pystix - Data processing pipeline for The Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX) onboard Solar Orbiter
pystix is a software suite running on the STIX data center (url: https://datacenter.stix.i4ds.net/). Its main functions include automatic data reception, raw telemetry parsing, data decompression, creation of L1A FITS files, flare detection, coarse flare location, calibration data analysis, telemetry data estimation, data monitoring, data management, and preparation of data for web browsing.
The package relies on python3 and some extra python modules.
on Linux (Ubuntu)
sudo apt-get install python3
sudo apt install python3-pipOn windows
-
Download python3.6 executable installer
64-bit Windows: https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.6.7/python-3.6.7-amd64.exe
32-bit Windows: https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.6.7/python-3.6.7.exe
-
Install python3
When installing python, choose
customize installation,install pipandadd python path to the system environment.
(1) Install pystix pip install git+https://github.com/drhlxiao/pystix.git
(2) Installation of dependencies
```cmd
pip3 install numpy xmltodict PyQt5 pyqtchart scipy pymongo python-dateutil
pip install -e .[dev]
Usage:
./bin/parser_guiIf you have installed the package to python library path, you just need to execute:
./bin/parse_rawArguments:
Usage: parse_raw [-h] -i [INPUT] [-o OUTPUT] [--idb IDB] [--opf {tuple,dict}]
[-t {binary,ascii,xml}] [--wdb] [--db-host DB_HOST]
[--db-port DB_PORT] [--db-user DB_USER] [--db-pwd DB_PWD]
[-m COMMENT] [--SPID [SPID [SPID ...]]]
[--services [SERVICES [SERVICES ...]]] [-v VERBOSE]
[-l LOGFILE]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Required arguments:
-i [INPUT] Input raw data filename.
Optional arguments:
-o OUTPUT Output python pickle filename.
--idb IDB IDB filename (sqlite3).
--opf {tuple,dict} format to store output parameters.
-t {binary,ascii,xml}
Input file type. Three types (binary, ascii or xml)
are supported. Filename extensions will be used to detect file types if not specified.
--wdb Write decoded packets to local MongoDB.
--db-host DB_HOST MongoDB host IP.
--db-port DB_PORT MongoDB host port.
--db-user DB_USER MongoDB username.
--db-pwd DB_PWD MongoDB password.
-m COMMENT comment
--SPID [SPID [SPID ...]]
Only to parse packets of the given SPIDs.
--services [SERVICES [SERVICES ...]]
Only to parse packets of the given service types.
-v VERBOSE Logger verbose level
-l LOGFILE, --log LOGFILE
Log filenameExample:
