This project was built with love and sweat by yours truly as part of the Android Developer Nanodegree by Udacity.
You are more than welcome to look at it for inspiration and use it as per the MIT Licence included.
However, if you feel like copying/pasting it and submitting it as your own work, remember that plagiarism is a violation of the Udacity Honor Code. The consequences of such act may include your expulsion from the ND program (without refund) and could go as far as having you banned for life from any Udacity course and/or scholarship offered in partnership with Udacity. Udacity can also revoke your graduation credential at anytime if plagiarism is detected after you graduate.
Your call.
Project #4 of the Android Developer Nanodegree by Udacity.
Create an app with multiple flavors that uses multiple libraries and Google Cloud Endpoints. The finished app will consist of four modules:
- A Java library that provides jokes
- A Google Cloud Endpoints (GCE) project that serves those jokes
- An Android Library containing an activity for displaying jokes
- An Android app that fetches jokes from the GCE module and passes them to the Android Library for display
As Android projects grow in complexity, it becomes necessary to customize the behavior of the Gradle build tool, allowing automation of repetitive tasks. Particularly, factoring functionality into libraries and creating product flavors allow for much bigger projects with minimal added complexity.
You will learn the role of Gradle in building Android Apps and how to use Gradle to manage apps of increasing complexity. You'll learn to:
- Add free and paid flavors to an app, and set up your build to share code between them
- Factor reusable functionality into a Java library
- Factor reusable Android functionality into an Android library
- Configure a multi-project build to compile your libraries and app
- Use the Gradle App Engine plugin to deploy a backend
- Configure an integration test suite that runs against the local App Engine development server
- Google Cloud Endpoint
- Gradle - Java library
- Android Framework
- Build variants: Flavors
- Espresso
- Android library
- Google Mobile Ads SDK
Download the starter code. It contains an activity with a banner ad and a button that purports to tell a joke, but actually just complains. The banner ad was set up following the instructions here. You may need to download the Google Repository from the Extras section of the Android SDK Manager. You will also notice a folder called backend in the starter code. It will be used in step 3 below, and you do not need to worry about it for now. When you can build an deploy this starter code to an emulator, you're ready to move on.
Your first task is to create a Java library that provides jokes. Create a new Gradle Java project either using the Android Studio wizard, or by hand. Then introduce a project dependency between your app and the new Java Library. If you need review, check out demo 4.01 from the course code. Make the button display a toast showing a joke retrieved from your Java joke telling library.
Create an Android Library containing an Activity that will display a joke passed to it as an intent extra. Wire up project dependencies so that the button can now pass the joke from the Java Library to the Android Library. For review on how to create an Android library, check out demo 4.03. For a refresher on intent extras, check this out.
This next task will be pretty tricky. Instead of pulling jokes directly from
our Java library, we'll set up a Google Cloud Endpoints development server,
and pull our jokes from there. The starter code already includes the GCE module
in the folder called backend.
Before going ahead you will need to be able to run a local instance of the GCE
server. In order to do that you will have to install the Cloud SDK.
Once installed, you will need to follow the instructions in the Setup Cloud SDK.
Note: You do not need to follow the rest of steps in the migration guide, only
the Setup Cloud SDK.
Start or stop your local server by using the gradle tasks as shown in the following
screenshot:  .
Once your local GCE server is started you should see the following at
localhost:8080
.
