Honeycomb
Next major version
The alpha of the next major version (v4) is released (see the changelog in the next branch). It's a complete rewrite in TypeScript with all new shiny "traversers" 😎.
I could really use your feedback about this new version, so please take a look at the readme in the next branch to see how you can start using it. Please open an issue and tell me what you like and/or don't like. Thanks! ✨
Another hex grid library made in JavaScript, heavily inspired by Red Blob Games' blog posts and code samples.
All existing JS hex grid libraries I could find are coupled with some form of view. Most often a <canvas> element or the browser DOM. I want more separation of concerns…and a new hobby project to spend countless hours on.
Features
- 🙌 Works in (modern) browsers and in Node.js.
- 📐 Create hex grids in different shapes: ▭ rectangles, △ triangles, ⬡ hexagons and ▱ parallelograms.
- 🌐 2 coordinate systems: cartesian (
xandy) and cube (q,rands). - ✨ Create your own hexes by extending the built-in hex factory.
- 🗺 Convert points to hexes and vice versa.
- ⬢ Pointy and ⬣ flat hexes.
- 🖥 Lets you decide if and how hexes are rendered.
Installation
NPM:
npm i --save honeycomb-gridYarn:
yarn add honeycomb-gridOr download the minified file from unpkg.com.
Getting started
Browser
Honeycomb works at least in recent versions of Chrome, Firefox, Edge and Safari.
<script src="honeycomb.js"></script>
<script>
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
Grid.rectangle({ width: 4, height: 4 })
</script>Node.js
const Honeycomb = require('honeycomb-grid')
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
Grid.rectangle({ width: 4, height: 4 })With ES2015 modules
import { defineGrid } from 'honeycomb-grid'
const Grid = defineGrid()
Grid.rectangle({ width: 4, height: 4 })Examples
Basic usage
Create a hex grid in 3 steps:
// 1. (optionally) create a Hex factory by extending the default:
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({
size: 30, // default: 1
orientation: 'flat' // default: 'pointy'
})
// 2. create a Grid factory that uses the Hex factory:
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
// 3a. create a grid with a "shape" method:
const grid1 = Grid.rectangle({ width: 4, height: 4 })
// [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: 0, y: 2 },
// …
// ]
// 3b. or create a grid from individual hexes/points:
const grid2 = Grid(Hex(1, 2), [3, 4], { x: 5, y: 6 })
// [
// { x: 1, y: 2 },
// { x: 3, y: 4 },
// { x: 5, y: 6 }
// ]Rendering
Honeycomb comes without the ability to render hexes to screen. Fortunately, it isn't very hard. Especially if you use a dedicated rendering library.
With PixiJS
const app = new PIXI.Application({ transparent: true })
const graphics = new PIXI.Graphics()
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 5 })
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
document.body.appendChild(app.view)
// set a line style of 1px wide and color #999
graphics.lineStyle(1, 0x999999)
// render 10,000 hexes
Grid.rectangle({ width: 100, height: 100 }).forEach(hex => {
const point = hex.toPoint()
// add the hex's position to each of its corner points
const corners = hex.corners().map(corner => corner.add(point))
// separate the first from the other corners
const [firstCorner, ...otherCorners] = corners
// move the "pen" to the first corner
graphics.moveTo(firstCorner.x, firstCorner.y)
// draw lines to the other corners
otherCorners.forEach(({ x, y }) => graphics.lineTo(x, y))
// finish at the first corner
graphics.lineTo(firstCorner.x, firstCorner.y)
app.stage.addChild(graphics)
})With SVG.js
const draw = SVG().addTo('body').size('100%', '100%')
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 5 })
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
// get the corners of a hex (they're the same for all hexes created with the same Hex factory)
const corners = Hex().corners()
// an SVG symbol can be reused
const hexSymbol = draw.symbol()
// map the corners' positions to a string and create a polygon
.polygon(corners.map(({ x, y }) => `${x},${y}`))
.fill('none')
.stroke({ width: 1, color: '#999' })
// render 10,000 hexes
Grid.rectangle({ width: 100, height: 100 }).forEach(hex => {
const { x, y } = hex.toPoint()
// use hexSymbol and set its position for each hex
draw.use(hexSymbol).translate(x, y)
})Grids extend Array.prototype
Most properties/methods of grids are the same as their Array counterpart:
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 4, height: 4 })
grid.length // 16
grid.pop() // { x: 3, y: 3 }
grid.length // 15
grid[4] // { x: 1, y: 0 }Some Grid methods are augmented. For example: Array#includes always returns false when passed an object literal because it uses strict equality internally. Grid#includes only accepts object literals (in the form of points):
const array = [{ x: 1, y: 0 }]
array.includes({ x: 1, y: 0 }) // false
const grid = Grid(Hex(1, 0))
grid.includes({ x: 1, y: 0 }) // trueGrid methods that mutate
Methods that mutate the grid in-place (Grid#push, Grid#splice and Grid#unshift) only accept valid hexes to prevent "grid corruption" 👮.
