Docs (state: in process): Gino-Admin docs
Play with Demo (current master 0.0.12) >>>> Gino-Admin demo <<<<
Admin Panel for PostgreSQL DB with Gino ORM and Sanic
- Auth by login/pass with cookie check
- Create(Add new) item by one for the Model
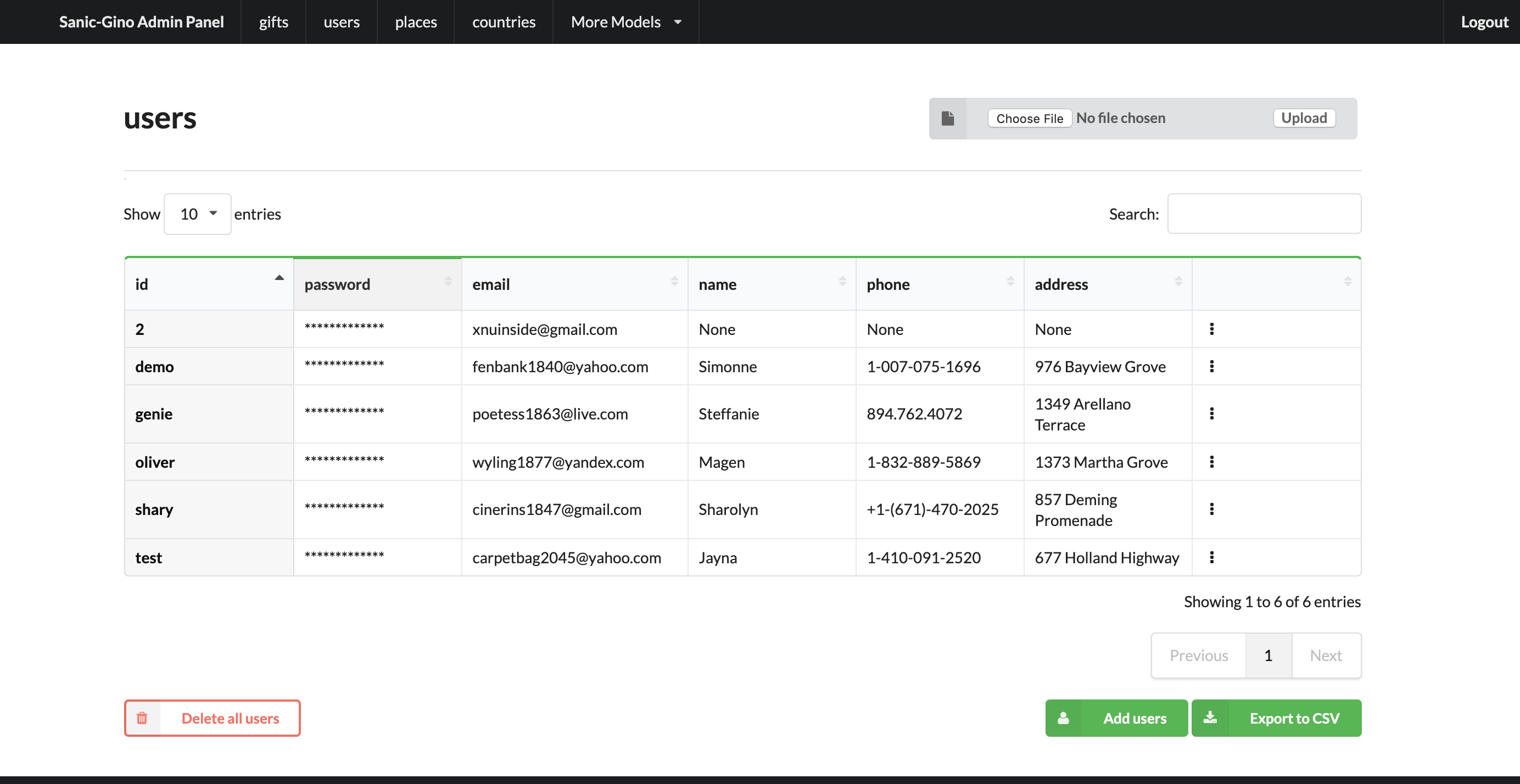
- Search/sort in tables
- Upload/export data from/to CSV
- Delete all rows/per element
- Copy existed element (data table row)
- Edit existed data (table row)
- SQL-Runner (execute SQL-queries)
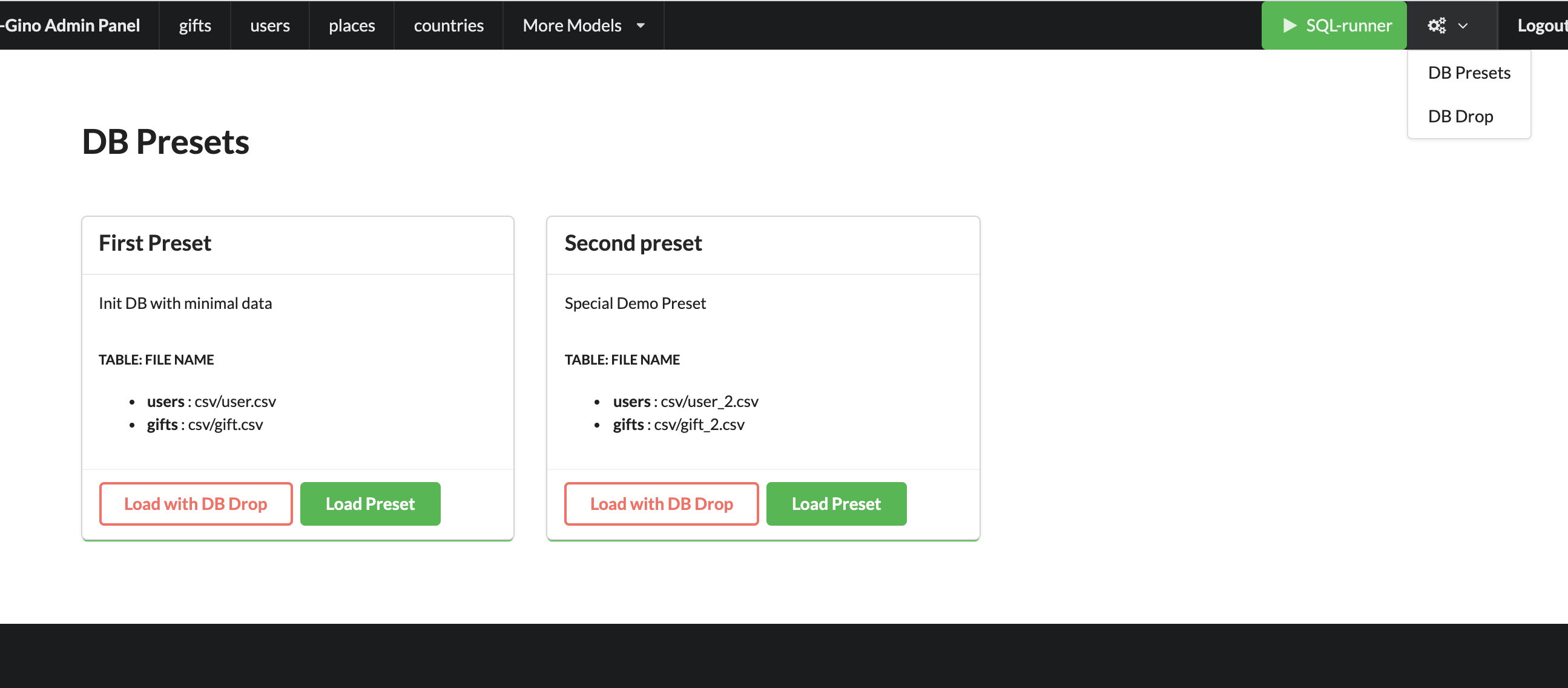
- Presets: Define order and Load to DB bunch of CSV-files
- Drop DB (Full clean up behavior: Drop tables & Recreate)
- Deepcopy element (recursive copy all rows/objects that depend on chosen as ForeignKey)
- Composite CSV: Load multiple relative tables in one CSV-file
- History logs on changes (log for admin panel actions - edit, delete, add, init_db, load presets and etc)
- Select multiple for delete/copy
- Edit multiple items (?)
- Roles & User store in DB
- Filters in Table's columns
- Add possible to add new Presets from GUI
- Other staff on Gino Project Dashboard
pip install gino-admin==0.1.0
- Added REST endpoint to upload data from CSV file to DB.
- Cleaned up styles in UI.
You can find several code examples in examples/ folder.
