-
Full documentation at https://www.doubango.org/SDKs/micr/docs/
-
Online demo at https://www.doubango.org/webapps/micr/
-
Open source Computer Vision Library: https://github.com/DoubangoTelecom/compv
This is state-of-the-art Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) dectector and recognizer using deep learning.
Unlike other solutions you can find on the web, you don't need to adjust the camera/image to define a Region Of Interest (ROI). We also don't try to use small ROI to decrease the processing time or false-positives. The whole image (up to 4K supported) is processed and every pixel is checked. No matter if the MICR lines are small, far away, blurred, partially occluded, skewed or slanted, our implementation can accurately detect and recognize every character.
The detector is agnostic and doesn't decode (recognize/OCR) the text to check it against some pre-defined rules (regular expressions) which means we support all MICR types regardless the font, content, shape or country. Both E-13B and CMC-7 formats are supported.
Automating Bank account information extraction from MICR (Magnetic ink character recognition) zones on bank scanned checks/document above human-level accuracy is a very challenging task. Our implementation reaches such level of accuracy using latest deep learning techniques. We outperform both ABBYY and LEADTOOLS in terms of accuracy and speed (almost #30 times faster).
Using a single model we're able to accurately locate the MICR (Magnetic ink character recognition) zones, infer the type (E-13B or CMC-7) and recognize the fields: one-shot deep model. The performance gap between us and the other companies is more important for CMC-7 format which is more challenging than E-13B.
The next video (https://youtu.be/1GiMcpYuQdo) shows MICRVideoRecognizer-E13B sample running on Android:
The next video (https://youtu.be/ManYVDj-Pt4) shows MICRVideoRecognizer-CMC7 sample running on Android:
This technology is a key component of Remote Deposit Capture applications to process bank checks sent using mobile phones or scanners. It's a must have technology for any FinTech company.
Don't take our word for it, come check our implementation. No registration, license key or internet connection is needed, just clone the code and start coding/testing. Everything runs on the device, no data is leaving your computer. The code released here comes with many ready-to-use samples to help you get started easily. You can also check our online cloud-based implementation (no registration required) at https://www.doubango.org/webapps/micr/ to check out the accuracy and precision before starting to play with the SDK.
- Github repo: https://github.com/DoubangoTelecom/ultimateMICR-SDK
- Cloud-based implementation: https://www.doubango.org/webapps/micr/
Sample applications
The source code comes with #3 sample applications: MICRVideoRecognizer-E13B, MICRVideoRecognizer-CMC7 and Benchmark. All sample applications are open source and don’t require registration or license key.
The source code is at samples.
MICRVideoRecognizer-E13B
This application should be used as reference code by any developer trying to add ultimateMICR to their products. It shows how to detect and recognize MICR E-13B lines in realtime using live video stream from the camera.
MICRVideoRecognizer-CMC7
This application should be used as reference code by any developer trying to add ultimateMICR to their products. It shows how to detect and recognize MICR CMC-7 lines in realtime using live video stream from the camera.
Benchmark
This application is used to check everything is ok and running as fast as expected. The information about the maximum frame rate on ARM devices could be checked using this application.