const grid = Grid() // []
// this silently fails:
grid.push('invalid hex') // 0 <- the grid's length, which remains 0
grid.includes('invalid hex') // falseKeep in mind that methods that return a new grid (e.g. Grid#map) can create grids with invalid hexes:
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 4, height: 4 })
const newGrid = grid.map(hex => 'invalid hex')
// [
// 'invalid hex',
// 'invalid hex',
// 'invalid hex',
// …
// ]Be careful with bracket notation
It's possible to add an invalid hex to a grid by using bracket notation:
const grid = Grid(Hex())
grid[0] // { x: 0, y: 0 }
grid[0] = 'invalid hex'
grid[0] // 'invalid hex' ⚠️Use Grid#get and Grid#set instead:
const grid = Grid(Hex())
grid.get(0) // { x: 0, y: 0 }
grid.set(0, 'invalid hex')
grid.get(0) // { x: 0, y: 0 } <- invalid hex is ignored
// Grid#set() also accepts a point:
grid.set({ x: 0, y: 0 }, Hex(-1, 3))
// …as does Grid#get():
grid.get([-1, 3]) // { x: -1, y: 3 }Point → Hex
Translating a screen point (pixel) to the corresponding hex in a grid is possible with Grid.pointToHex().
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 30 })
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 10, height: 10 })
document.addEventListener('click', ({ offsetX, offsetY }) => {
// convert point to hex (coordinates)
const hexCoordinates = Grid.pointToHex(offsetX, offsetY)
// get the actual hex from the grid
console.log(grid.get(hexCoordinates))
})See a more elaborate example in JSFiddle.
Grid shapes
Honeycomb offers 4 shape methods: rectangle, triangle, hexagon and parallelogram. Try them out in JSFiddle.
Coordinate systems
The standard coordinate system is a cartesian one. It's intuitive and easy to reason about. A lot of methods internally use a "cube" coordinate system. See this redblobgames.com blog post for an explanation between the two (he calls the cartesian system "offset coordinates").
Hexes have getters for each of the cube coordinates q, r and s:
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
const hex = Hex(3, 4)
hex.q // 1
hex.r // 4
hex.s // -5
hex.cartesian() // { x: 3, y: 4 }
hex.cube() // { q: 1, r: 4, s: -5 }There are methods for converting between cartesian and cube:
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
const hex = Hex()
hex.toCube({ x: 3, y: 4 }) // { q: 1, r: 4, s: -5 }
// Hex#toCartesian doesn't require the s coordinate:
hex.toCartesian({ q: 1, r: 4 }) // { x: 3, y: 4 }These methods always require coordinates to be passed and don't work on a hex instance, even though they're instance methods. This will be fixed in a future release 🙃
Hexes can also be created from cube coordinates:
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
Hex({ q: 1, r: 4, s: -5 }) // { x: 3, y: 4 }Odd or even hex offsets
In a grid with pointy hexes, each row is offsetted half a hex relative to the previous row. In grids with flat hexes, this applies to the columns. Redblobgames.com has a visual example.
Set the offset property to 1 or -1 (default) to control whether the even or odd rows/columns are offsetted. Try it out in JSFiddle.
(De)serialization
Since version 3 it's possible to properly serialize and deserialize grids (including their Hex factory). This can be done using JSON.stringify() and JSON.parse():
const hexPrototype = { size: 10, custom: 'some value' }
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex(hexPrototype)
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 2, height: 2 })
const serializedGrid = JSON.stringify(grid)
// [{"x":0,"y":0},{"x":1,"y":0},{"x":0,"y":1},{"x":1,"y":1}]
const deserializedGrid = JSON.parse(serializedGrid)
// [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 1, y: 0 },
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: 1, y: 1 }
// ]You can define a toJSON() method on your Hex prototype to control how a grid is serialized:
const hexPrototype = {
toJSON() { return [this.x, this.y] }
}
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex(hexPrototype)
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 2, height: 2 })
const serializedGrid = JSON.stringify(grid)
// [[0,0],[1,0],[0,1],[1,1]]Any Hex factory has a (static) toJSON() method that makes it easy to get a Hex's prototype:
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({
size: 10,
custom: 'some value'
})
Hex.toJSON() // {size: 10, custom: "some value"}
// Hex.toJSON() is called automatically when passed to JSON.stringify():
JSON.stringify(Hex) // {"size":10,"custom":"some value"}API
Table of Contents
- Honeycomb
- Grid
- Hex
- Point
- Instances
- Constants
- Other
Honeycomb
Type: Object
defineGrid
This function can be used to create Grid factories by passing it a Hex factory.
