This repo contains tools for testing and experimenting with Hashicorp software.
But not only that..you can play with OpenFaas serverless stuff too! Keep reading.
It will deploy a cluster for Vault, Consul and Nomad where each component will be connected together to form a perfect environment for testing your applications with service mesh.
Table of Contents
WARNING: At the moment the clusters will be loaded in
devmode. If the services will fail, you will lose every data since the backends are loaded in memory.
Vagrant file is taken partially from here hashicorp's nomad-guides It's been revisited and modified (and it will be upgraded in the future).
You can choose respective software versions and VM specs with these environment variables:
| ENV | description | default value | Ubuntu ARM alternative | Centos 7 alternative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
BASE_BOX |
Vagrant Base Box |
generic/ubuntu2110 |
rkrause/ubuntu-21.10-arm64 |
bento/centos-7 |
BOX_VERSION |
Vagrant Base Box Version |
3.5.2 |
1.0.0 |
202103.18.0 |
VAGRANT_CPU_NUM |
Number of cpu used by VM |
2 |
||
VAGRANT_MEM |
Memory used by VM |
8192 |
||
VAGRANT_VMWARE |
If set, uses VMware provider |
false |
||
VAULT_VERSION |
Vault version |
1.8.4 |
||
CONSUL_VERSION |
Consul version |
1.10.4 |
||
NOMAD_VERSION |
NOMAD version |
1.1.6 |
||
CNI_VERSION |
CNI plugin version |
0.9.1 |
||
CONTAINERD_VERSION |
Containerd version |
1.4.11-1 |
1.4.9-3.1 |
|
DOCKER_CE_VERSION |
Docker CE version |
20.10.10~3-0~ubuntu |
20.10.8-3 |
|
DOCKER_SCAN_VERSION |
Docker Scan version |
Not installed |
0.8.0-3 |
|
ENVOY_VERSION |
Envoy version |
1.18.2 |
||
TF_VAR_faasd_version |
Faasd provider version |
0.13.0 |
||
TF_VAR_faas_nats_version |
NATS version version |
0.22.0 |
||
TF_VAR_faas_auth_plugin_version |
Faas Auth plugin version |
0.21.0 |
||
TF_VAR_faas_gateway_version |
Faas Gateway version |
0.21.0 |
||
TF_VAR_faas_queue_worker_version |
Faas Queue Worker version |
0.12.2 |
You need Hashicorp Terraform (version >= 0.13.1, < 1.0.0 ) and Vagrant installed (version >= 2.2.1).
To provision and deploy the workload simply do:
./deploy.shor through Makefile:
makewith make help you'll find some other useful make targets to launch.
By default it will use VirtualBox. To use VMware add VAGRANT_VMWARE=true to you're environment variables.
Now you can install it also in ARM based hosts (like Macbook M1 pro on hypervisor VMWare Fusion). With Ubuntu 21.10.
Tested with Centos 7, Ubuntu 21.04, 21.10 and Ubuntu 21.10 ARM edition Boxes: bentos/centos-7, generic/ubuntu2104, generic/ubuntu2110, rkrause/ubuntu-21.10-arm64
Makefile useful tips
- You can run
make teststo perform some tests to the Vault, Consul and Nomad endpoints.- With
make provisionand with the env varTAGS_ONLYset as a comma-separated list, you can provision only certain Ansible roles (ex.:TAGS_ONLY="consul,nomad" make provision).- To deploy only Hashicorp stack (Vault, Consul and Nomad) without Terraforming any services, run
make vagrant.
