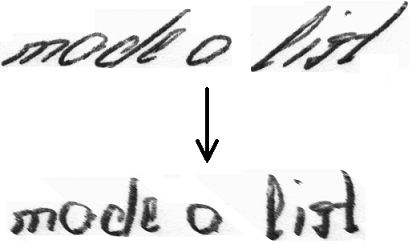Update 2021: added Python implementation
This algorithm sets handwritten text in images upright, i.e. it removes the cursive writing style.
One can use it as a preprocessing step for handwritten text recognition.
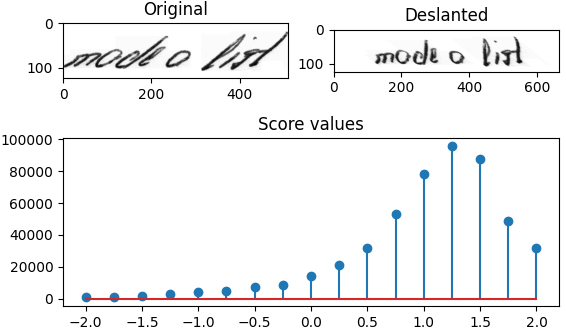
The following illustration shows input and output of the algorithm for a given image (data/test1.png).
Three implementations are provided:
- Python
- C++: all computations are done on the CPU using OpenCV
- OpenCL: each column and shear angle is processed in parallel using OpenCL to compute the optimal shear angle, the remaining work is done on the CPU using OpenCV
- Install required packages by running
pip install -r requirements.txt - Go to the directory
src/py - Run
python main.pyto process the images in thedatadirectory (images taken from IAM and Bentham dataset) - This opens a window showing the input image, deslanted image and score values
- The script can be configured via command line, see available options by running
python main.py -h
- Use
./build.shto build the CPU version or./build.sh gputo build the GPU version on Linux using g++ - Run
./DeslantImgto process the images in thedata/directory - Two processed images are saved in the repositories root directory
Some notes on how to compile the demo manually and how to compile for Windows or other operating systems:
- Build CPU implementation on Linux (OpenCV must be installed):
g++ --std=c++11 src/cpp/main.cpp src/cpp/DeslantImgCPU.cpp `pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv` -o DeslantImg - If the macro USE_GPU is defined, the computation takes place on the GPU. Build CPU and GPU implementation on Linux (OpenCV and OpenCL must be installed):
g++ --std=c++11 -D USE_GPU src/cpp/main.cpp src/cpp/DeslantImgCPU.cpp src/cpp/DeslantImgGPU.cpp src/cpp/CLWrapper.cpp `pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv` -lOpenCL -o DeslantImg - On Windows, the easiest way is to use Microsoft Visual Studio, put all files into a C++ project, set include and library paths for OpenCV and optionally OpenCL, and finally compile and run the program
Command line options of main.py:
--data: directory containing the input images--optim_algo: either do grid search ('grid'), or apply Powell's derivative-free optimizer ('powell')--lower_bound: lower bound of shear values--upper_bound: upper bound of shear values--num_steps: if grid search is used, this argument defines the number if grid points--bg_color: color to fill the gaps of the sheared image that is returned
Call function deslantImg(img, bgcolor) with the input image (grayscale), and the background color (to fill empty image space).
It returns the deslanted image computed on the CPU.
#include "DeslantImgCPU.hpp"
...
// read grayscale image
const cv::Mat img = cv::imread("data/test1.png", cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
// deslant it
const cv::Mat res = htr::deslantImg(img, 255);
// and save the result
cv::imwrite("out1.png", res);
The GPU version additionally takes an instance of CLWrapper which holds all relevant information needed for OpenCL: deslantImg(img, bgcolor, clWrapper).
As the construction of a CLWrapper instance takes time, it makes sense to only create one instance and use it for all future calls to deslantImg(img, bgcolor, clWrapper).
#include "DeslantImgGPU.hpp"
...
// read grayscale image
const cv::Mat img = cv::imread("data/test1.png", cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
// deslant it
htr::CLWrapper clWrapper;
const cv::Mat res = htr::deslantImg(img, 255, clWrapper);
// and save the result
cv::imwrite("out1.png", res);
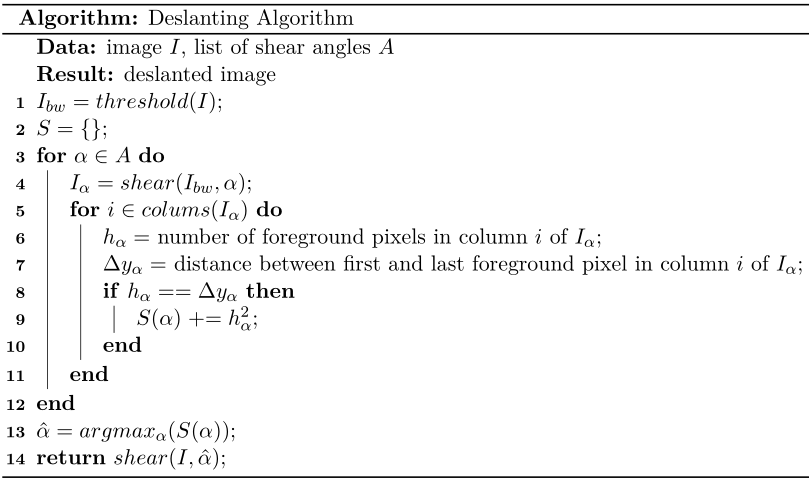
Vinciarelli and Luettin describe the algorithm in their paper. Here is a short outline of the algorithm: