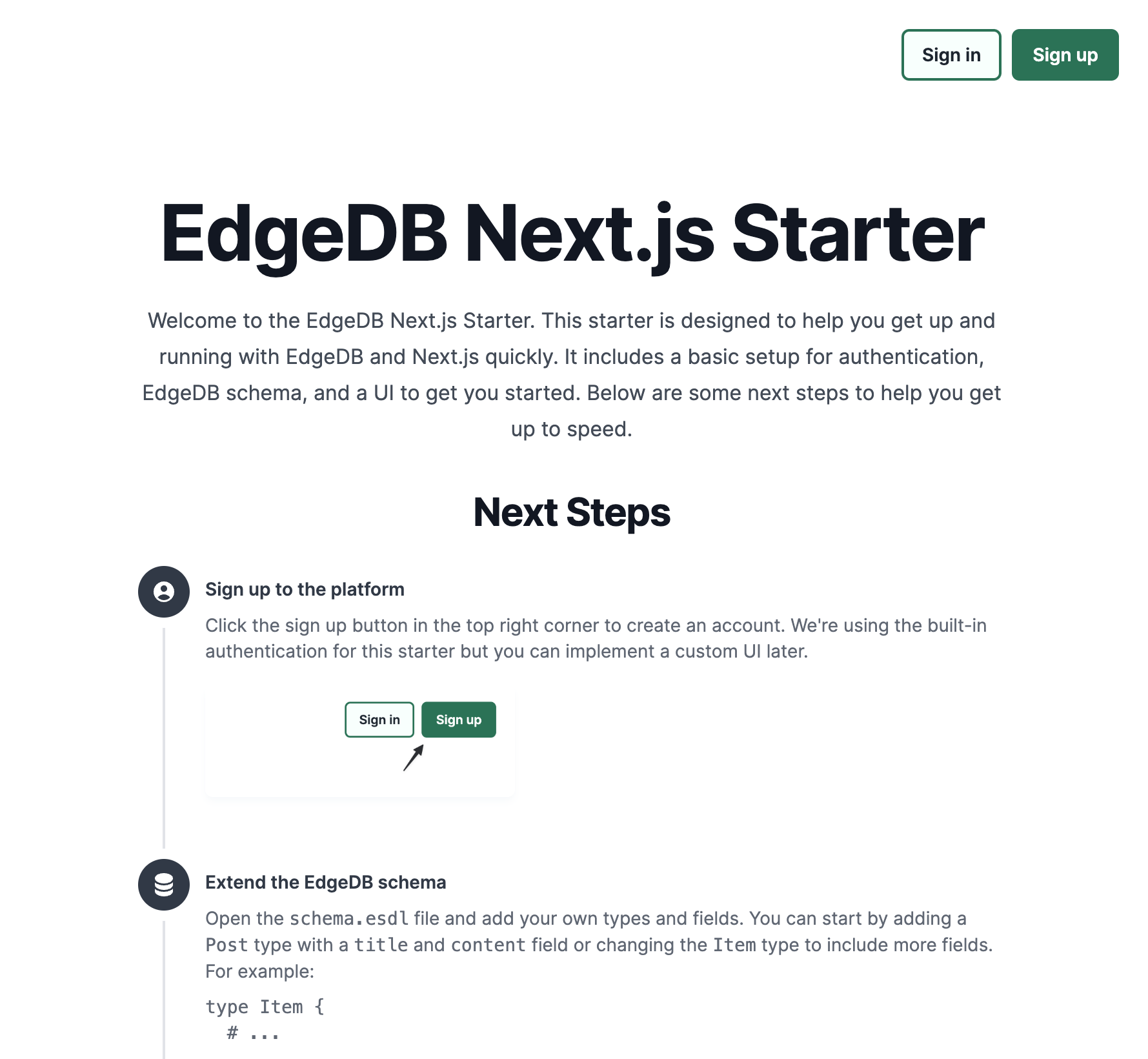
npx edgedb uiClick the sign up button in the top right corner to create an account. We're using the built-in authentication for this starter but you can implement a custom UI later.
Open the dbschema/default.esdl file and add your own types and
fields. You can start by adding a Post type with a
title and content field or changing the
Item type to include more fields. For example:
type Item {
# ...
# Add your new fields here:
required title: str;
required content: str;
}Open the app/dashboard/page.tsx file and update the query
to include your new fields. You can add a new field to the query or
change the existing fields to include your new data.