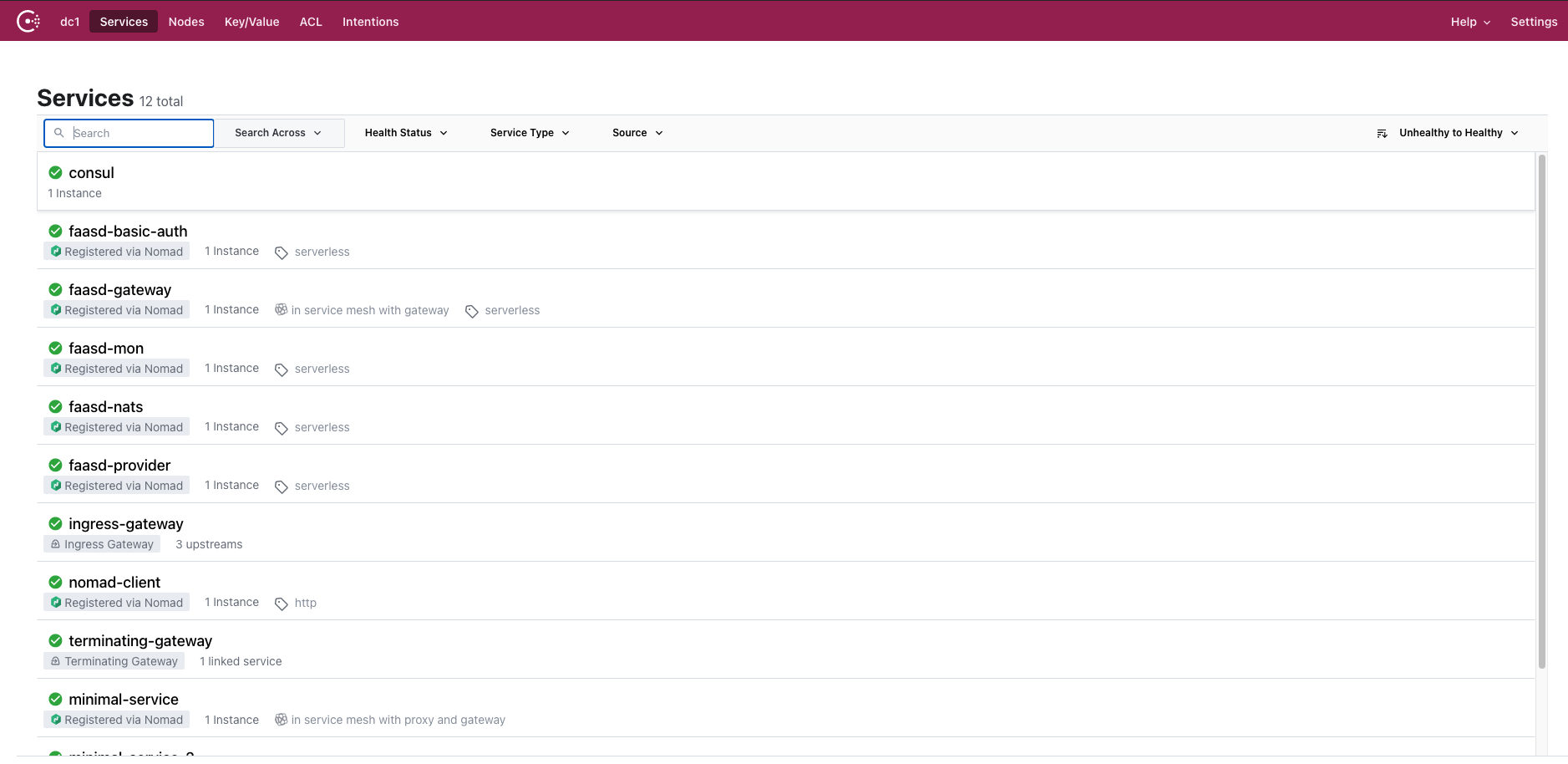
At the end, if everything went fine, you can reach the services Vault, Consul and Nomad at localhost, respectively at 8200, 8500, 4646.
While Consul Ingress Gateway is listening at port 8080, where you can find some preinstalled services.
