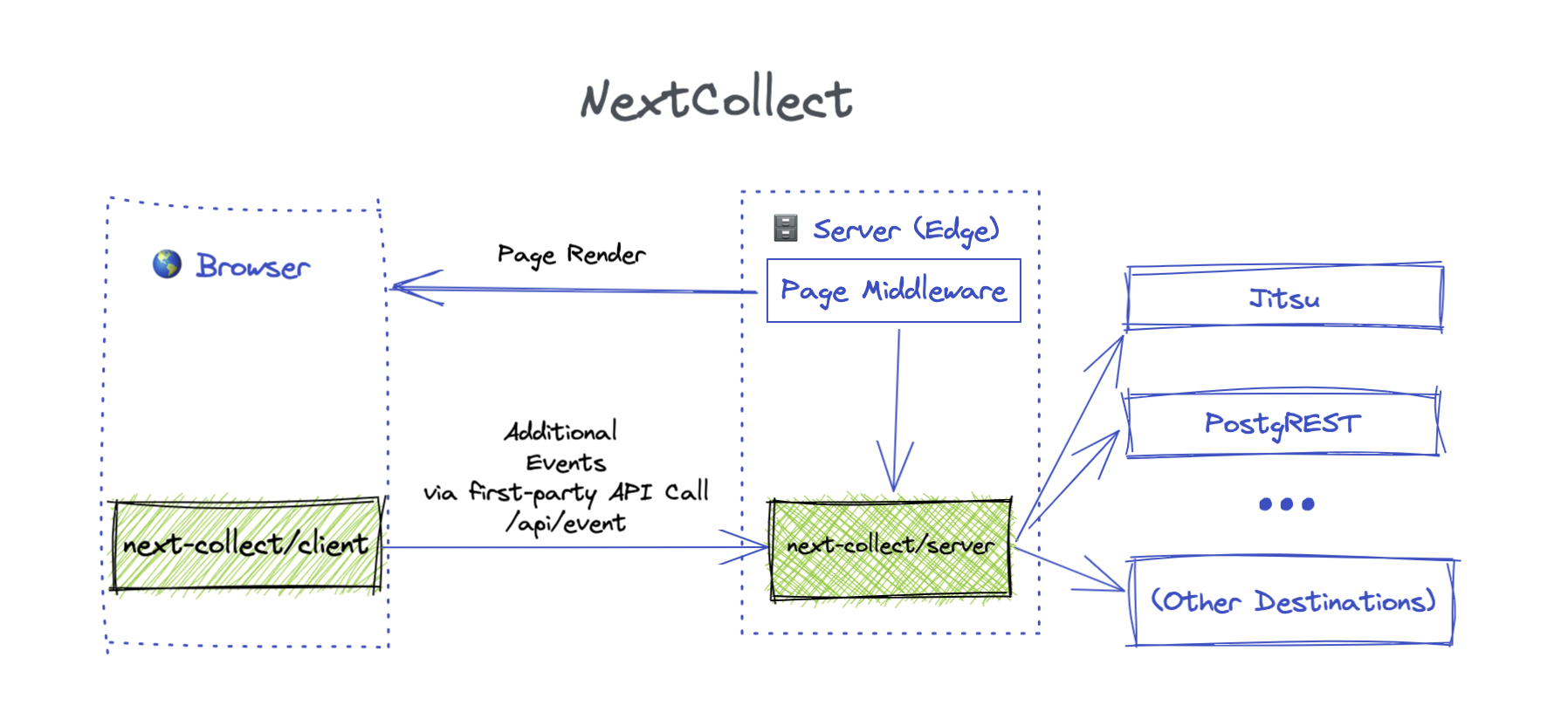
Overview
next-collect is a framework for server-side user event collection for Next.Js. It is designed from the ground up to work in Serverless environment
to take advantage of the Vercel Edge Runtime.
