Istio is part of a new category of products known as "service mesh" software designed to manage the complexity of service resilience in a microservice infrastructure. It defines itself as a service management framework built to keep business logic separate from the logic to keep your services up and running. In other words, it provides a layer on top of the network that will automatically route traffic to the appropriate services, handle circuit breaker logic, enforce access and load balancing policies, and generate telemetry data to gain insight into the network and allow for quick diagnosis of issues.
For more information on Istio, please refer to the Istio documentation. Some familiarity with Istio is assumed.
In this demo, we leverage Google Kubernetes Engine (Kubernetes Engine) and Google Compute Engine (GCE) to learn more about how Istio can manage services that reside in the network outside of the Kubernetes Engine environment. This demo uses Kubernetes Engine to construct a typical Istio infrastructure and then setup a GCE instance running a MySQL microservice that will be integrated into the Istio infrastructure. We will use the sample BookInfo application and extend it by using the MySQL microservice to house book reviewer ratings. The demo serves as a learning tool and addresses the use case of users who want to leverage Istio to manage other services in their Google Cloud Platform (GCP) environment that may not be ready for migration to Kubernetes Engine just yet.
Istio has two main pieces that create the service mesh: the control plane and the data plane.
The control plane is made up of the following set of components that act together to serve as the hub for the infrastructure's service management:
-
Mixer: a platform-independent component responsible for enforcing access control and usage policies across the service mesh and collecting telemetry data from the Envoy proxy and other services
-
Pilot: provides service discovery for the Envoy sidecars, traffic management capabilities for intelligent routing, (A/B tests, canary deployments, etc.), and resiliency (timeouts, retries, circuit breakers, etc.)
-
Citadel: provides strong service-to-service and end-user authentication using mutual TLS, with built-in identity and credential management.
The data plane comprises all the individual service proxies that are distributed throughout the infrastructure. Istio uses Envoy with some Istio-specific extensions as its service proxy. It mediates all inbound and outbound traffic for all services in the service mesh. Istio leverages Envoy’s many built-in features such as dynamic service discovery, load balancing, TLS termination, HTTP/2 & gRPC proxying, circuit breakers, health checks, staged roll-outs with percentage-based traffic splits, fault injection, and rich metrics.
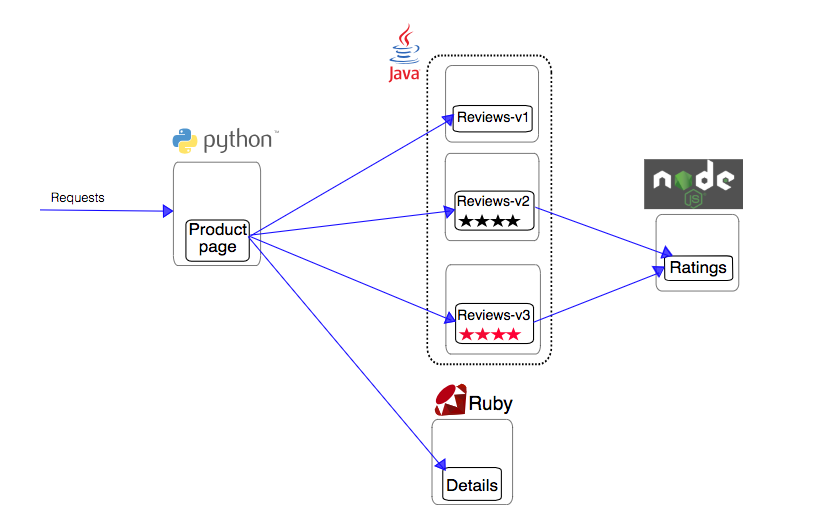
The sample BookInfo application displays information about a book, similar to a single catalog entry of an online book store. Displayed on the page is a description of the book, book details (ISBN, number of pages, and so on), and a few book reviews.
The BookInfo application is broken into four separate microservices and calls on various language environments for its implementation:
- productpage - The productpage microservice calls the details and reviews microservices to populate the page.
- details - The details microservice contains book information.
- reviews - The reviews microservice contains book reviews. It also calls the ratings microservice.
- ratings - The ratings microservice contains book ranking information that accompanies a book review.
There are 3 versions of the reviews microservice:
- Version v1 doesn’t call the ratings service.
- Version v2 calls the ratings service, and displays each rating as 1 to 5 black stars.
- Version v3 calls the ratings service, and displays each rating as 1 to 5 red stars.
To learn more about Istio, please refer to the project's documentation.