In Consul you should see something like:
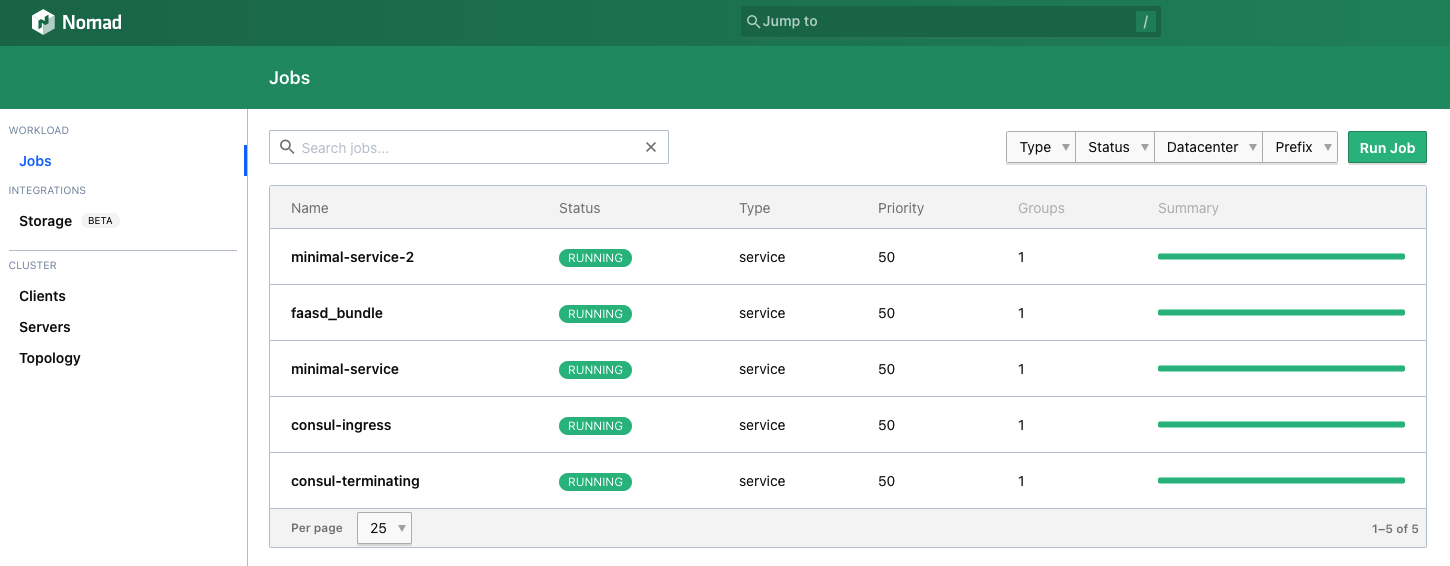
While in Nomad:
You can disable terraform applying by set the environment variable TERRAFORM_LABS to false. This will only provision the Hashicorp stack without deploying in Nomad.
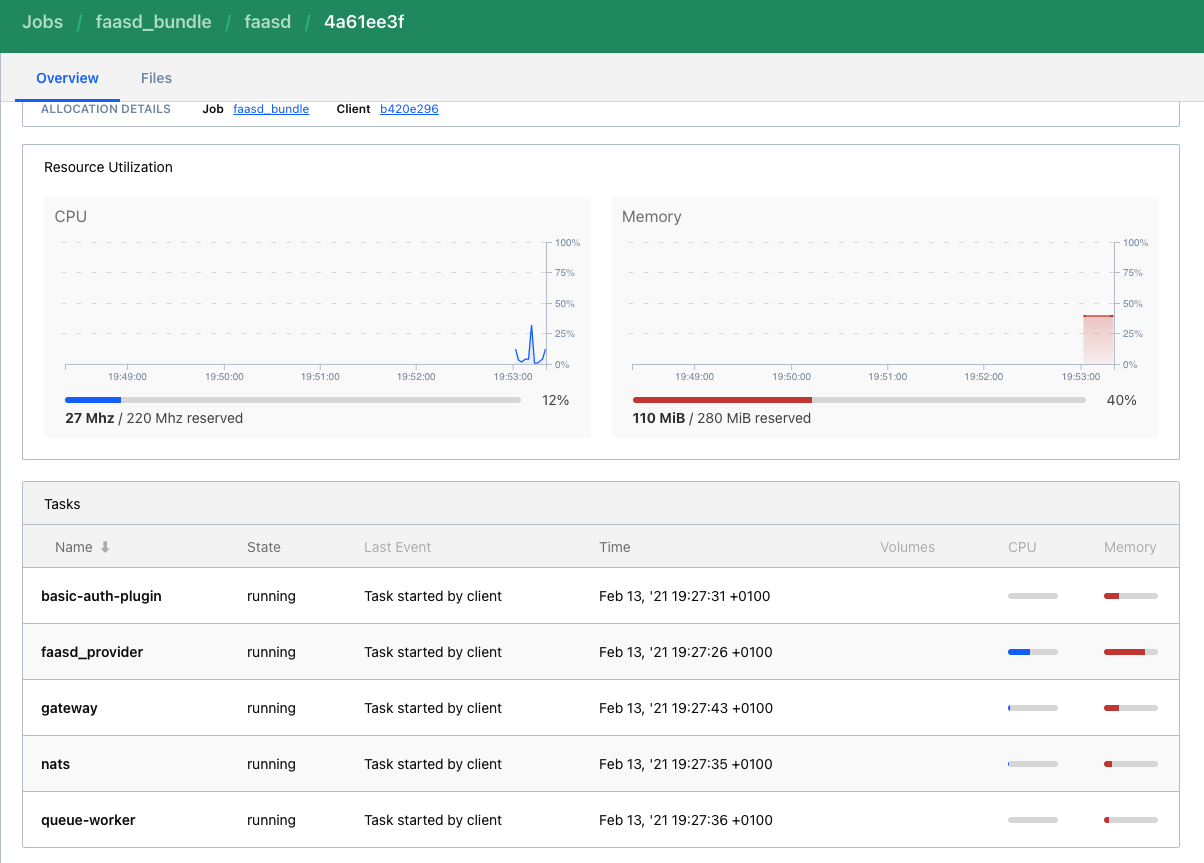
With the provided code you could deployed two microservices minimal-service and minimal-service-2 that can talk to each other.
If you go inside terraform folder and do:
terraform apply -var deploy_example_jobs=true -auto-approveyou'll find both in the cluster.
Both are deployed by Nomad with Envoy as sidecar, so they are inside the Consul service mesh.
Do some intra-services communication test:
nomad alloc exec -task minimal-service \
$(curl -s http://127.0.0.1:4646/v1/job/minimal-service/allocations | \
jq -r '.[0].ID'| \
cut -c -8) curl -s 127.0.0.1:8080 | \
jq
{
"host": "127.0.0.1:9090",
"statuscode": 200,
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Content-Length": "0",
"Duration": "0.030891",
"Request-time": "2021-02-13 19:08:03.673759094 +0000 UTC",
"Response-time": "2021-02-13 19:08:03.673789985 +0000 UTC",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.69.1",
"X-Envoy-Expected-Rq-Timeout-Ms": "15000",
"X-Forwarded-Proto": "http",
"X-Request-Id": "cd6dcc66-f73c-4d16-8783-e4c7690bb929"
},
"protocol": "HTTP/1.1",
"requestURI": "/",
"servedBy": "6194ce0dea8d",
"method": "GET"
}with this command we go inside minimal-service container and execute a GET request to localhost at port 8080. At that port Envoy proxy is listening to requests, in this case it will proxy the request to minimal-service-2. This is just an example.