Parameters
HexHex A Hex factory. If nothing is passed, the default Hex factory is used by callingHoneycomb.extendHex()internally. (optional, defaultHoneycomb.extendHex())
Examples
// create a Grid factory that uses the default Hex Factory:
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const hex = Grid.Hex()
hex.size // { xRadius: 1, yRadius: 1 }
// create your own Hex factory
const CustomHex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 10, custom: '🤓' })
// …and pass it to defineGrid() to create a Grid factory that produces your custom hexes
const CustomGrid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(CustomHex)
const customHex = CustomGrid.Hex()
customHex.size // { xRadius: 10, yRadius: 10 }
customHex.custom // 🤓Returns Grid A Grid factory.
extendHex
This function can be used to create custom hexes by extending the default Hex prototype.
All properties of the object passed to extendHex() will be added to the prototype of the resulting Hex factory.
To add properties to individual hexes (instances), pass them to the Hex factory.
Parameters
prototypeObject An object that's used as the prototype for all hexes in a grid. Warning: properties in this object will overwrite properties with the same name in the default prototype. (optional, default{})
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({
size: 50,
orientation: 'flat',
customProperty: `I'm custom 😃`,
customMethod() {
return `${this.customProperty} and called from a custom method 😎`
}
})
const hex = Hex(5, -1)
hex.coordinates() // { x: 5, y: -1 }
// size is normalized to an object containing an x radius and y radius:
hex.size // { xRadius: 50, yRadius: 50 }
hex.customProperty // I'm custom 😃
hex.customMethod() // I'm custom 😃 and called from a custom method 😎
// every hex created with Hex() shares these properties:
const hex2 = Hex(3, 0)
hex2.size // { xRadius: 50, yRadius: 50 }
hex2.customProperty // I'm custom 😃
// to set properties on individual hexes, pass them to Hex():
const hex3 = Hex(-2, -1, { instanceProperty: `I'm a unique snowflake 😌` })
hex3.instanceProperty // I'm a unique snowflake 😌Returns Hex A function to produce hexes that are all linked to the same prototype.
Point
See Point.
Grid
A function to create hex grids and perform various operations on them.
A Grid factory has several static methods that return grids of hexes in a certain shape. It can also be called with 1 or more points/hexes or an array of points/hexes to create a grid instance.
A grid extends Array.prototype, with some methods overwritten and some new methods added.
Parameters
points...point? An array of points/hexes or separate arguments that are points/hexes.
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
// the Hex factory used by the Grid to produce hexes is available as a property
const Hex = Grid.Hex
Grid(Hex(3, -1), Hex(2, 0)) // [{ x: 3, y: -1 }, { x: 2, y: 0 }]
Grid([Hex(3, -1), Hex(2, 0)]) // [{ x: 3, y: -1 }, { x: 2, y: 0 }]
// it also accepts points
Grid({ x: 3, y: -1 }, [2, 0]) // [{ x: 3, y: -1 }, { x: 2, y: 0 }]
Grid([{ x: 3, y: -1 }, [2, 0]]) // [{ x: 3, y: -1 }, { x: 2, y: 0 }]
// clone a grid:
const grid = Grid(Hex(), Hex(1), Hex(2))
const clonedGrid = Grid(grid) // [{ x: 0, y: 0 }, { x: 1, y: 1 }, { x: 2, y: 2 }]
grid === clonedGrid // falseReturns grid A grid instance containing only valid hexes.
fill
- Throws TypeError It makes no sense for a grid to fill it with arbitrary values, because it should only contain valid hexes.
Returns TypeError An error.
get
Get a hex from a grid.
Parameters
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 2, height: 2 })
grid.get(0) // { x: 0, y: 0 }
grid.get(Hex(0, 1)) // { x: 0, y: 1 }
grid.get({ x: 0, y: 1 }) // { x: 0, y: 1 }
grid.get([0, 1]) // { x: 0, y: 1 }
grid.get(42) // undefined
grid.get(Hex(6, -2)) // undefinedReturns hex The found hex or undefined.
hexesBetween
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Parameters
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 4, height: 4 })
grid.hexesBetween(Hex(), Hex(3)) // [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: 1, y: 1 },
// { x: 2, y: 2 },
// { x: 3, y: 2 },
// { x: 3, y: 3 },
// ]Returns Array<hex> Array (not a grid) of hexes in a straight line from firstHex to (and including) lastHex.
hexesInRange
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Parameters
centerHexhex A hex to get surrounding hexes from.rangenumber The range (in hexes) surrounding the center hex. (optional, default0)includeCenterHexboolean Whether to include the center hex in the result (optional, defaulttrue)
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ orientation: 'pointy' })
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 5, height: 5 })
grid.hexesInRange(Hex(2, 2), 2) // [
// { x: 0, y: 2 },
// { x: 0, y: 3 },
// { x: 1, y: 4 },
// ...
// { x: 3, y: 0 },
// { x: 3, y: 1 },
// { x: 4, y: 2 }
// ]
// only returns hexes that exist in the grid:
grid.hexesInRange(Hex(0, 0), 1) // [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: 1, y: 0 }
// ]
// exclude center hex:
grid.hexesInRange(Hex(2, 2), 1, false) // [
// { x: 1, y: 2 },
// { x: 1, y: 3 },
// { x: 1, y: 1 },
// { x: 2, y: 3 },
// { x: 3, y: 2 }
// ]- Throws Error When no valid hex is passed.
