Welcome to RouterFleet - the next step in centralized router backup and management. This open source project is designed to revolutionize the way we handle backups and configurations for routers and network equipment, focusing primarily on simplifying and securing network management tasks.
RouterFleet is developed with the aim of easing the management of a fleet of devices, particularly focusing on Mikrotik devices during its initial launch phase. This project is a testament to countless hours of dedication towards developing a system that not only simplifies but also secures network management tasks across various devices.
- Centralized Backup Management: Easily manage backups for your routers and network equipment from a single interface.
- Backup diffing: Compare backups to identify changes and track configuration history.
- Multiple backup profiles: Create multiple backup profiles to manage different schedules and retention polices.
- Mikrotik Device Compatibility: Initial support for Mikrotik devices with plans to expand based on community feedback.
- Continuous Updates: Regular updates to introduce new functionalities, performance enhancements, and bug fixes.
- Integration with wireguard: Integration with wireguard_webadmin to easily manage WireGuard VPNs.
- Open Source: Dive into the code, contribute, and be a part of a growing community.
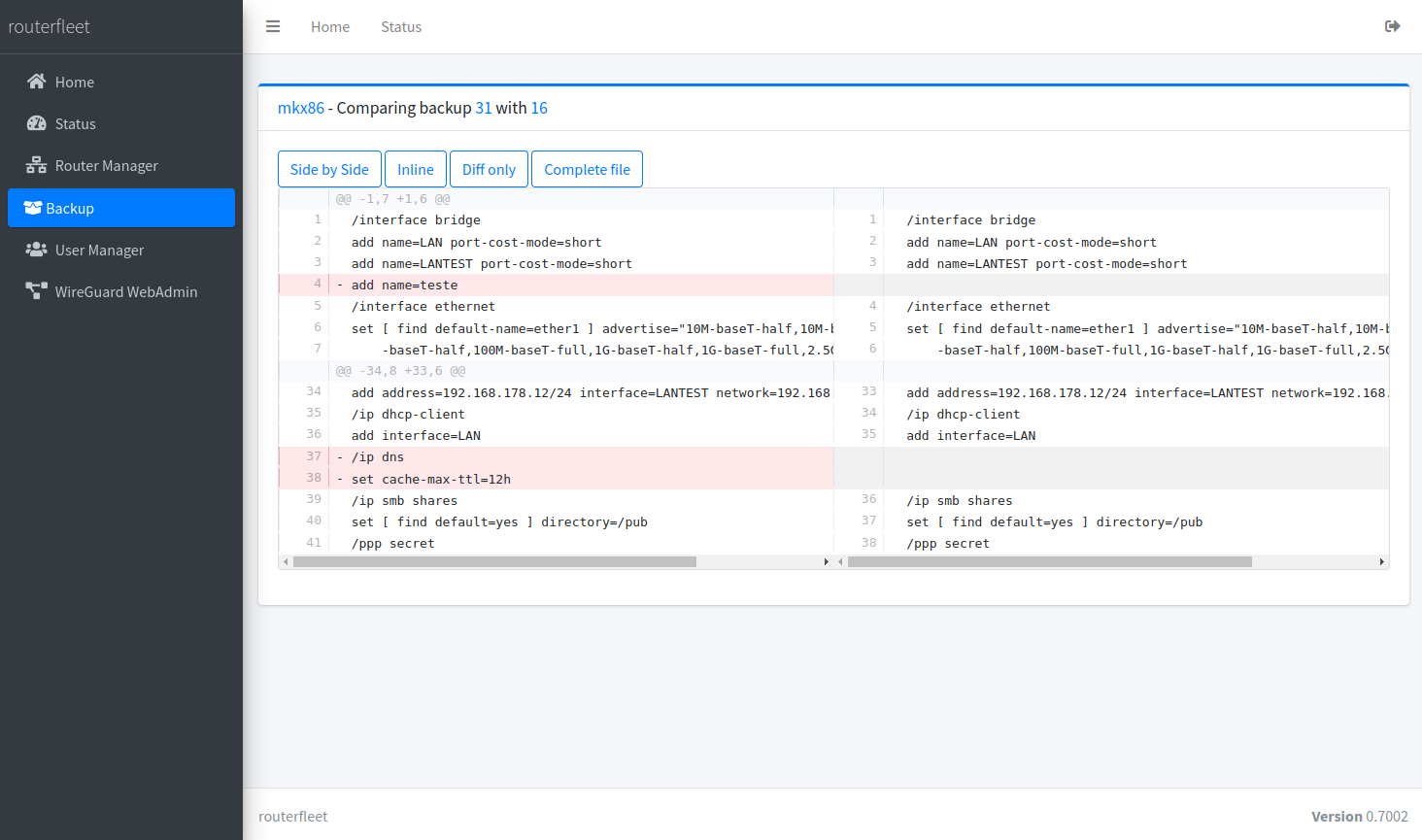
Easily compare backups to identify changes and track configuration history.