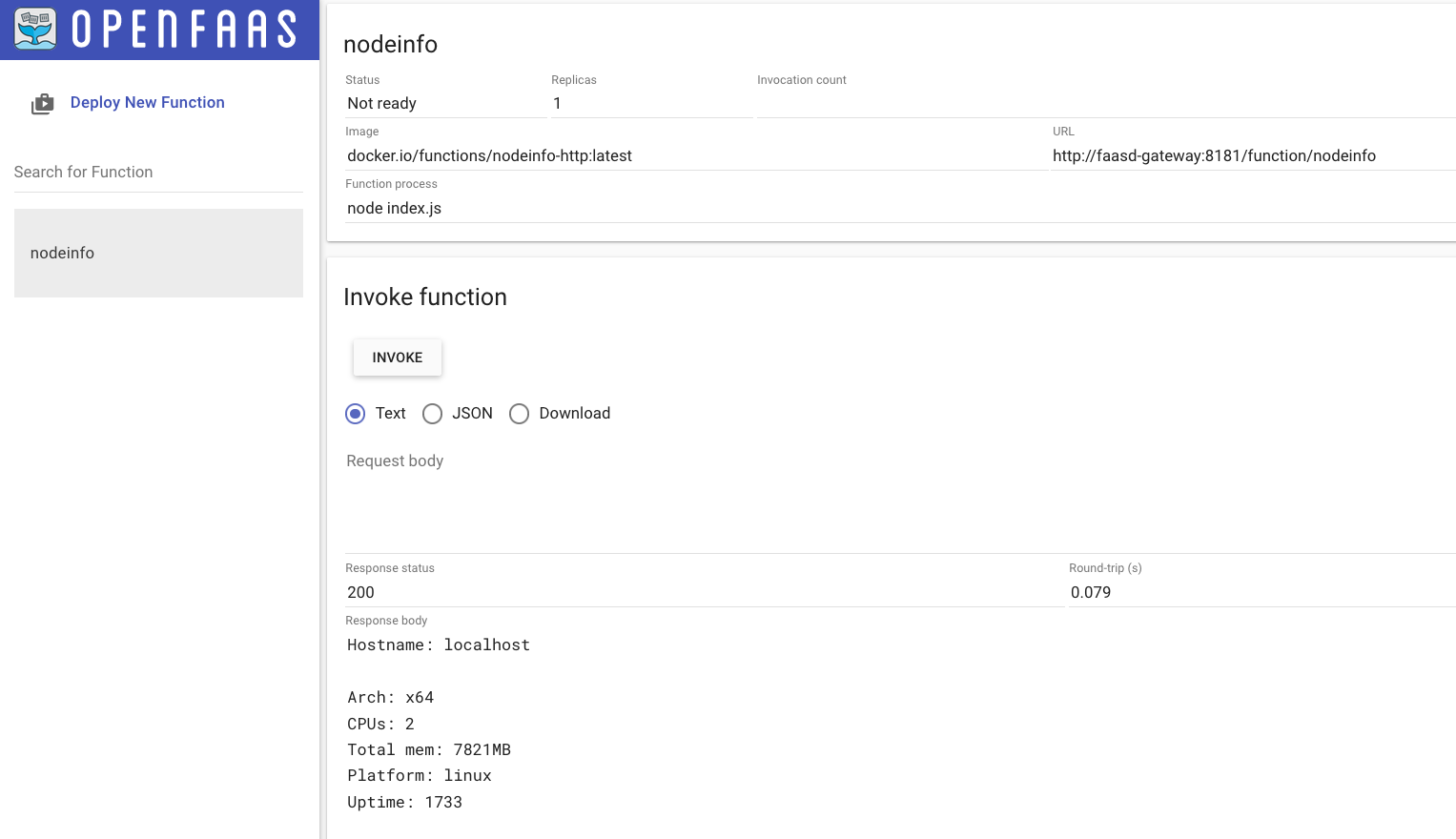
In this cluster, by default, we have also deployed faasd! So now we can reach OpenFaas gateway and use OpenFaas for our serverless testing!
Just add 127.0.0.1 faasd-gateway to your /etc/hosts file and you're done.
Go to http://faasd-gateway:8080 to enjoy the beautiful OpenFaas homepage.
Add 127.0.0.1 grafana to your /etc/hosts file and go to http://grafana:8080.
Both dashboard are taken from Grafana dashboard repos with few modifications:
OpenFaas needs docker credentials to pull and push images.
The utility script docker-login-faasd.sh does that:
$ ./docker-login.sh <username> <password>
Docker login for Faasd..
WARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /root/.docker/config.json.
Configure a credential helper to remove this warning. See
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-store
Login Succeeded
Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed.
Done.
For cleaning up just execute clean.sh or make clean