Trying the samples
Android
To try the sample applications on Android:
-
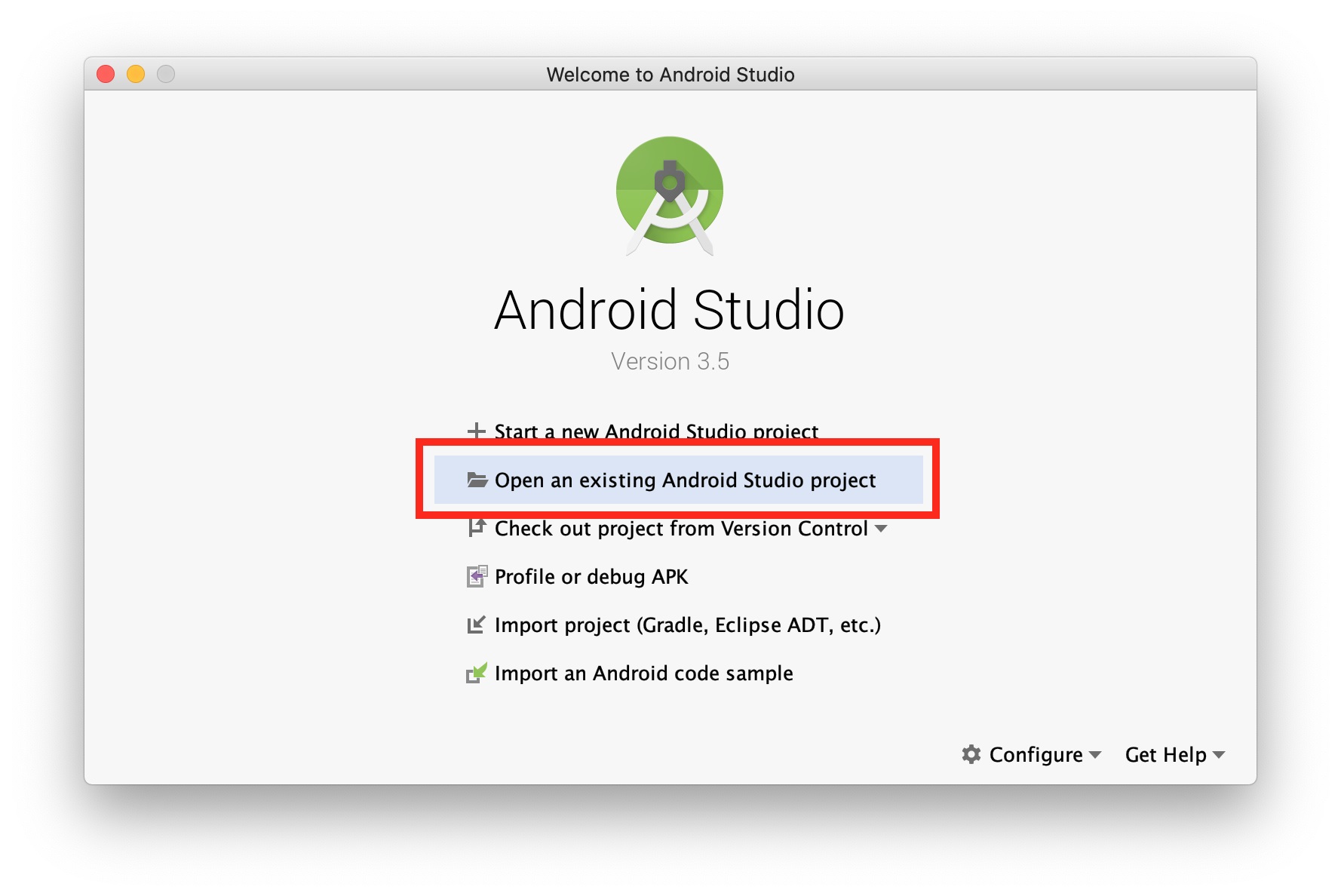
Open Android Studio and select Open an existing Android Studio project
-
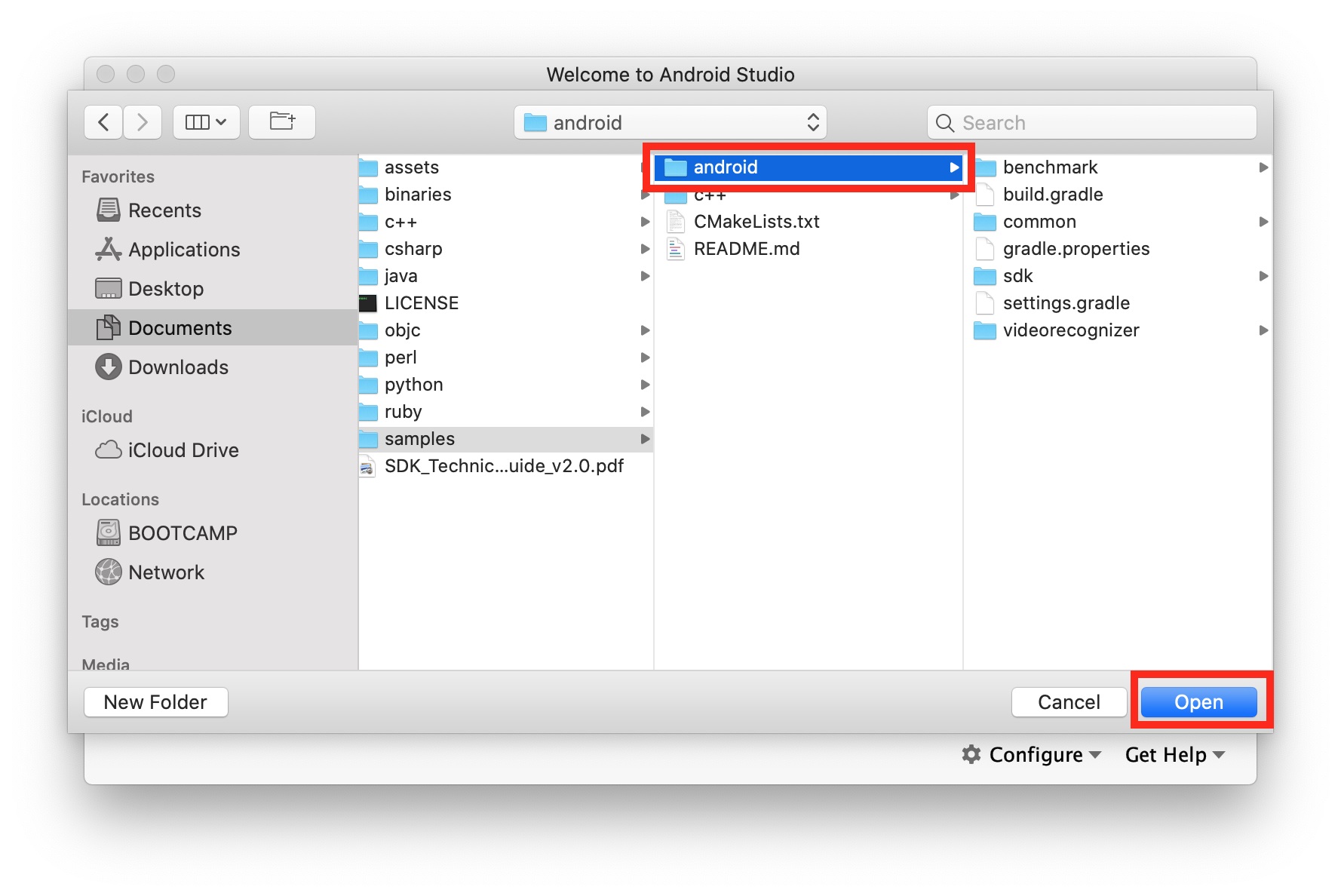
Navigate to /samples, select android folder and click Open
-
Select the sample you want to try (e.g. videorecognize), the device (e.g. samsung SM-G975F) and press run
Linux, Windows, Raspberry Pi and Others
For Raspberry Pi and other Linux systems you need to build the sample applications from source. More info at samples/c++/README.md.
Getting started
The SDK works on many platforms and comes with support for many programming languages.
Adding the SDK to your project
This Github repository contains binaries for Android and Raspberry Pi. The next sections explain how to add the SDK to an existing project.
Android
The SDK is distributed as an Android Studio module and you can add it as reference or you can also build it and add the AAR to your project. But, the easiest way to add the SDK to your project is by directly including the source. In your build.gradle file add:
android {
# This is the block to add within "android { } " section
sourceSets {
main {
jniLibs.srcDirs += ['path-to-your-ultimateMICR-SDK/binaries/android/jniLibs']
java.srcDirs += ['path-to-your-ultimateMICR-SDK/java/android']
assets.srcDirs += ['path-to-your-ultimateMICR-SDK/assets/models']
}
}
}Linux, Windows, Raspberry Pi and Others
The shared libraries are under ultimateMICR-SDK/binaries/. The header file at c++. You can use any C++ compiler/linker.
Using the API
It's hard to be lost when you try to use the API as there are only 3 useful functions: init, process and deInit.
The C++ API is defined at https://www.doubango.org/SDKs/micr/docs/cpp-api.html.