python3 stix_parser/apps/parser.py -i <RAW_DATA_FILENAME> -o <OUTPUT> -v <Verbose level>Here are several examples.
-
Example 1
Parse a raw data file and dump the decode packets to a python pickle file
#!/usr/bin/python3
from stix_parser.core import stix_parser
parser = stix_parser.StixTCTMParser()
parser.parse_file('raw.binary', 'output.pkl')- Example 2 Parse a raw data file and print the content of the decoded packets:
#!/usr/bin/python3
from stix_parser.core import stix_parser
f=open('raw.binary','rb')
buffer=f.read()
parser = stix_parser.StixTCTMParser()
packets=parser.parse_binary(buffer)
for packet in packets:
print(packet['header'])
print(packet['parameters'])- Example 3:
Parse a hexadecimal string:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import pprint
from stix_parsr.core import stix_parser
parser = stix_parser.StixTCTMParser()
data='0d e5 c3 ce 00 1a 10 03 19 0e 80 00 87 46 6e 97 04 80 00 87 46 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00'
packets=parser.parse_hex(data)
pprint.pprint(packets)Output:
{
'header': {'APID': 1509,
'APID_pid': 94,
'PUS': 16,
'SCET': 2147518278.4319916,
'SPID': 54103,
'SSID': 4,
'TMTC': 'TM',
'TPSD': -1,
'UTC': '2068-01-19T12:51:18.431',
'category': 5,
'coarse_time': 2147518278,
'descr': 'STIX HK report - SID 4',
'destination': 14,
'fine_time': 28311,
'header_flag': 1,
'length': 17,
'packet_id': 3557,
'packet_type': 0,
'process_id': 222,
'seg_flag': 3,
'segmentation': 'stand-alone packet',
'seq_count': 974,
'service_subtype': 25,
'service_type': 3,
'unix_time': 3094203078.4319916,
'version': 0},
'parameters': [('NIX00020', 4, '', []),
('NIX00059', 2147518278, '', []),
('NIXD0059', 0, 'NotAvailable', []),
('NIXD0060', 0, 'NoSignNThrFlux', []),
('NIXD0061', 0, 'NoFlareDetect', []),
('NIXG0020', 0, '', []),
('NIX00283', 0, '', []),
('NIX00284', 0, '', []),
('NIX00063', 0, '', []),
('NIXD0064', 0,, 'False', []),
('NIXG0064', 0, '', []),
('ZZPAD032', 0, '', [])]}Each parameter has a structure as follows:
- The first column: Parameter name,
- The second column: raw value,
- The third column: engineering value, decompressed value, or an empty string
- The fourth column: an empty list, or its children if it is a repeater.
python stix_parser/apps/stix_parser_gui.pyor
stix-parser-guiif you have installed the package to python library path.
The GUI allows parsing/loading and displaying STIX packets in the following data formats/sources:
- STIX raw data
- SOC XML format
- MOC ASCII format
- packets stored in python pickle files (pkl and pklz)
- packets stored in NoSQL database MongoDB