NextCollect is destination agnostic. It could send data to multiple destinations at once. So far it supports Jitsu, Segment, PostgREST (compatible with Supabase) and free-form HTTP-Destiation
Server-Side vs Client-Side event collection
Client-Side user tracking means that once user loads the page (or makes another action), piece of JavaScript code sends the data to collector server. This is how most of the analytics trackers works: GoogleAnalytics, Segment, Amplitude, etc. Server-Side tracking happens when server (backend) renders the page or answers API call. No JavaScript code is touched.
Why go Server-Side
- Reliability. 100% events will be recorded. Unlike client-side trackers, server side trackers are insusceptible to AdBlockers and Safari's Tracking Prevention.
- Better user identification. Server-side cookies are more reliable, especially when cookies are set under the same domain name as the main app
- Better user experience. Less javascript request means faster website
- No middleman. It's possible to distribute data to end destinations directly, bypassing Segment and other similar platforms
Best of the both worlds
next-collect can client-side collect data too. It exposes a first-party api route /api/collect, so the events can be sent client-side.
A good example of such event is user actions which do not call any server API (e.g. button click)
The data will be sent to /api/collect, and sensitive params such userId, ip address and so on will be resolved server-side. Since the api call is first-party
(goes to the same host), it won't be blocked by AdBlockers or tracking prevention.
See a full instruction on how to use client-side tracking below
Getting Started
npm install --save next-collect. Make sure that Next.Js >= 12.0
Usage
See a demo Next.JS Demo app for an example.
Step 1. Create next-collect.config.[js|ts] in the root of your Next.JS
This file will contain shared settings of next-collect:
export const nextCollectOpts: NextCollectOpts = {
drivers: [...],
eventTypes: [...],
}NextCollectiOptions has a few configuration options, but most of them are optional. Mandatory options are:
drivers— a list of destinations wherenext-collectwill send data. Each driver could be either a string or an object. String means that the driver should read configuration from globally defined environment variables. Objects are for advanced manual configurationeventTypes— a list of event types thatnext-collectwill collect. It could be a function that decides if a call to a certain URL should be recorded, or a list of routes
Map example:
import { NextCollectOpts } from "next-collect/server"
export const nextCollectOpts: NextCollectOpts = {
eventTypes: [
{ "/api*": "api_call" },
{ "/img*": null }, //ignore all and favicon calls
{ "/favicon*": null },
{ "/*": "page_request" },
],
}
⚠️ page_requestwon't be counted accurately due to Next.JS prefetch. In nutshell, you'll see more requests than actually happened. It's probably not an issue if your metrics are based on unique users, but can lead to incorrect number of visit metrics. See details belowYou can count
page_loadwithuseCollect()hook, but it will lead to an extra async request and is susceptible to some ad-blockers.
Instead of next-collect.config.ts you can use any other file name, it just should be consistent with imports in middleware.ts and
collect.ts (see below)
Step 2. Create middleware.[js|ts] file within you Next App:
import { collectEvents } from 'next-collect/server'
import { nextCollectOpts } from "./next-collect.config";
export default collectEvents(nextCollectOpts);or wrap an existing middleware:
import { collectEvents } from 'next-collect/server'
import { nextCollectOpts } from "./next-collect.config";
const middleware = (req, res) => {
....
}
export default collectEvents({
middleware: middleware,
...nextCollectOpts
});Step 3. Create pages/api/collect.ts:
import { nextCollectOpts } from "next-collect";
import { nextCollectOpts } from "../../next-collect.config";
export default collectApiHandler(nextCollectOpts);This step is required if you're going to use useCollect() hook (see below)
Drivers (destinations) configuration
NextCollect is destination agnostic. It could send data to multiple destinations at once. We support Jitsu, Segment, PostgREST (Supabase) and arbitary HTTP destinations. See destination reference below
Most reads config from env variables, or config can be passed to destination directly. Example:
import { NextCollectOpts } from "next-collect/server"
export const nextCollectOpts: NextCollectOpts = {
destinations: [
{type: "jitsu", opts: {key: "{API KEY}", host: "{JITSU HOST}"}},
process.env.SEGMENT_KEY && "segment",
]
}Client-Side Data Collection - useCollect() hook
Not all events can be tracked on server-side. Some events happen when user interacts with UI, and no server code is touched.