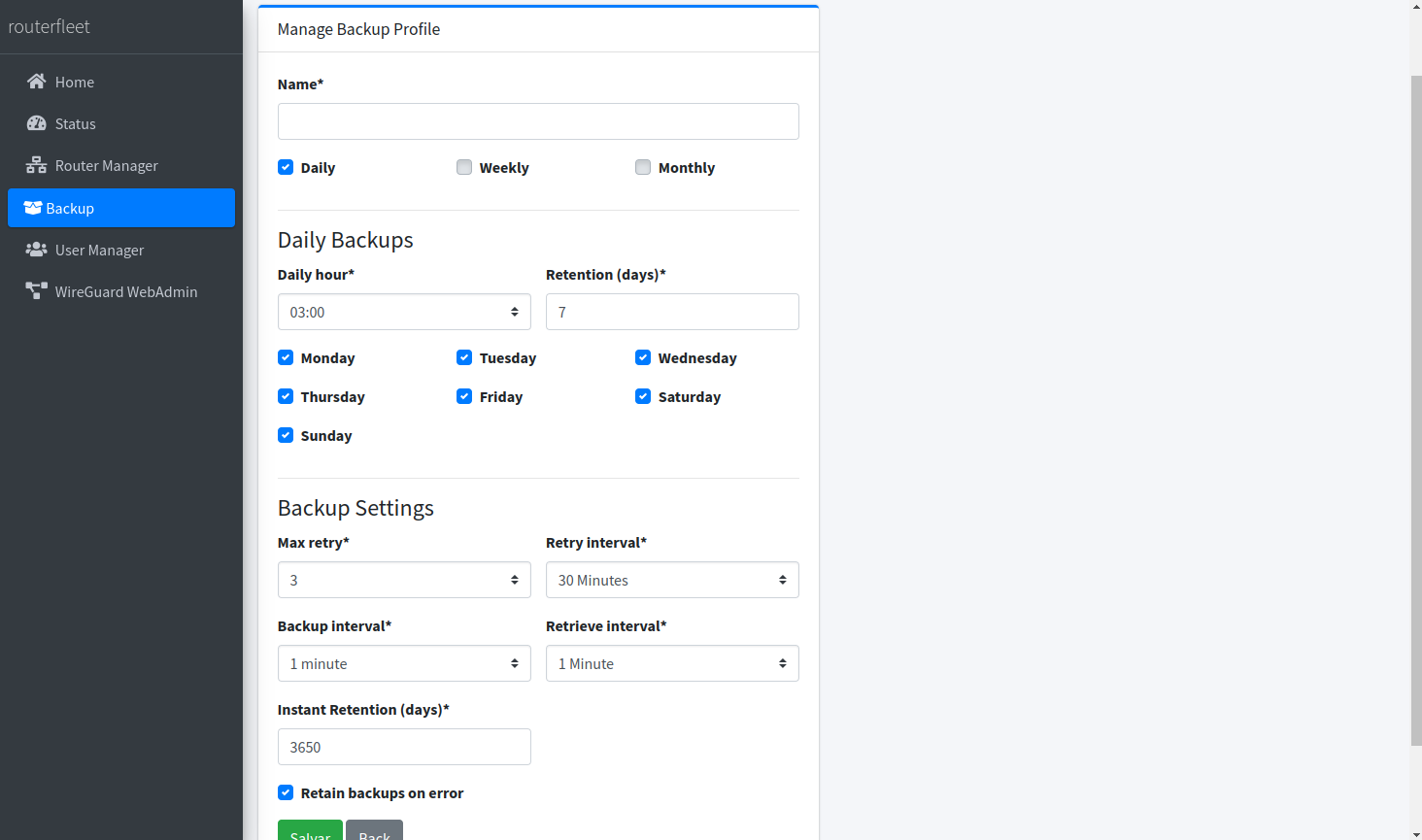
Create multiple backup profiles to manage different schedules and retention policies.