const items = await client.query<Props["items"][number]>(`
select Item {
id,
name,
created,
updated,
created_by: {
name,
email
}
};
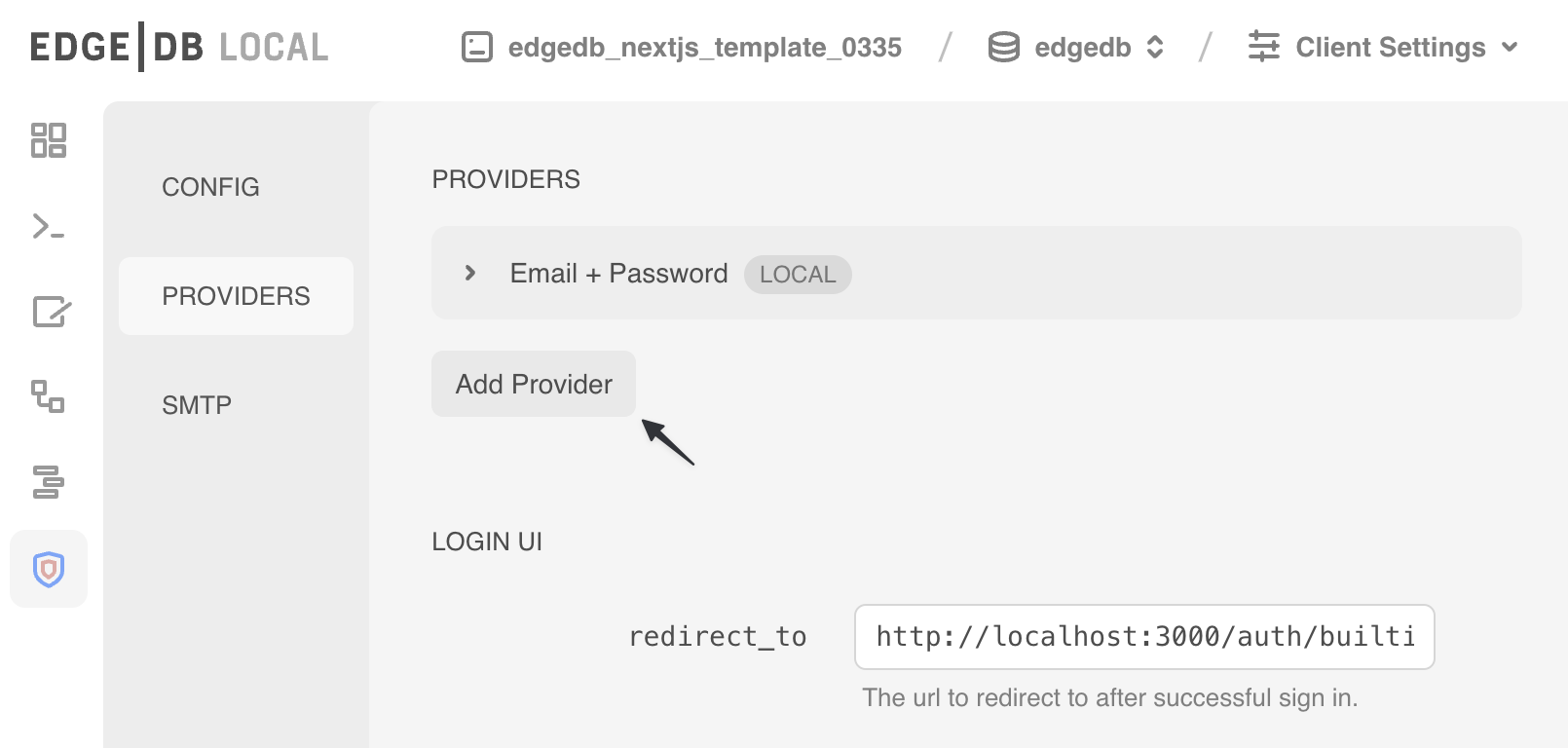
`);Open the EdgeDB UI with the edgedb ui command and navigate
to the Auth tab. Go to the "Providers" section and add a new Auth
provider by clicking the "Add Provider" button and following the
instructions.
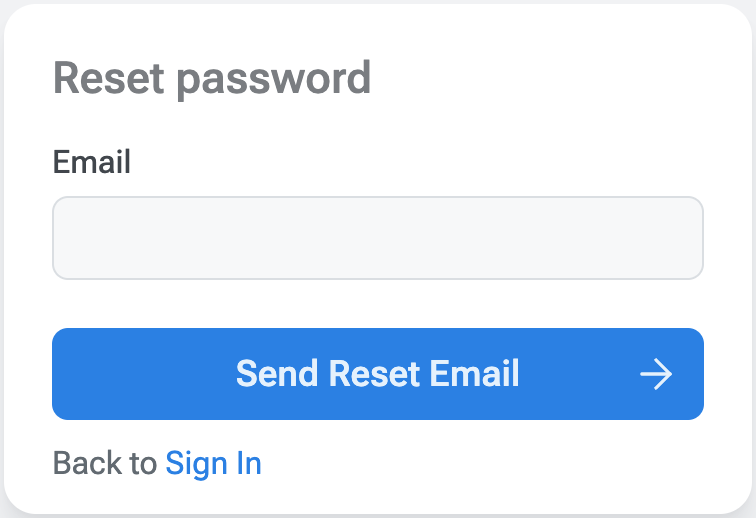
Sign out of your account and try to reset your password. Click the "Forgot Password" link on the login page and follow the instructions to reset your password. You should receive an email with a link to reset your password. To test it locally, you can use the Mailpit tool.
To set up the Mailpit tool, run the following command:
brew install mailpitOr follow the instructions in the Mailpit docs.
Next, run the following command to start the Mailpit server:
mailpitAfter that, you can open the Mailpit UI in your browser at http://localhost:8025.