Run Admin Panel from cli
gino_admin run #module_name_with_models -d postgresql://%(DB_USER):%(DB_PASSWORD)@%(DB_HOST):%(DB_PORT)/%(DB)
Optional params:
-d --db
Expected format: postgresql://%(DB_USER):%(DB_PASSWORD)@%(DB_HOST):%(DB_PORT)/%(DB)
Example: postgresql://gino:gino@%gino:5432/gino (based on DB settings in examples/)
Notice: DB credentials can be set up as env variables with 'SANIC_' prefix
-h --host
-p --port
-c --config Example: -c "presets_folder=examples/base_example/src/csv_to_upload;some_property=1"
Notice: all fields that not supported in config will be ignored, like 'some_property' in example
--no-auth Run Admin Panel without Auth in UI
-u --user Admin User login & password
Expected format: login:password
Example: admin:1234
Notice: user also can be defined from env variable with 'SANIC_' prefix - check Auth section example
Example:
Create in your project 'admin.py' file and use add_admin_panel from from gino_admin import add_admin_panel
Code example in: examples/base_example How to run example in: examples/base_example/how_to_run_example.txt
Example:
from from gino_admin import add_admin_panel
# your app code
add_admin_panel(
app, db, [User, Place, City, GiftCard], custom_hash_method=custom_hash_method
)
Where:
- 'app': your Sanic application
- 'db' : from gino.ext.sanic import Gino; db = Gino() and
- [User, Place, City, GiftCard] - list of models that you want to add in Admin Panel to maintain
- custom_hash_method - optional parameter to define you own hash method to encrypt all '_hash' columns of your Models.
In admin panel _hash fields will be displayed without '_hash' prefix and fields values will be hidden like '******'
You can use Gino Admin as stand alone web app. Does not matter what Framework used for your main App.
Code example in: examples/use_with_any_framework_in_main_app/ How to run example in: examples/use_with_any_framework_in_main_app/how_to_run_example.txt
- In module where you define DB add 'if block'. We will use Fast API as main App in our example.
We have db.py where we import Gino as
from gino.ext.starlette import Gino
db = Gino(
dsn='postgresql://gino:gino@localhost:5432/gino'
)
But if we use this module in Admin Panel we need to have initialisation like this:
from gino.ext.sanic import Gino
db = Gino()
To get this, we will add some flag and based on this flag module will init db in needed to as way:
if os.environ.get('GINO_ADMIN'):
from gino.ext.sanic import Gino
db = Gino()
else:
from gino.ext.starlette import Gino
db = Gino(dsn='postgresql://gino:gino@localhost:5432/gino')
So, if now 'db' used by Gino Admin - we use init for Sanic apps, if not - we use for our Main application Framework
Now, we need to create admin.py to run admin panel:
import os
from gino_admin import create_admin_app
os.environ["GINO_ADMIN"] = "1"
# gino admin uses Sanic as a framework, so you can define most params as environment variables with 'SANIC_' prefix
# in example used this way to define DB credentials & login-password to admin panel
os.environ["SANIC_DB_HOST"] = "localhost"
os.environ["SANIC_DB_DATABASE"] = "gino"
os.environ["SANIC_DB_USER"] = "gino"
os.environ["SANIC_DB_PASSWORD"] = "gino"
os.environ["SANIC_ADMIN_USER"] = "admin"
os.environ["SANIC_ADMIN_PASSWORD"] = "1234"
if __name__ == "__main__":
# variable GINO_ADMIN must be set up before import db module, this is why we do import under if __name__
import db # noqa E402
# host & port - will be used to up on them admin app
# config - Gino Admin configuration,
# that allow set path to presets folder or custom_hash_method, optional parameter
# db_models - list of db.Models classes (tables) that you want to see in Admin Panel
create_admin_app(host="0.0.0.0", port=5000, db=db.db, db_models=[db.User, db.City, db.GiftCard])
All environment variables you can move to define in docker or .env files as you wish, they not needed to be define in '.py', this is just for example shortness.
Load multiple CSV to DB in order by one click. Presets described that CSV-s files and in that order need to be loaded in DB.
Read the docs: Presets
Composite CSV - one file that contains data for several relative tables.
Read the docs: Composite CSV to Upload
Read the docs: Config
Init DB feature used for doing full clean up DB - it drop all tables & create them after Drop for all models in Admin Panel.
Files-samples for example project can be found here: examples/base_example/src/csv_to_upload
Read in docs: Authorization
For correct work of Admin Panel all models MUST contain at least one unique and primary_key Column (field).
This column used to identify row (one element) for Copy & Edit & Delete operations. Name of unique and primary_key column and type does not matter.
So if you define model, for example, User, you can have column user_id as unique and primary_key:
class User(db.Model):
__tablename__ = "users"
user_id = db.Column(db.String(), unique=True, primary_key=True)
Or for model 'Country' it can be 'code'
class Country(db.Model):
__tablename__ = "countries"
code = db.Column(db.String(8), unique=True, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String())
Check in docs: UI Screens