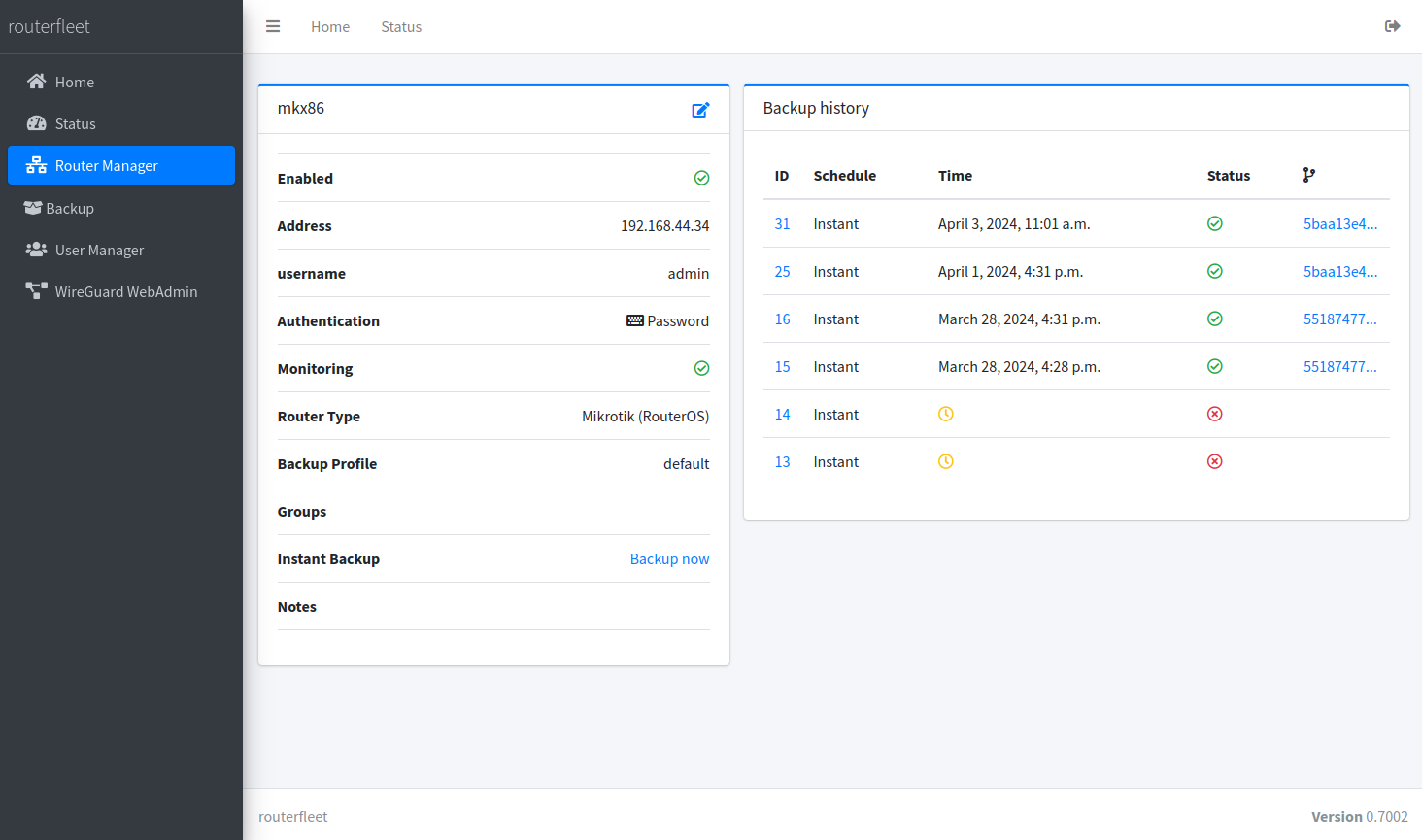
View detailed information about your routers, including the complete backup history.