Returns Array<hex> An array with all hexes surrounding the passed center hex. Only hexes that are present in the grid are returned.
includes
Identical to Array#includes, but searches the passed hex (which can also be a point.
Parameters
pointpoint The coordinates to search for.fromIndexnumber Optional index to start searching. (optional, default0)
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid(Hex(0)) // [ { x: 0, y: 0 } ]
grid.includes(Hex(0)) // true
grid.includes([0, 0]) // true
grid.includes(Hex(0), 1) // false
grid.includes(Hex(5, 7)) // falseReturns boolean Whether the hex is included in the grid.
indexOf
Identical to Array#indexOf, but accepts a point and internally uses Hex#equals as a comparator.
Parameters
pointpoint The coordinates to search for.fromIndexnumber Optional index to start searching. If negative, it is taken as the offset from the end of the grid. (optional, default0)
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid(Hex(0), Hex(1), Hex(0))
// [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 1, y: 1 },
// { x: 0, y: 0 }
// ]
grid.indexOf(Hex(0)) // 0
grid.indexOf([0, 0]) // 0
grid.indexOf(Hex(0), 1) // 2
grid.indexOf(Hex(5, 7)) // -1Returns number The index of the found hex (first from the left) or -1 if the hex wasn't found.
lastIndexOf
Identical to Array#lastIndexOf, but accepts a point and internally uses Hex#equals as a comparator.
Because all hexes will have different coordinates in most grids, this method behaves the same as Grid#indexOf. This method might have a slightly better performance if you know the search hex is at the end of the grid.
Parameters
pointpoint The coordinates to search for.fromIndexnumber Optional index to start searching back from. If negative, it is taken as the offset from the end of the grid. (optional, defaultlength-1)
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid(Hex(0), Hex(1), Hex(0))
// [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 1, y: 1 },
// { x: 0, y: 0 }
// ]
grid.lastIndexOf(Hex(0)) // 2
grid.lastIndexOf([0, 0]) // 2
grid.lastIndexOf(Hex(0), 1) // 0
grid.lastIndexOf(Hex(5, 7)) // -1Returns number The last index of the found hex or -1 if the hex wasn't found.
neighborsOf
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Parameters
hexhex A hex to get 1 or more neighbors from.directions(Array<(COMPASS_DIRECTION | number)> | COMPASS_DIRECTION | number | all) 1 or more directions. Either (an array of) compass directions or numbers or the string'all'. (optional, defaultall)diagonalboolean Whether to get the diagonal neighbor. See redblobgames.com. (optional, defaultfalse)
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ orientation: 'pointy' })
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
// conveniently creates a grid consisting of a hex surrounded by 6 hexes:
const grid = Grid.hexagon({ radius: 1 })
// all neighbors:
grid.neighborsOf(Hex()) // [
// { x: 1, y: 0 },
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: -1, y: 1 },
// { x: -1, y: 0 },
// { x: -1, y: -1 },
// { x: 0, y: -1 },
// ]
// specific neighbor:
grid.neighborsOf(Hex(), 'NW') // [{ x: -1, y: -1 }]
grid.neighborsOf(Hex(), 4) // [{ x: -1, y: -1 }]
// multiple neighbors:
grid.neighborsOf(Hex(), ['SE', 'SW']) // [
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: -1, y: 1 }
// ]
grid.neighborsOf(Hex(), [1, 2]) // [
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: -1, y: 1 }
// ]
// diagonal neighbor:
grid.neighborsOf(Hex(-1, 0), 'E', true) // [{ x: 0, y: -1 }]
// returns undefined for hexes that aren't present in the grid:
grid.neighborsOf(Hex(-1, -1), 'NW') // [undefined]Returns Array<hex> An array with the neighboring hex for each queried direction or undefined if the hex doesn't exist in the grid.
pointHeight
Returns number The heigth of the grid in points/pixels.
pointWidth
Returns number The width of the grid in points/pixels.
push
Identical to Array#push, but filters out any passed invalid hexes.
Parameters
hexes...hex? Hexes to add to the end of the grid. Invalid hexes are ignored.
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid(Hex(0)) // [{ x: 0, y: 0 }]
grid.push(Hex(1)) // 2
grid // [{ x: 0, y: 0 }, { x: 1, y: 1 }]
grid.push('invalid') // 2
grid // [{ x: 0, y: 0 }, { x: 1, y: 1 }]Returns number The new length of the grid.
set
Replace a hex with another hex. This is a safe alternative to using bracket notation (grid[0] = 'invalid').
If the target hex isn't present in the grid, the new hex is added (using Grid#push) to the grid. If the new hex is invalid, nothing changes.
Parameters
keyOrPoint(number | point) The coordinates of the hex that must be replaced.newHexhex The replacing hex.