Once your local GCE server is started you should see the following at
localhost:8080
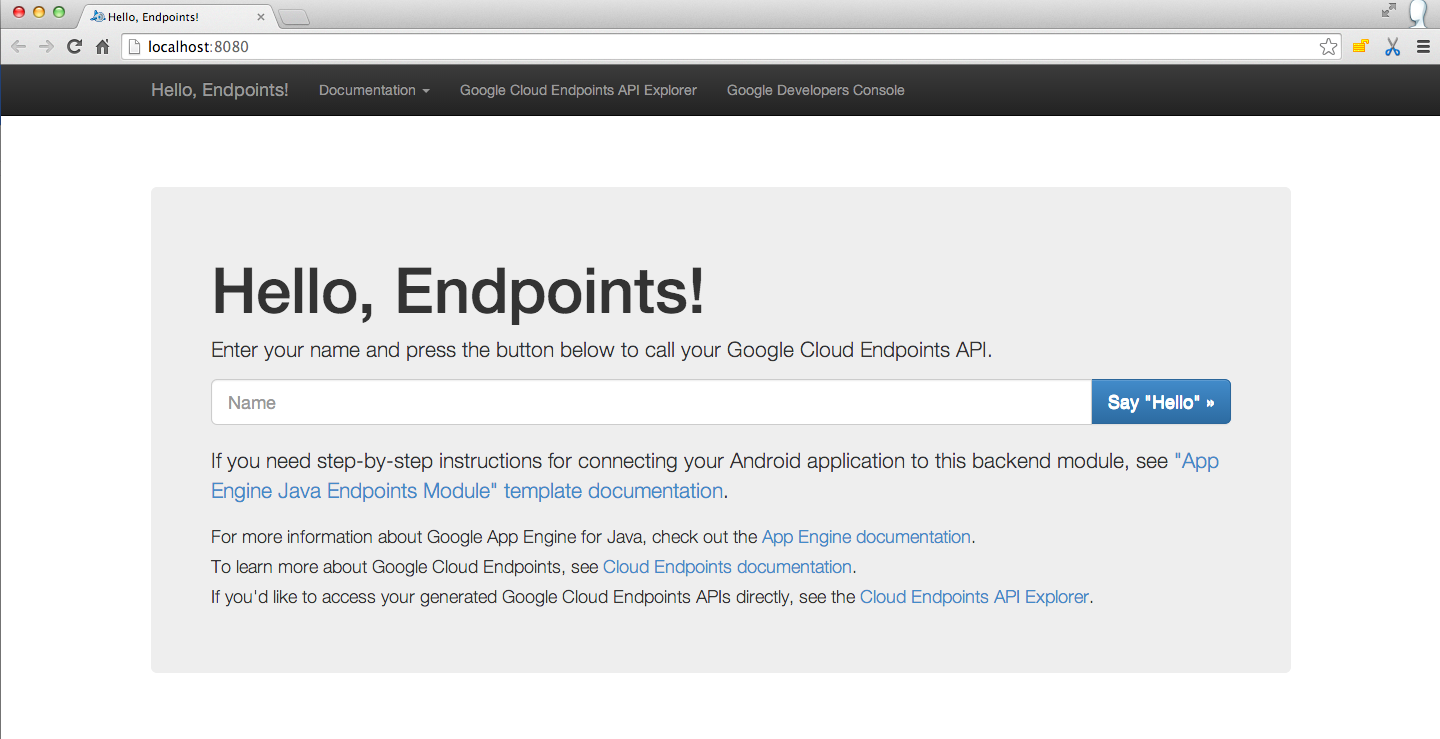 Now you are ready to continue!
Introduce a project dependency between your Java library
and your GCE module, and modify the GCE starter code to pull jokes from your Java library.
Create an AsyncTask to retrieve jokes using the template included int these
instructions.
Make the button kick off a task to retrieve a joke,
then launch the activity from your Android Library to display it.
Now you are ready to continue!
Introduce a project dependency between your Java library
and your GCE module, and modify the GCE starter code to pull jokes from your Java library.
Create an AsyncTask to retrieve jokes using the template included int these
instructions.
Make the button kick off a task to retrieve a joke,
then launch the activity from your Android Library to display it.
Add code to test that your Async task successfully retrieves a non-empty string. For a refresher on setting up Android tests, check out demo 4.09.
Add free and paid product flavors to your app. Remove the ad (and any dependencies you can) from the paid flavor.
- Required Components
- Project contains a Java library for supplying jokes.
- Project contains an Android library with an activity that displays jokes passed to it as intent extras.
- Project contains a Google Cloud Endpoints module that supplies jokes from the Java library. Project loads jokes from GCE module via an AsyncTask.
- Project contains connected tests to verify that the AsyncTask is indeed loading jokes.
- Project contains paid/free flavors. The paid flavor has no ads and no unnecessary dependencies.
- Ads are required in the free version.
- Required Behavior
- App retrieves jokes from Google Cloud Endpoints module and displays them via an Activity from the Android Library. Note that the GCE module need only be deployed locally.
- App conforms to common standards found in the Android Nanodegree General Project Guidelines.