In this case, you should use useCollect() hook. Event is sent to a /api/collect, and the "hydrated" on server
const collect = useCollect()
return <button onClick={() => collect.event("button_click", {buttonId: "Sign Up"})}>Click Me!</button>page_load events
The code below sends a page_load event each time page has been loaded (See demo app for the full example):
const collect = useCollector()
const router = useRouter()
useEffect(() => {
collect.event("page_load", {})
}, [router.asPath])Advanced: Custom API Route
Instead of /api/collect you can use any other route. Just don't forget to move your collectApiHandler() to the correct api route
file (pages/api/alt-collect.ts in this example)
<EventCollectionProvider options={{apiPath: "/api/alt-collect"}}>
...
</EventCollectionProvider>Next.JS 12.1 -> 12.2 Migration
Next.JS team has changed page middleware API in between versions. Here's a detailed changelog,
and >=0.2.0 version is only compatible with Next.Js 12.2. For older versions, you can a legacy 0.1.* versions.
Next.JS middleware and prefetch
When browser loads Next.JS page, it will also prefetch most of the links coming out from this page. This technique is called prefetching and can't be turned off.
During the prefetch request, Next.JS will call middleware code and page_request event
will be recorded. If user doesn't follow the link, the request still be processed. If user follows the
link, the page will be displayed and no subsequent middleware call will be made. In other
words, there's no way to tell if user actually visited the page or it has been just prefetch. See discussion on Next.JS GitHub.
If this is not desirable, you should use client-side collection with useCollect() hook
Advanced usage
Custom properties
next-collect allows adding custom properties to the event. You probably want to do so if you authorize users,
hence you want to see user id / email attached to the event. Here's an example of next-collect.config.ts:
import { NextCollectOpts } from "next-collect/server"
function getUser(userCookie) {
return {id: ..., email:...}
}
export const nextCollectOpts: NextCollectOpts = {
destinations: [],
extend: (req: NextRequest | NextApiRequest) => {
if (req instanceof NextRequest) {
return {
user: parseUserCookie(req.cookies.get("user")),
anotherProperty: ...
}
} else {
return {
user: parseUserCookie(req.cookies["user"]),
anotherProperty: ...
}
}
}
}Note that extend takes NextRequest | NextApiRequest as an argument. Unfortunately, Next.JS exposes to different
APIs in different environments, so you would need to implement this logic for both NextRequest and NextApiRequest
The easiest way to get user id and email is to save it to cookies, and get it from req.cookies in getUser() function.
Furthermore, this example adds anotherProperty to event. You can add as many properties as you want
Destination Reference
At the moment, NextCollect supports Jitsu (jitsu), Segment(segment) and PostgREST (postgres).
Jitsu
Config
| Parameter | Documentation |
opts.key or process.env.JITSU_KEY(required *) |
Jitsu Server API key |
opts.key or process.env.JITSU_KEY(required *) |
Jitsu host. Must start with https:// or http://. Example: `t.jitsu.com |
Segment
Config
| Parameter | Documentation |
opts.key or process.env.SEGMENT_KEY(required *) |
Segment write API key |
PostgREST
Jitsu supports PostgREST (including Supabase which is based on PostgREST).
A table with all fields should be created prior to using this destination.
Config
| Parameter | Documentation |
opts.url or process.env.POSTGREST_URL(required *) |
Url of PostgREST server |
opts.url or process.env.POSTGREST_URL(required *) |
Url of PostgREST server |
Contributing
Please see CONTRIBUTING.md