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid(Hex(0, 0)) // [ { x: 0, y: 0 } ]
// replace a hex:
grid.set(0, Hex(1, 1))
grid // [ { x: 1, y: 1 } ]
// the target hex can also be a point:
grid.set([1, 1], Hex(2, 2))
grid // [ { x: 2, y: 2 } ]
// invalid replace values are ignored:
grid.set(0, 'invalid')
grid // [ { x: 2, y: 2 } ]
// when the target hex isn't present in the grid, the replacing hex is added instead:
grid.set({ x: 9, y: 9 }, Hex(3, 3))
grid // [ { x: 2, y: 2 }, { x: 3, y: 3 } ]Returns grid Itself.
splice
Identical to Array#splice, but filters out any passed invalid hexes.
Parameters
startnumber Index at which to start changing the grid.deleteCountnumber Amount of hexes to delete. (optional, defaultlength-start)hexes...hex The hexes to add to the grid, beginning at thestart. (optional, default[])
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid.rectangle({ width: 2, height: 1 })
// [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 1, y: 0 },
// { x: 0, y: 1 },
// { x: 1, y: 1 }
// ]
grid.splice(2) // [{ x: 0, y: 1 }, { x: 1, y: 1 }] <- deleted hexes
grid // [{ x: 0, y: 0 }, { x: 1, y: 0 }] <- leftover hexes
grid.splice(2, 1) // [{ x: 0, y: 1 }]
grid // [{ x: 0, y: 0 }, { x: 1, y: 0 }, { x: 1, y: 1 }]
grid.splice(2, 1, Hex(2)) // [{ x: 0, y: 1 }]
grid
// [
// { x: 0, y: 0 },
// { x: 1, y: 0 },
// { x: 2, y: 2 },
// { x: 1, y: 1 }
// ]Returns Array<hex> A grid with the deleted hexes (if any).
unshift
Identical to Array#unshift, but filters out any passed invalid hexes.
Parameters
hexes...hex? Hexes to add to the start of the grid. Invalid hexes are ignored.
Examples
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid()
const Hex = Grid.Hex
const grid = Grid(Hex(0)) // [{ x: 0, y: 0 }]
grid.unshift(Hex(1)) // 2
grid // [{ x: 1, y: 1 }, { x: 0, y: 0 }]
grid.unshift('invalid') // 2
grid // [{ x: 1, y: 1 }, { x: 0, y: 0 }]Returns number The new length of the grid.
Hex
The Hex factory the Grid factory was created with.
hexagon
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Creates a grid in the shape of a hexagon ⬡.
Parameters
optionsObject An options object.
Returns grid Grid of hexes in a hexagon arrangement.
isValidHex
Parameters
valueany Any value.
Returns boolean Whether the passed value is a valid hex.
parallelogram
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Creates a grid in the shape of a parallelogram ▱.
Parameters
optionsObject An options object.options.widthnumber The width (in hexes).options.heightnumber The height (in hexes).options.starthex The start hex. (optional, defaultHex(0))options.direction(1|3|5) The direction (from the start hex) in which to create the shape. Each direction corresponds to a different arrangement of hexes. (optional, default1)options.onCreateonCreate Callback that's called for each hex. Defaults to a no-op. (optional, defaultno-op)
Returns grid Grid of hexes in a parallelogram arrangement.
pointToHex
- **See: Hex#fromPoint **
Converts the passed point to a hex. Internally calls Hex#fromPoint.
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 50 })
const Grid = Honeycomb.defineGrid(Hex)
const Point = Honeycomb.Point
Grid.pointToHex(Point(120, 280)) // { x: 0, y: 3 }
Grid.pointToHex(120, 280) // { x: 0, y: 3 }
Grid.pointToHex({ x: 120, y: 280 }) // { x: 0, y: 3 }
Grid.pointToHex([ 120, 280 ]) // { x: 0, y: 3 }Returns hex A hex (with rounded coordinates) that contains the passed point.
rectangle
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Creates a grid in the shape of a rectangle ▭.
Parameters
optionsObject An options object.options.widthnumber The width (in hexes).options.heightnumber The height (in hexes).options.starthex The start hex. (optional, defaultHex(0))options.direction(COMPASS_DIRECTION | number) The direction (from the start hex) in which to create the shape. Defaults to0(E) for pointy hexes and1(S) for flat hexes. Each direction corresponds to a different arrangement of hexes. (optional, defaultE|S)options.onCreateonCreate Callback that's called for each hex. Defaults to a no-op. (optional, defaultno-op)
Returns grid Grid of hexes in a rectangular arrangement.
ring
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Creates a grid in the shape of a ring.
Parameters
optionsObject An options object.
Returns grid Grid of hexes in a ring arrangement.
spiral
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Creates a grid in the shape of a spiral starting from the center outward. The result is the same as a hexagon, but the order of hexes is different.
Parameters
optionsObject An options object.
Returns grid Grid of hexes in a spiral arrangement.
triangle
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Creates a grid in the shape of a (equilateral) triangle △.