Android (Java)
import org.doubango.ultimateMicr.Sdk.ULTMICR_SDK_IMAGE_TYPE;
import org.doubango.ultimateMicr.Sdk.UltMicrSdkEngine;
import org.doubango.ultimateMicr.Sdk.UltMicrSdkResult;
// JSON configuration string
// More info at https://www.doubango.org/SDKs/micr/docs/Configuration_options.html
final static String CONFIG = "{" +
"\"debug_level\": \"info\"," +
"\"debug_write_input_image_enabled\": false," +
"\"debug_internal_data_path\": \".\"," +
"" +
"\"num_threads\": -1," +
"\"gpgpu_enabled\": true," +
"\"gpgpu_workload_balancing_enabled\": true," +
"" +
"\"segmenter_accuracy\": \"high\"," +
"\"interpolation\": \"bilinear\"," +
"\"roi\": [0, 0, 0, 0]," +
"\"score_type\": \"min\"," +
"\"min_score\": 0.3" +
"}";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Initialize the engine
assert UltMicrSdkEngine.init(
getAssets(),
CONFIG
).isOK();
}
// Camera listener: https://developer.android.com/reference/android/media/ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener
final ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener mOnImageAvailableListener = new ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener() {
@Override
public void onImageAvailable(ImageReader reader) {
try {
final Image image = reader.acquireLatestImage();
if (image == null) {
return;
}
// MICR recognition
final int exifOrientation = 1; // Normal (landscape) - no rotation
final Image.Plane[] planes = image.getPlanes();
final UltMicrSdkResult result = UltMicrSdkEngine.process(
ULTMICR_SDK_IMAGE_TYPE.ULTMICR_SDK_IMAGE_TYPE_YUV420P,
planes[0].getBuffer(),
planes[1].getBuffer(),
planes[2].getBuffer(),
image.getWidth(),
image.getHeight(),
planes[0].getRowStride(),
planes[1].getRowStride(),
planes[2].getRowStride(),
planes[1].getPixelStride(),
exifOrientation
);
assert result.isOK();
image.close();
} catch (final Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// DeInitialize the engine
assert UltMicrSdkEngine.deInit().isOK();
super.onDestroy();
}Linux, Windows, Raspberry Pi and Others (C++)
The C++ API is defined at https://www.doubango.org/SDKs/micr/docs/cpp-api.html.
#include <ultimateMICR-SDK-API-PUBLIC.h> // Include the API header file
// JSON configuration string
// More info at https://www.doubango.org/SDKs/micr/docs/Configuration_options.html
static const char* __jsonConfig =
"{"
"\"debug_level\": \"info\","
"\"debug_write_input_image_enabled\": false,"
"\"debug_internal_data_path\": \".\","
""
"\"num_threads\": -1,"
"\"gpgpu_enabled\": true,"
#if defined(__arm__) || defined(__thumb__) || defined(__TARGET_ARCH_ARM) || defined(__TARGET_ARCH_THUMB) || defined(_ARM) || defined(_M_ARM) || defined(_M_ARMT) || defined(__arm) || defined(__aarch64__)
"\"gpgpu_workload_balancing_enabled\": true,"
#else // Disable GPGPU/CPU work balancing on x86 and enable it on ARM -> https://devtalk.nvidia.com/default/topic/494659/execute-kernels-without-100-cpu-busy-wait-/
"\"gpgpu_workload_balancing_enabled\": false,"
#endif
""
"\"segmenter_accuracy\": \"high\","
"\"interpolation\": \"bilinear\","
"\"roi\": [0, 0, 0, 0],"
"\"score_type\": \"min\","
"\"min_score\": 0.3"
"}";
// Local variable
UltMicrSdkResult result(0, "OK", "{}");
// Initialize the engine (should be done once)
ULTMICR_SDK_ASSERT((result = UltMicrSdkEngine::init(
__jsonConfig
)).isOK());
// Processing (detection + recognition)
// Call this function for every video frame
const void* imageData = nullptr;
ULTMICR_SDK_ASSERT((result = UltMicrSdkEngine::process(
ULTMICR_SDK_IMAGE_TYPE_RGB24,
imageData,
imageWidth,
imageHeight
)).isOK());
// DeInit
// Call this function before exiting the app to free the allocate resources
// You must not call process() after calling this function
ULTMICR_SDK_ASSERT((result = UltMicrSdkEngine::deInit()).isOK());Again, please check the sample applications for more information on how to use the API.
Technical questions
Please check our discussion group or twitter account