A high-throughput CBIR system for very large image collections
- Deep hierarchical index construction, built top-down
- Approximate k-NN search
- Defaults to a single cluster but supports search-expansion as a run-time setting
- High-Throughput search
- Achieved by batching hundreds or thousands of queries into a single search
- End-to-end CBIR search engine
- Takes images (text file with paths) as input and prints out text-based ranked results (with paths to result images).
This version of DeCP does not have a built-in interface. We recomend using this as a back-end for the web-based inteface called DeCP-Live available here or to download the the ready-to-go virtual machine with both DeCP and DeCP-Live pre-installed, available here.
- DeCP-Live provides a web-interface where a search batch can be created and the results browsed an visualized.
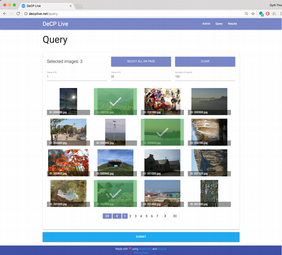
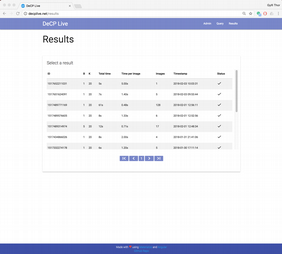
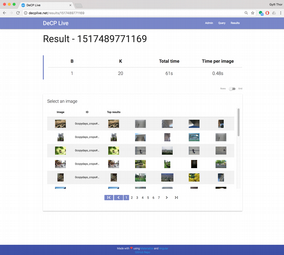
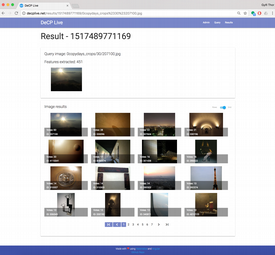
The virtual machine is installed into Oracle's VirtualBox.
- Google drive link to VM (it is a ~7GB .zip file).
- Login info for VM is; username: decp and password: decplive
- The VM is configured to nat ports to the host and thus you can access the DeCP-Live web-interface by opening your favorite browser and navigate to http://localhost:9080 once the VM is up and running.
- To use the search engine you will however need to log in and start it manually (see ~/README file in VM).
The DeCP engine uses a custom syntax for its input and output text files (the batch-query, batch-result and image results). All files have in common a header line that represents colon separated parameters. All other lines of the files are paths to files, either images or other result files.
-
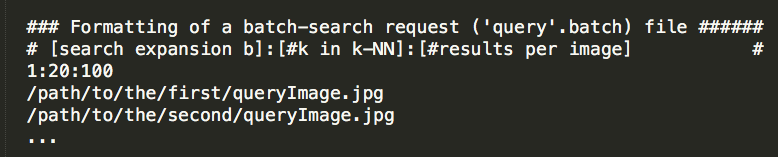
Query ("query".batch)
-
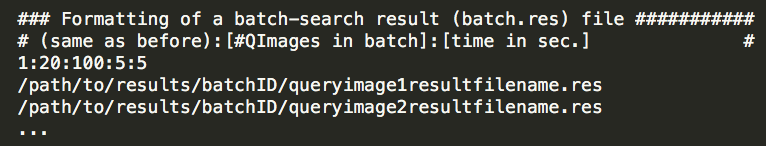
Batch result (batch.res)
- For each batch a specific folder (directory) is created named after the "query".batch. In this folder a "batch.res" file is created that holds info on the batch search and links result files for each image in the batch.
- The fields of the header line in "batch.res" is "b : k : m : t", where b is the search expansion factor; k is the size of the k-nearest neighborhood used; m is the number of result images to keep for each query image; and t is the total time the search of this batch took in seconds.
- The other n-lines are paths to the result-file for each query image in the batch.
-
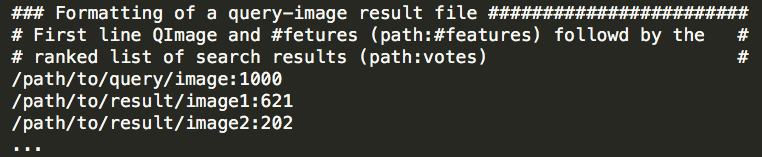
Image result ("imagename".res)
- For each query image in a search batch a result file is created in the search batch folder. The header of this file holds "p:f" where p is the path to the query image and f is the number of SIFT features extracted from it.
- The other m-lines are a ranked list of results. Each line is also colon separated lines:, the first value is the path to the result images and the second is the number of features that matched matched.
- Java 8 - Programming language and run-time engine
- Scala - Programming language
- BoofCV - SIFT Feature Extraction
- Spark - Distributed data processing
- Towards Engineering a Web-Scale Multimedia Service: A Case Study Using Spark, published in the proceedings of the 8th ACM conference on Multimedia Systems (MMSys), June, 2017.
- Prototyping a Web-Scale Multimedia Retrieval Service Using Spark, published in ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), Volume 14, Issue 3s, Article No. 65, August, 2018.
This project is licensed under the MIT licence
This work was supported in part by the Inria@SiliconValley program, DHS Award HSHQDC-16-3-00083, NSF CISE Expeditions Award CCF-1139158, DOE Award SN10040 DE-SC0012463, and DARPA XData Award FA8750-12-2-0331, and gifts from Amazon Web Services, Google, IBM, SAP, The Thomas and Stacey Siebel Foundation, Apple Inc., Arimo, Blue Goji, Bosch, Cisco, Cray, Cloudera, Ericsson, Facebook, Fujitsu, HP, Huawei, Intel, Microsoft, Mitre, Pivotal, Samsung, Schlum-berger, Splunk, State Farm and VMware.