Parameters
optionsObject An options object.options.sizenumber The side length (in hexes).options.starthex The start hex. Note: it's not the first hex, but rather a hex relative to the triangle. (optional, defaultHex(0))options.direction(1|5) The direction in which to create the shape. Each direction corresponds to a different arrangement of hexes. In this case a triangle pointing up (direction: 1) or down (direction: 5) (with pointy hexes) or right (direction: 1) or left (direction: 5) (with flat hexes). Each direction corresponds to a different arrangement of hexes. (optional, default1)options.onCreateonCreate Callback that's called for each hex. Defaults to a no-op. (optional, defaultno-op)
Returns grid Grid of hexes in a triangle arrangement.
Hex
Factory function to create hexes. Use Honeycomb.extendHex to create a Hex factory.
Parameters
xOrProps(number | Object | Array<number>)? The x coordinate, or an object containing any of the cartesian (xandy) coordinates and optional custom properties, or an object containing all of the cube (q,r, ands) coordinates and optional custom properties, or an array containing any of the cartesian (x and y) coordinates.ynumber? The y coordinate.customPropsobject Any custom properties. The coordinates are merged into this object, ignoring any coordinates present incustomProps. (optional, default{})
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
// passing numbers:
Hex() // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Hex(1) // { x: 1, y: 1 }
Hex(1, 2) // { x: 1, y: 2 }
// passing an object with cartesian coordinates:
Hex({}) // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Hex({ x: 1 }) // { x: 1, y: 1 }
Hex({ y: 2 }) // { x: 2, y: 2 }
Hex({ x: 1, y: 2 }) // { x: 1, y: 2 }
// passing an object with cube coordinates:
Hex({ q: 1, r: 2, s: -3 }) // { x: 2, y: 2 }
Hex({ q: 1 }) // throws an error because of missing cube coordinates
// passing an array:
Hex([]) // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Hex([1]) // { x: 1, y: 1 }
Hex([1, 2]) // { x: 1, y: 2 }
// custom properties:
Hex(1, 2, { a: 3 }) // { a: 3, x: 1, y: 2 }
Hex({ x: 1, y: 2, a: 3 }) // { a: 3, x: 1, y: 2 }
// cloning a hex:
const someHex = Hex(4, -2) // { x: 4, y: -2 }
const clone = Hex(someHex) // { x: 4, y: -2 }
someHex === clone // falseReturns hex A hex. It always contains only the cartesian (x and y) coordinates and any custom properties.
add
Parameters
pointpoint The hex (or point) that will be added to the current.
Returns hex A new hex where the passed hex's coordinates are added to the current. Any custom properties are copied.
cartesian
Alias for Hex#coordinates.
cartesianToCube
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
const Point = Honeycomb.Point
Hex().cartesianToCube(Point(4, -2)) // { q: 5, r: -2, s: -3 }
Hex().cartesianToCube(4, -2) // { q: 5, r: -2, s: -3 }
Hex().cartesianToCube({ x: 4, y: -2 }) // { q: 5, r: -2, s: -3 }
Hex().cartesianToCube([4, -2]) // { q: 5, r: -2, s: -3 }Returns Object The hex's cube q, r and s coordinates.
center
Examples
const Hex1 = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 10 })
Hex1().center() // { x: 8.660254037844386, y: 10 }
const Hex2 = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 10, origin: [5, 5] })
Hex2().center() // { x: 3.6602540378443855, y: 5 }Returns point Point relative to the hex's origin.
Note that the default origin is the top left corner, so the default center is
{ x: hexWidth / 2, y: hexHeight / 2 }.
coordinates
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
Hex().coordinates() // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Hex(1, 2).coordinates() // { x: 1, y: 2 }Returns Object The hex's cartesian x and y coordinates.
corners
Examples
// a hex's origin defaults to its top left corner (as if it's a rectangle)
const Hex1 = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 30 })
Hex1().corners() // [
// { x: 51.96152422706631, y: 15 },
// { x: 51.96152422706631, y: 45 },
// { x: 25.980762113533157, y: 60 },
// { x: 0, y: 45 },
// { x: 0, y: 15 },
// { x: 25.980762113533157, y: 0 }
// ]
// set the origin to a hex's center
const Hex2 = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 30, origin: [25.980762113533157, 30] })
Hex2().corners() // [
// { x: 25.980762113533157, y: -15 },
// { x: 25.980762113533157, y: 15 },
// { x: 0, y: 30 },
// { x: -25.980762113533157, y: 15 },
// { x: -25.980762113533157, y: -15 },
// { x: 0, y: -30 }
// ]Returns Array<point> Array of corner points relative to the hex's origin. Starting at the top right corner for pointy hexes and the right corner for flat hexes.
cube
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
Hex().cube() // { q: 0, r: 0, s: 0 }
Hex(1, 2).cube() // { q: 0, r: 2, s: -2 }Returns Object The hex's cube q, r and s coordinates.
cubeToCartesian
Parameters
cubeCoordinatesObject At least theqandrcube coordinates.