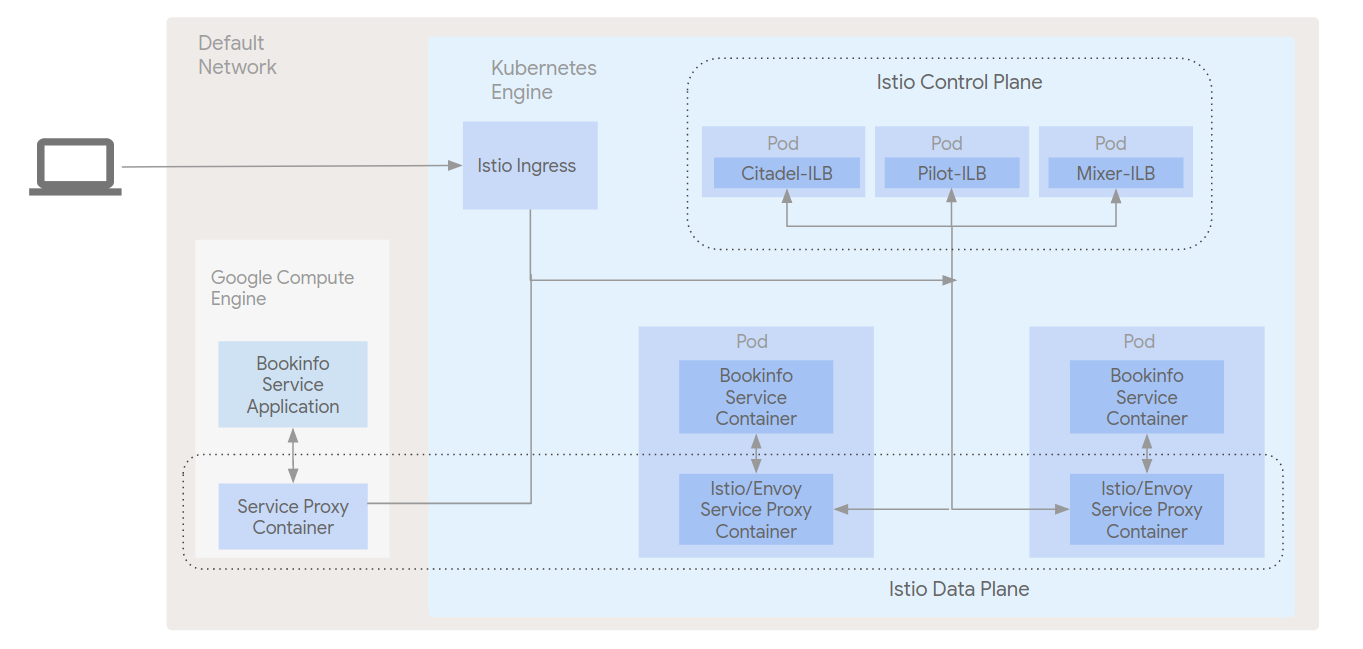
The pods and services that make up the Istio control plane are the first components of the architecture that will be installed into Kubernetes Engine. An Istio service proxy is installed along with each microservice during the installation of the BookInfo application, as are our telemetry add-ons. At this point, in addition to the application microservices there are two tiers that make up the Istio architecture: the Control Plane and the Data Plane.
In the diagram, note:
- All input and output from any BookInfo microservice goes through the service proxy.
- Each service proxy communicates with each other and the Control Plane to implement the features of the service mesh, circuit breaking, discovery, etc.
- The Mixer component of the Control Plane is the conduit for the telemetry add-ons to get metrics from the service mesh.
- The Istio ingress component provides external access to the mesh.
- The environment is setup in the Kubernetes Engine default network.
This demo can be run from MacOS, Linux, or, alternatively, directly from Google Cloud Shell. The latter option is the simplest as it only requires browser access to GCP and no additional software is required. Instructions for both alternatives can be found below.
NOTE: This section can be skipped if the cloud deployment is being performed without Cloud Shell, for instance from a local machine or from a server outside GCP.
Google Cloud Shell is a browser-based terminal that Google provides to interact with your GCP resources. It is backed by a free Compute Engine instance that comes with many useful tools already installed, including everything required to run this demo.
Click the button below to open the demo in your Cloud Shell:
Use the --recursive argument to download dependencies provided via a git submodule.
git submodule update --init --recursiveTo prepare gcloud for use in Cloud Shell, execute the following command in the terminal at the bottom of the browser window you just opened:
gcloud initRespond to the prompts and continue with the following deployment instructions. The prompts will include the account you want to run as, the current project, and, optionally, the default region and zone. These configure Cloud Shell itself-the actual project, region, and zone, used by the demo will be configured separately below.
NOTE: If the demo is being deployed via Cloud Shell, as described above, this section can be skipped.
For deployments without using Cloud Shell, you will need to have access to a computer providing a bash shell with the following tools installed:
Use git to clone this project to your local machine:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/gke-istio-gce-demoNote that the --recursive argument is required to download dependencies provided via a git submodule.
When downloading is complete, change your current working directory to the new project:
cd gke-istio-gce-demoContinue with the instructions below, running all commands from this directory.
NOTE: The following instructions are applicable for deployments performed both with and without Cloud Shell.
- Copy the properties file to properties.env and set the following variables in the properties.env file:
YOUR_PROJECT- the name of the project you want to useYOUR_REGION- the region in which to locate all the infrastructureYOUR_ZONE- the zone in which to locate all the infrastructure
- Run the following command
make createThe script should deploy all of the necessary infrastructure and install Istio. The script will end with a line like this, though the IP address will likely be different:
Update istio service proxy environment file
104.196.243.210/productpage
You can open this URL in your browser and see the simple web application provided by the demo.
To validate that everything is working correctly, first open your browser to the URL provided at the end of the setup script, make note of stars for first book review. Once the ratings service is running correctly, run:
make validateIf you refresh the page in your browser, the first rating should display a different number for rating. This shows that the rating has made it from the database to the ratings service. While the database microservice isn't contained within the GKE cluster, it works seamlessly via the Istio data plane.
To tear down the resources created by this demonstration, run:
make teardownNOTE: Keep an eye on quotas. The teardown script deletes resources of which it is aware but it is possible some resources were created in setup and not torn down.
This demo was created with help from the following links
- https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/tutorials/istio-on-gke
- https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/tutorials/istio-on-compute-engine
- https://istio.io/docs/guides/bookinfo.html
- https://istio.io/docs/setup/kubernetes/mesh-expansion.html
- https://istio.io/docs/guides/integrating-vms.html
This is not an officially supported Google product