To test the reset password flow with Mailpit, you need to update the SMTP settings in the EdgeDB UI. Open the EdgeDB UI with the edgedb ui command and navigate to the Auth tab. Go to the "SMTP" section and update the settings with the following values:
- Host:
localhost - Port:
1025
The remaining fields can be left empty.
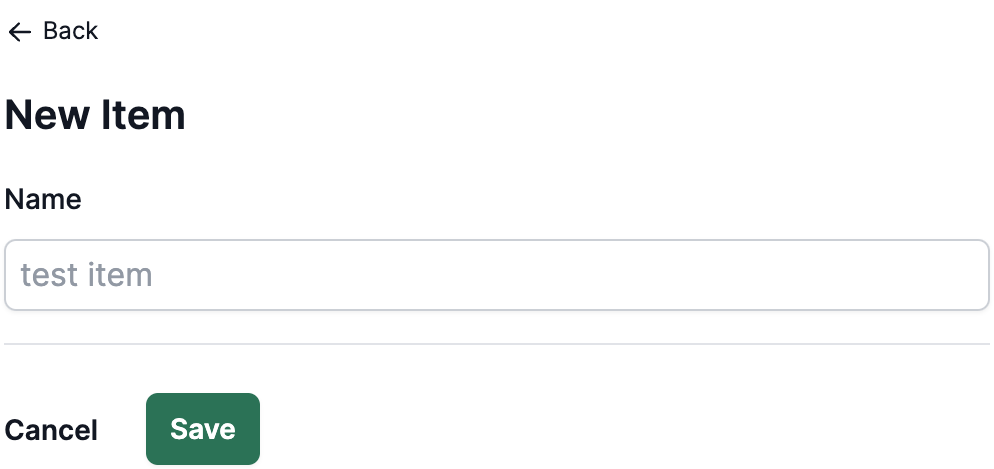
Open the components/AddItem.tsx file and update the form to
include your new fields. You can add a new field to the form or change
the existing fields to include your new data.
Try deleting an item that you don't own. You shouldn't be able to delete it. You can test this by creating a new item and then trying to delete it with a different account. As a next step you can conditionally render the delete button based on the user's permissions.
In the app/auth/[...auth]/route.ts file, you can find the user creation flow. You can modify this flow to include additional steps. For example, you can send a custom email to the new user or store additional data in the database.
In the dbschema/default.esdl file, you can find the EdgeDB schema for this template. It includes the User and Item types with some basic fields and access policies. Here's a quick look at the schema:
using extension auth;This line enables the EdgeDB Auth extension, which provides built-in authentication and authorization features.
scalar type Role extending enum<admin, user>;
global current_user := (
assert_single((
select User
filter .identity = global ext::auth::ClientTokenIdentity
))
);
type User {
required identity: ext::auth::Identity;
required name: str;
email: str;
userRole: Role {
default := "user";
};
created: datetime {
rewrite insert using (datetime_of_statement());
}
updated: datetime {
rewrite insert using (datetime_of_statement());
rewrite update using (datetime_of_statement());
}
}This block defines the Role and User types.
-
The
identityfield is an EdgeDB Auth identity that uniquely identifies the user. It's created when the user signs up and is used for authentication. We link it to our customUsertype with theext::auth::Identitytype. -
The
global current_userwill be set to theUserobject is linked to the currently signed in user through theext::auth::ClientTokenIdentitywhich is set by the EdgeDB auth server library for signed in users. -
The
userRolefield is an enum that defines the user's role. It defaults to "user" but can be set to "admin" for users with admin privileges. -
The
createdandupdatedfields are timestamps that are set when the user is created or updated.
type Item {
required name: str;
required created_by: User {
default := global current_user;
}
created: datetime {
rewrite insert using (datetime_of_statement());
}
updated: datetime {
rewrite insert using (datetime_of_statement());
rewrite update using (datetime_of_statement());
}
access policy admin_has_full_access
allow all
using (global current_user.userRole ?= Role.admin);
access policy creator_has_full_access
allow all
using (.created_by ?= global current_user);
access policy others_read_only
allow select, insert;
}This block defines the Item type. It includes fields for the item's name, creator, and timestamps for when the item was created and updated.
-
The
created_byfield is a reference to theUsertype that stores the user who created the item. It defaults to the currently authenticated user. -
The
createdandupdatedfields are timestamps that are set when the item is created or updated. -
The
access policyblocks define the access policies for theItemtype. They specify who can read, insert, update, or delete items based on the user's role and the item's creator.- The
admin_has_full_accesspolicy allows users with the "admin" role to perform all actions on items. - The
creator_has_full_accesspolicy allows the item's creator to perform all actions on the item. - The
others_read_onlypolicy allows other users to read and insert items but not update or delete them.
- The
To learn more about Next.js, take a look at the following resources:
- Next.js Documentation - learn about Next.js features and API.
- Learn Next.js - an interactive Next.js tutorial.
You can also check out the EdgeDB documentation to learn more about EdgeDB and EdgeDB Auth.
Follow the deployment instructions in the EdgeDB documentation to deploy your Next.js app to EdgeDB Cloud and Vercel.