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
Hex().cubeToCartesian({ q: 1, r: 2, s: -3 }) // { x: 2, y: 2 }
// the `s` coordinate isn't required:
Hex().cubeToCartesian({ q: -3, r: 5 }) // { x: -1, y: 5 }Returns Object The hex's cartesian x and y coordinates.
distance
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Parameters
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
Hex().distance(Hex(1, 0)) // 1
Hex(-2, -2).distance(Hex(4, 1)) // 8Returns number The amount of hexes from the current to (and excluding) the last hex.
equals
Parameters
pointpoint The hex (or point) whose coordinates will be compared against the current hex.
Returns boolean Whether the coordinates of the current and the passed point are equal.
fromPoint
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Returns a hex from the passed point.
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 50 })
const Point = Honeycomb.Point
const hex = Hex()
hex.fromPoint(Point(120, 280)) // { x: 0, y: 3 }
hex.fromPoint(120, 280) // { x: 0, y: 3 }
hex.fromPoint({ x: 120, y: 280 }) // { x: 0, y: 3 }
hex.fromPoint([ 120, 280 ]) // { x: 0, y: 3 }Returns hex A hex (with rounded coordinates) that contains the passed point.
height
Returns number The (vertical) height of a hex.
isFlat
Returns boolean Whether hexes have a flat ⬣ orientation.
isPointy
Returns boolean Whether hexes have a pointy ⬢ orientation.
lerp
Returns an interpolation between the current hex and the passed hex for a t between 0 and 1.
More info on wikipedia.
Parameters
Returns hex A new hex (likely with floating point coordinates). Any custom properties are copied.
nudge
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Returns hex A new hex with a tiny offset from the current hex. Useful for interpolating in a consistent direction.
offset
- **See: OFFSET **
Used to calculate the coordinates of rows for pointy hexes and columns for flat hexes.
Defaults to -1 (odd offset).
See OFFSET for details.
See redblobgames.com why this is needed.
Type: number
orientation
Either ⬢ pointy or ⬣ flat. Defaults to pointy.
Type: string
origin
Distance from a hex's top left corner (as if it were a rectange). Defaults to Point(0).
Can be anything the Honeycomb.Point factory accepts.
When a hex is converted to a point, it is converted to this origin.
Type: point
q
Getter for q cube coordinate. Calls Hex#cartesianToCube internally.
Type: number
r
Getter for r cube coordinate. Calls Hex#cartesianToCube internally.
Type: number
round
- **See: redblobgames.com **
Rounds the current floating point hex coordinates to their nearest integer hex coordinates.
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
Hex(3.1415, 0.5).round() // { x: 3, y: 1 }Returns hex A new hex with rounded coordinates. Any custom properties are copied.
s
Getter for s cube coordinate. Calls Hex#cartesianToCube internally.
Type: number
set
Parameters
coordinatesany Same parameters as the Hex factory.
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
const hex = Hex({ x: 1, y: 2, a: 3, b: 4 }) // { a: 3, b: 4, x: 1, y: 2 }
const updatedHex = hex.set({ x: 0, y: -1, b: 5 }) // { a: 3, b: 5, x: 0, y: -1 }
hex === updatedHex // true: hex is updated in-placeReturns hex Itself with the passed parameters merged into it.
size
A hex's size that can be set as:
- an object with
widthandheight, representing the total width and height of the hex - an object with
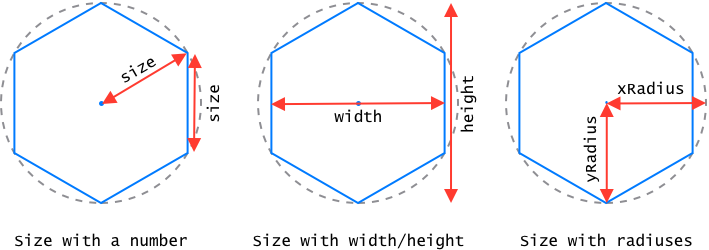
xRadiusandyRadius. This can be visualized as if the hex was enclosed in an ellipse.xRadiuswould be the distance from the center to the left or right of the ellipse (semi-major axis) andyRadiuswould be the distance from the center to the top or bottom of the ellipse (semi-minor axis). - a number, represening the length of each side and the distance from the center to any corner of the hex (which are the same in regular hexagons).
When setting size with a number the hex will be regular. When setting size with an object it's possible to "stretch" a hex; having a (very) different width and height.
Defaults to { xRadius: 1, yRadius: 1 }.
Type: ({width: number, height: number} | {xRadius: number, yRadius: number} | number)
subtract
Parameters
pointpoint The hex (or point) that will be subtracted from the current.
Returns hex A new hex where the passed hex's coordinates are subtracted from the current. Any custom properties are copied.
toCartesian
Alias for Hex#cubeToCartesian.
toCube
Alias for Hex#cartesianToCube.
toPoint
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex({ size: 30 })
Hex().toPoint() // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Hex(-2, -5).toPoint() // { x: -77.94228634059947, y: -225 }Returns point The hex's origin point.
toString
Returns string A string representation of the hex.
width
Returns number The (horizontal) width of a hex.
thirdCoordinate
Calculates the third cube coordinate from the other two. The sum of all three coordinates must be 0.