- packets received from TSC via socket
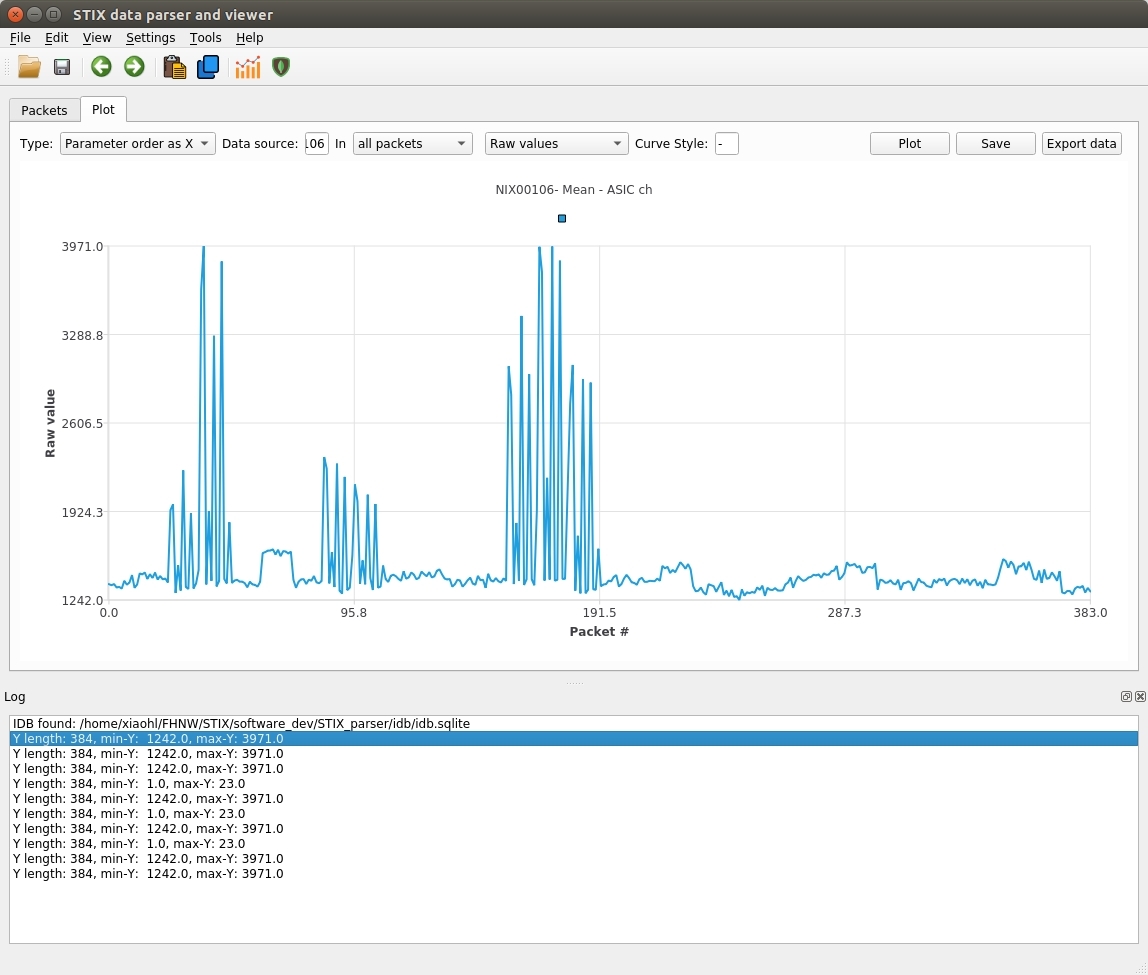
- STIX TM binary hex string copied from the clipboard The GUI also allows plotting parameters as a function of timestamp or packet number.
One could create plugins to analyze the packets displayed in the GUI. The plugin manager can be loaded by clicking "Tool->Plugins" or the plugin icon in the toolbar. Here is a plugin example:
#plugin example
import pprint
class Plugin:
def __init__(self, packets=[], current_row=0):
self.packets=packets
self.current_row=current_row
print("Plugin loaded ...")
def run(self):
# your code goes here
print('current row')
print(self.current_row)
if len(self.packets)>1:
pprint.pprint(self.packets[self.current_row])
More plugin examples are available in stix_parser/plugins/
- Install mdbtools and sqlite3
sudo apt-get install mdbtools sqlite3 - Use the script idb/mdb2sql.sh to convert mdb to sql
sh idb/mdb2sql.sh STIX_IDB.mdb > idb.sql
- Append the following lines to the end of the generated sql file
update PCF set PCF_WIDTH=16 where PCF_NAME="NIX00123";
update PCF set PCF_WIDTH=8 where PCF_NAME="ZZPAD008";
update PCF set PCF_WIDTH=16 where PCF_NAME='ZZPAD016';
update PCF set PCF_WIDTH=24 where PCF_NAME='ZZPAD024';
update PCF set PCF_WIDTH=32 where PCF_NAME='ZZPAD032';
drop table if exists IDB;
create table IDB(
creation_datetime datetime,
version varchar(64) not null
);
insert into IDB (creation_datetime, version) values (current_timestamp, '2.26.28');Please replace the string "2.26.28" with your actual IDB version.
- Create IDB sqlite3 database using the sql file
sqlite3 idb.sqlite3 < idb.sqlOne may see some errors. For example, " table Name AutoCorrect Save Failures already exists".
Those tables are not used by this parser. They can be removed from the sql script.
- Copy idb.sqlite3 to idb/
execute
python3 compile.py build_ext --inplaceThe generated *.c and the original *py files can be deleted for distribution.
- Parser daemons
nohup python3 stix/app/parser_daemon.py &It checks the directories defined in stix/core/config.py if there is a new data file every minute. If so, the file will be parsed and the decoded packets will be written to MongoDB 2) Calibration
nohup python3 stix/analysis/calibration.py &It performs calibration analysis every 10 minutes for new calibration spectrum.
-
download the latest SPICE kernel from STIX GFTS server
-
Unzip the zip file, replace the following file with the latest version stix/data/SPICE/kernels/sclk/solo_ANC_soc-sclk_xxxx_V01.tsc
-
Edit stix/core/config.py, update the tsc filename