CodeMirror 6 extension that adds Emmet support to text editor.
Extension development is sponsored by Replit
This extension can be installed as a regular npm module:
npm i @emmetio/codemirror6-plugin
The plugin API follows CodeMirror 6 design: it’s an ES6 module and provides a number of exported extensions which you should import and add into your EditorState instance.
In most cases, this package exports Emmet actions as StateCommand, which should be used as follows:
import { EditorState, EditorView, basicSetup } from '@codemirror/basic-setup';
import { html } from '@codemirror/lang-html';
import { keymap } from '@codemirror/view';
// Import Expand Abbreviation command
import { expandAbbreviation } from '@emmetio/codemirror6-plugin';
new EditorView({
state: EditorState.create({
extensions: [
basicSetup,
html(),
// Bind Expand Abbreviation command to keyboard shortcut
keymap.of([{
key: 'Cmd-e',
run: expandAbbreviation
}]),
]
}),
parent: document.body
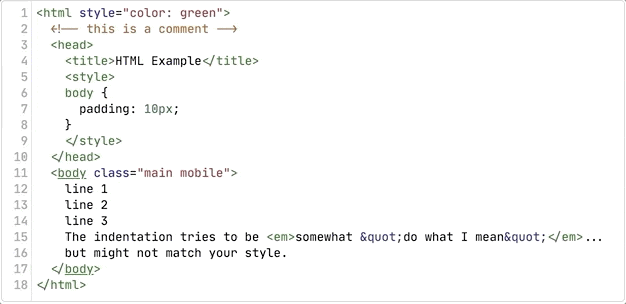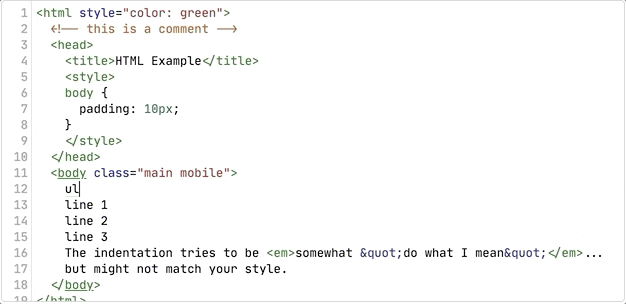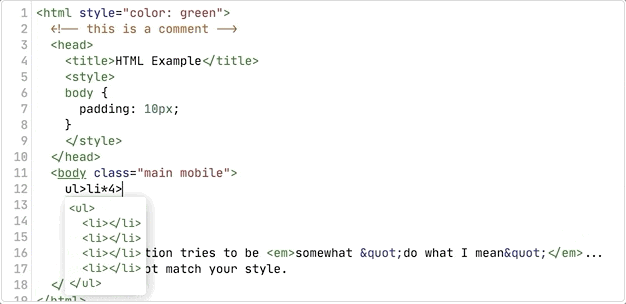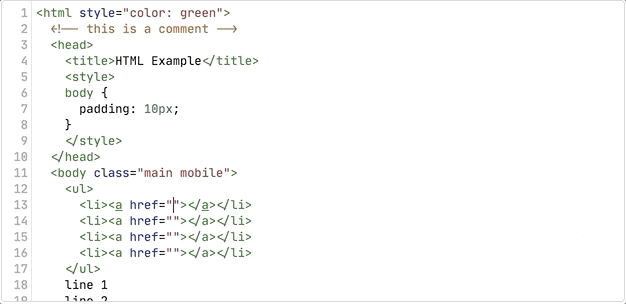
});Emmet extension can track abbreviations that user enters in some known syntaxes like HTML and CSS. When user enters something that looks like Emmet abbreviation, extension starts abbreviation tracking (adds emmet-abbreviation class to a text fragment). WHen abbreviation becomes complex (expands to more that one element), it displays abbreviation preview:
To enable abbreviation tracker, you should import abbreviationTracker function and add its result to editor extensions:
import { EditorState, EditorView, basicSetup } from '@codemirror/basic-setup';
import { html } from '@codemirror/lang-html';
import { abbreviationTracker } from '@emmetio/codemirror6-plugin';
new EditorView({
state: EditorState.create({
extensions: [
basicSetup,
html(),
abbreviationTracker()
]
}),
parent: document.body
});Abbreviation tracker is context-aware: it detect current syntax context and works only where abbreviation expected. For example, in HTML syntax it works in plain text context only and doesn’t work, for example, in attribute value or tag name.
To expand tracked abbreviation, hit Tab key while caret is inside abbreviation, or hit Esc key to reset tracker.
In case if abbreviation tracking is unavailable or you want to give user an opportunity to enter and expand abbreviation with interactive preview, a special abbreviation mode is available. Run enterAbbreviationMode command to enter this mode: everything user types will be tracked as abbreviation with preview and validation. To expand tracked abbreviation, hit Tab key while caret is inside abbreviation, or hit Esc key to reset tracker.
Currently, CodeMirror API doesn’t provide viable option to get document syntax to allow plugins to understand how to work with document. So you have to specify document syntax manually in Emmet plugin. You can do so via emmetConfig facet or as an option to abbreviationTracker:
import { EditorState, EditorView, basicSetup } from '@codemirror/basic-setup';
import { html } from '@codemirror/lang-html';
import { keymap } from '@codemirror/view';
import { emmetConfig, abbreviationTracker } from '@emmetio/codemirror6-plugin';
const editor1 = new EditorView({
state: EditorState.create({
extensions: [
basicSetup,
html(),
// Option 1: specify document syntax as config facet
emmetConfig.of({
syntax: 'css'
}),
// Option 2: pass syntax as config value of abbreviation tracker
abbreviationTracker({
syntax: 'jsx'
})
...
]
}),
parent: document.body
});Note that syntax is most important option Emmet: it controls how abbreviation is parsed in document (wether it’s markup, stylesheet or JSX syntax) and style of generated output (HTML or XML style, CSS or SASS dialect and so on).
Some common syntaxes:
html,xml: HTML or XML document; inhtmlalso tries to detect inline CSS fragments.jsxfor JSX syntax. By default, requires abbreviation to start with<in order to skip false-positive abbreviation capturing for variables and functions, also modifies output to match JSX specs (e.g. renameclassattribute toclassNameetc.)css,scss,sass,stylus: various options of stylesheet abbreviations and output.haml,jade,pug,slim: supported markup preprocessors.
Default syntax is html.
The following commands are available in current package:
expandAbbreviation– expand abbreviation left to current caret position. Unlike abbreviation tracker, this command works anywhere and doesn’t respect current context.enterAbbreviationMode– enters abbreviation mode.wrapWithAbbreviation— Wrap with Abbreviation. Note that this is not a StateCommand but a function that you should call and pass returned result as extension. You can optionally pass keyboard shortcut as argument (Ctrl-w by default).balanceOutward/balanceInward— Balance.toggleComment— Toggle CommentevaluateMath— Evaluate Math ExpressiongoToNextEditPoint/goToPreviousEditPoint— Go to Edit PointgoToTagPair— Go to Matching PairincrementNumberN/decrementNumberN— Increment/Decrement Number whereNis1,01or10.removeTag— Remove TagsplitJoinTag— Split/Join TagselectNextItem/selectPreviousItem— Select Item