Parameters
firstCoordinatenumber The first other cube coordinate.secondCoordinatenumber The second other cube coordinate.
Examples
const Hex = Honeycomb.extendHex()
Hex.thirdCoordinate(3, -2) // -1Returns number The third cube coordinate.
Point
Factory function for creating two-dimensional points.
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Examples
const Point = Honeycomb.Point
Point() // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Point(1) // { x: 1, y: 1 }
Point(1, 2) // { x: 1, y: 2 }
Point([]) // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Point([1]) // { x: 1, y: 1 }
Point([1, 2]) // { x: 1, y: 2 }
Point({}) // { x: 0, y: 0 }
Point({ x: 1 }) // { x: 1, y: 1 }
Point({ y: 2 }) // { x: 2, y: 2 }
Point({ x: 1, y: 2 }) // { x: 1, y: 2 }Returns point A point.
add
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Returns point The sum of the passed point's coordinates to the current point's.
divide
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Returns point The division of the current point's coordinates and the passed point's.
multiply
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Returns point The multiplication of the passed point's coordinates and the current point's.
subtract
Parameters
pointOrX(number | Array<number> | point)? The x coordinate or an array with 2 numbers or an object with anxandycoordinate.ynumber? The y coordinate.
Returns point The difference between the passed point's coordinates and the current point's.
Instances
grid
Extends Array
Type: Object
Properties
lengthnumber Amount of hexes in the grid.
hex
An object with x and y properties and several methods in its prototype chain, created by a Hex factory.
Type: Object
Properties
point
An object with just an x and a y property.
Create your own:
const point = { x: 1, y: 2 }Or use the included Point factory:
const point = Honeycomb.Point(1, 2)Type: Object
Properties
Constants
OFFSET
- **See: redblobgames.com **
How rows/columns of hexes are placed relative to each other.
An even offset:
- places even rows of pointy hexes half a hex right of the odd rows;
- places even columns of flat hexes half a hex down of the odd rows;
An odd offset:
- places odd rows of pointy hexes half a hex right of the even rows;
- places odd columns of flat hexes half a hex down of the even rows;
Type: number
Properties
COMPASS_DIRECTION
There's an (approximate) compass direction for each side of a hex. The right side of a pointy hex has the east ('E') compass direction.
The bottom right side the southeast ('SE') direction, etc. This also means that pointy hexes don't have a north and south compass direction
and flat hexes don't have a west and east compass direction.
Number directions map to a side of a hex. A pointy hex's right side is 0, its bottom right side 1, its bottom left side 2, etc.
Number directions of flat hexes start at their bottom right side (0), their bottom side is 1, etc.
Type: COMPASS_DIRECTION
Properties
ECOMPASS_DIRECTION → eastSECOMPASS_DIRECTION ↘ southeastSCOMPASS_DIRECTION ↓ southSWCOMPASS_DIRECTION ↙ southwestWCOMPASS_DIRECTION ← westNWCOMPASS_DIRECTION ↖ northwestNCOMPASS_DIRECTION ↑ northNECOMPASS_DIRECTION ↗ northeast
Other
onCreate
Callback of a Grid shape method. Gets called for each hex that's about to be added to the grid.
Type: Function
Parameters
hexhex The freshly created hex, just before it's added to the grid.gridgrid The grid (for as far as it's created).
Returns void Nothing.
Backlog
🐛 Bugs
🚀 Features
- Add src to package and point
moduleto it? Also pointmainto unminified version by default? Also: addbrowserproperty to package.json? See jimp for an example of a library that's used on the server and the browser. - Hex methods that do nothing with a hex's coordinates should be static (e.g.
cubeToCartesian,isPointy,width)? Hex.cornersshould return points relative toHex.origin(likeHex#cornersdoes now) andHex#cornersshould return points relative to the hex (so it's not needed to add the hex's point to them).- Make some Grid instance methods also Grid static methods and vice versa?
- Make some methods getters (e.g.
Hex#width)? - Maybe make entities immutable?
- Add logger that "renders" a grid using
console.log. - Overwrite
Grid#sortso it can sort by 1 or more dimensions, ascending/descending (and also accepts a custom comparator)? - Add
Grid.union,Grid.subtract,Grid.intersectandGrid.difference(or maybe as prototype methods?). More info. - Shiny github.io pages 😎
- Maybe
Honeycomb.defineGridshould accept a prototype too (as a second parameter). - Maybe
Honeycombshould (also) be a function that accepts a hex prototype and returns a Grid factory? - Investigate how instance properties are set vs prototype properties. When creating a custom hex it should be possible to set properties that are copied when creating new hexes and properties that only exist in the prototype. Similar to how stampit solves this.
🛠 Refactorings
- Rewrite in typescript and use classes internally?
- Don't use
thisat all and just inject a context. Functional programming yo 🤓.