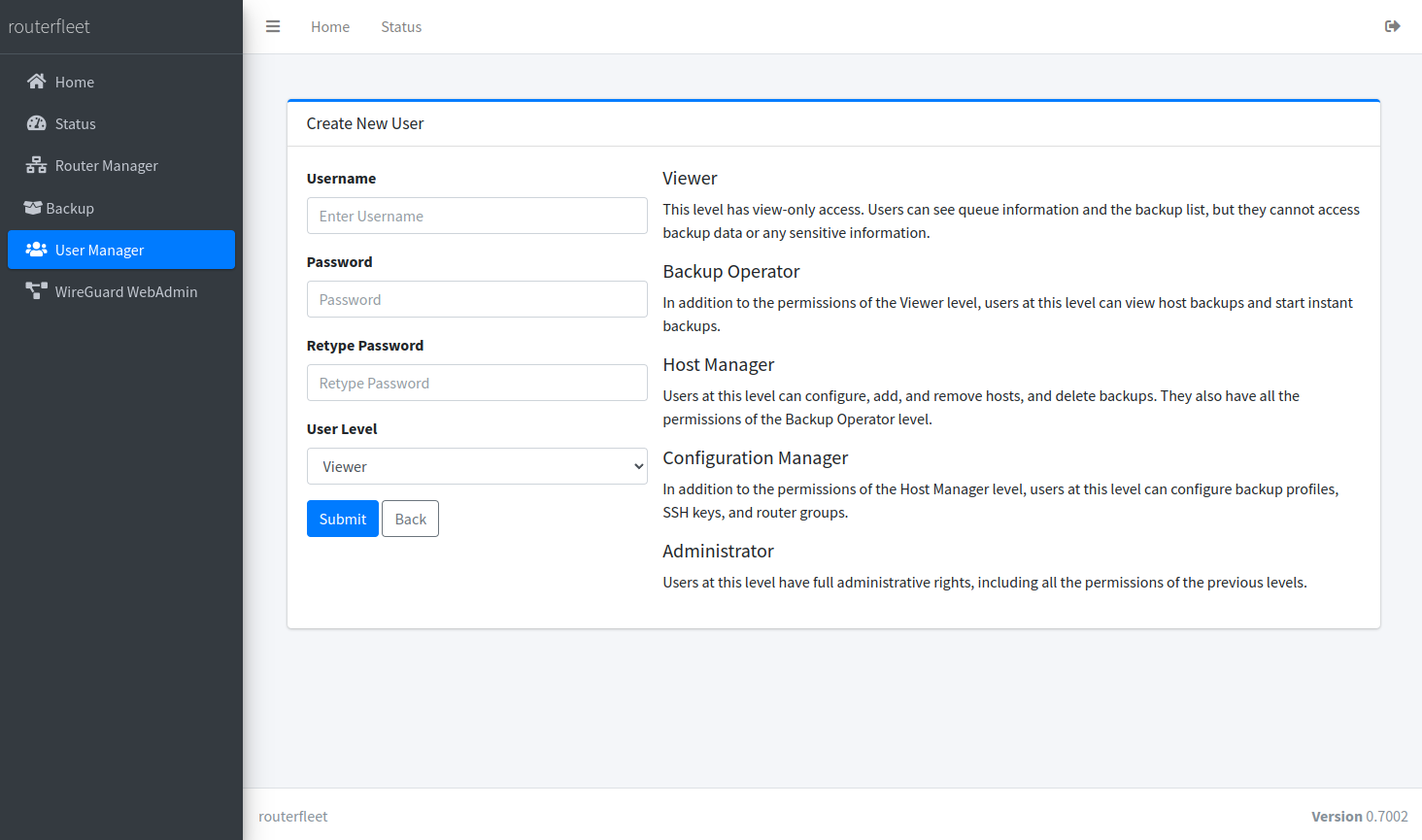
Manage users and their permissions to ensure secure access to RouterFleet.
These steps will guide you through deploying the RouterFleet project:
Create a dedicated directory for the RouterFleet project and navigate into it. This directory will serve as your working environment for the deployment.
mkdir routerfleet && cd routerfleetDownload the appropriate docker-compose.yml file directly into your working directory to ensure you're using the latest deployment configuration. Choose one of the following based on your deployment scenario:
This is the recommended setup for production environments. Download the docker-compose.yml that includes the Postgres database container:
wget -O docker-compose.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eduardogsilva/routerfleet/main/docker-compose.ymlIf you prefer to use SQLite or a remote database, download the docker-compose-no-postgres.yml file:
wget -O docker-compose.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eduardogsilva/routerfleet/main/docker-compose-no-postgres.ymlGenerate a .env file in the same directory as your docker-compose.yml with the necessary environment variables:
# Configure SERVER_ADDRESS to match the address of the server. If you don't have a DNS name, you can use the IP address.
# A missconfigured SERVER_ADDRESS will cause the app to have CSRF errors.
SERVER_ADDRESS=my_server_address
DEBUG_MODE=False
# Choose a timezone from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones
TIMEZONE=America/Sao_Paulo
# Available options are 'sqlite', 'postgres'
DATABASE_ENGINE=postgres
# If you want to use sqlite or postgres outside of docker, you should use docker-compose-no-postgres.yml
# and provide POSTGRES_HOST, POSTGRES_PORT below.
#POSTGRES_HOST=
#POSTGRES_PORT=
POSTGRES_DB=routerfleet
POSTGRES_USER=routerfleet
POSTGRES_PASSWORD=your_database_passwordAdjust the variables according to your setup.
If you are upgrading from a previous version, you should consider running docker compose pull to ensure you are using the latest images.
Start the RouterFleet services using Docker Compose:
docker compose up -dIf you prefer to use your own SSL certificates instead of the auto-generated self-signed certificate:
- Access the
certificatesvolume. - Replace
nginx.pemandnginx.keywith your certificate files.
Visit https://yourserver.example.com in your web browser to access the RouterFleet web interface. Remember, if you're using the self-signed certificate, you'll need to accept the certificate exception in your browser.
Following these steps will set up RouterFleet on your server, ensuring you're utilizing the latest configurations for optimal performance and security.
To maintain security, performance, and access to new features in RouterFleet, it's important to follow these steps when upgrading:
Begin by navigating to your routerfleet directory:
cd path/to/routerfleetIf you're upgrading from an existing git clone installation, navigate to your current project directory.
cd /path/to/routerfleet_git_cloneBefore starting the upgrade, it's crucial to back up your database. This step ensures you can revert to the previous state if the upgrade encounters problems. For the database, we recommend manually running a pg_dump command to create a backup.
docker exec -e PGPASSWORD=your_password routerfleet-postgres pg_dump -U routerfleet -d routerfleet > /root/routerfleet-$(date +%Y-%m-%d-%H%M%S).sqlPrevent data loss by stopping all RouterFleet services gracefully:
docker compose downFollow the previously outlined Deployment Instructions.
Don't forget to update the docker-compose.yml file to the latest version by re-downloading it from the repository.
- Verify Operation: After the services start, access the web interface to ensure routerfleet functions as expected. Examine the application logs for potential issues.
- Support and Troubleshooting: For any complications or need for further information, consult the project's Discussions page or relevant documentation.
Following these instructions will help ensure a smooth upgrade process for your RouterFleet installation, keeping it secure and efficient.
As an open source project, RouterFleet thrives on community support. Whether you're a developer, a network engineer, or just someone interested in network management, there are many ways you can contribute:
- Code Contributions: Submit pull requests with bug fixes, new features, and improvements.
- Feedback: Share your experiences, suggest improvements, and help shape the future of RouterFleet.
- Documentation: Help improve the documentation to make RouterFleet more accessible to everyone.
- Testing: Report bugs, test new features, and help ensure RouterFleet is stable and reliable.
Join our community to get support, share ideas, and collaborate:
- GitHub Issues for reporting bugs and feature requests.
- Discussions for sharing ideas and getting help from the community.
Your support and involvement are crucial in shaping the future of RouterFleet. Let's make network management easier and more secure together!
RouterFleet is released under the MIT License. Feel free to explore, modify, and distribute the software as per the license agreement.
We look forward to your contributions and are excited to see how RouterFleet evolves with your help and feedback. Let's build a robust community around efficient and secure network management. Thank you for your support!