The Ax is software for rapid workflow automation. If you are still using spreadsheets and email to manage your work, use Ax to automate it!
What is Ax
- The Ax is a software for building and running workflow applications.
- It is a python program distributed by PyPi package manager.
- It is self-hosted and uses super-fast Sanic framework
How does it work
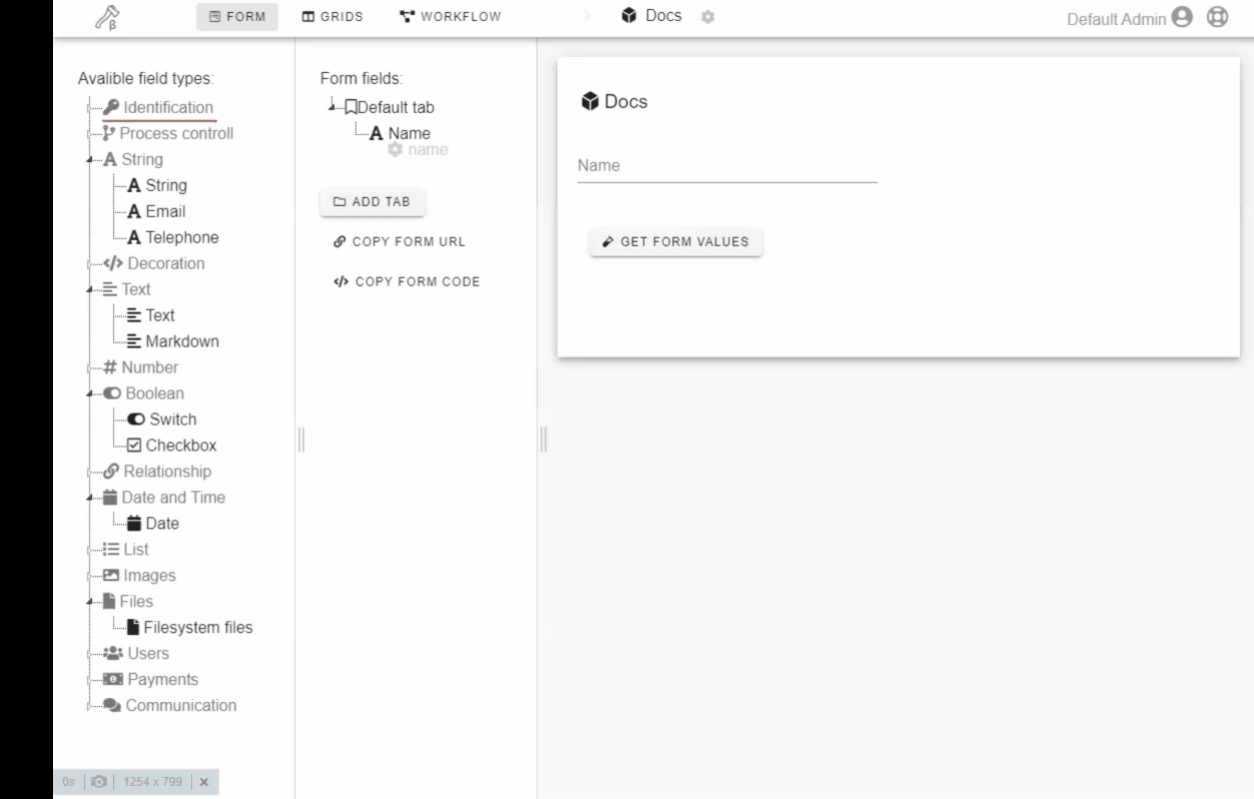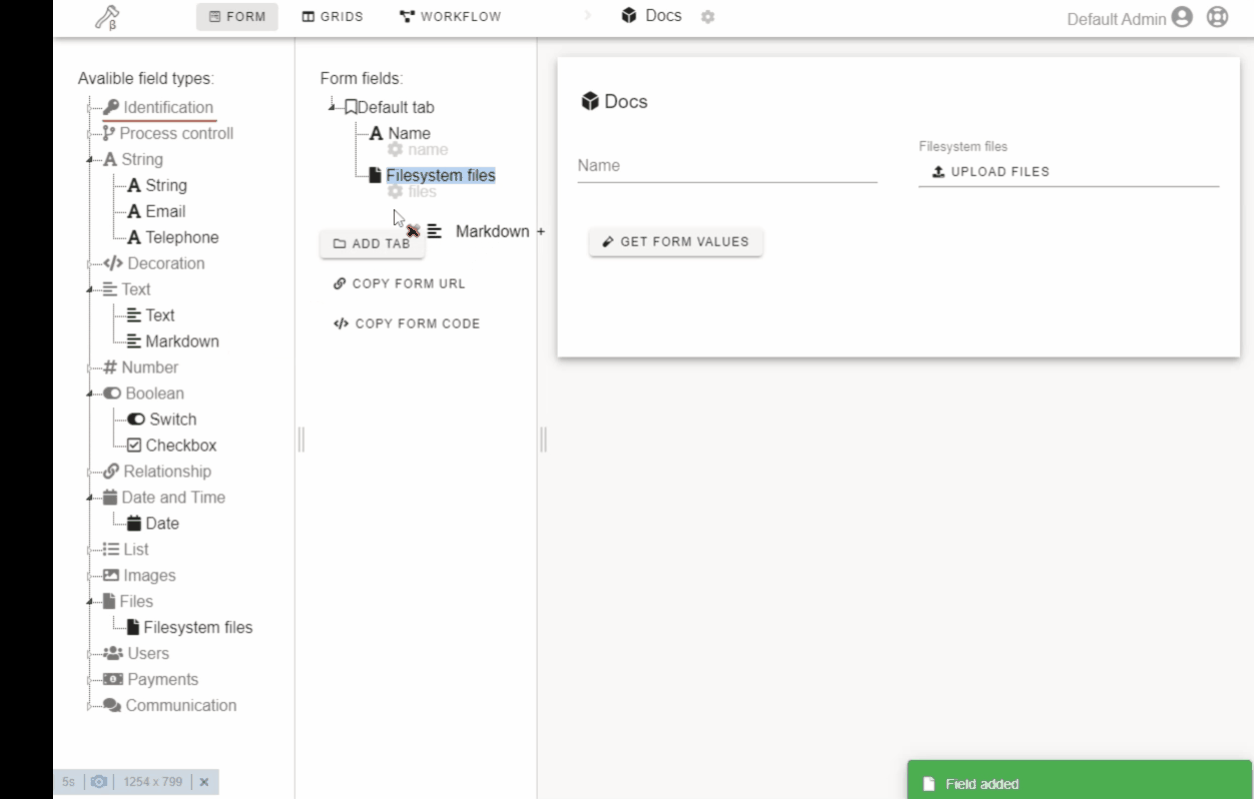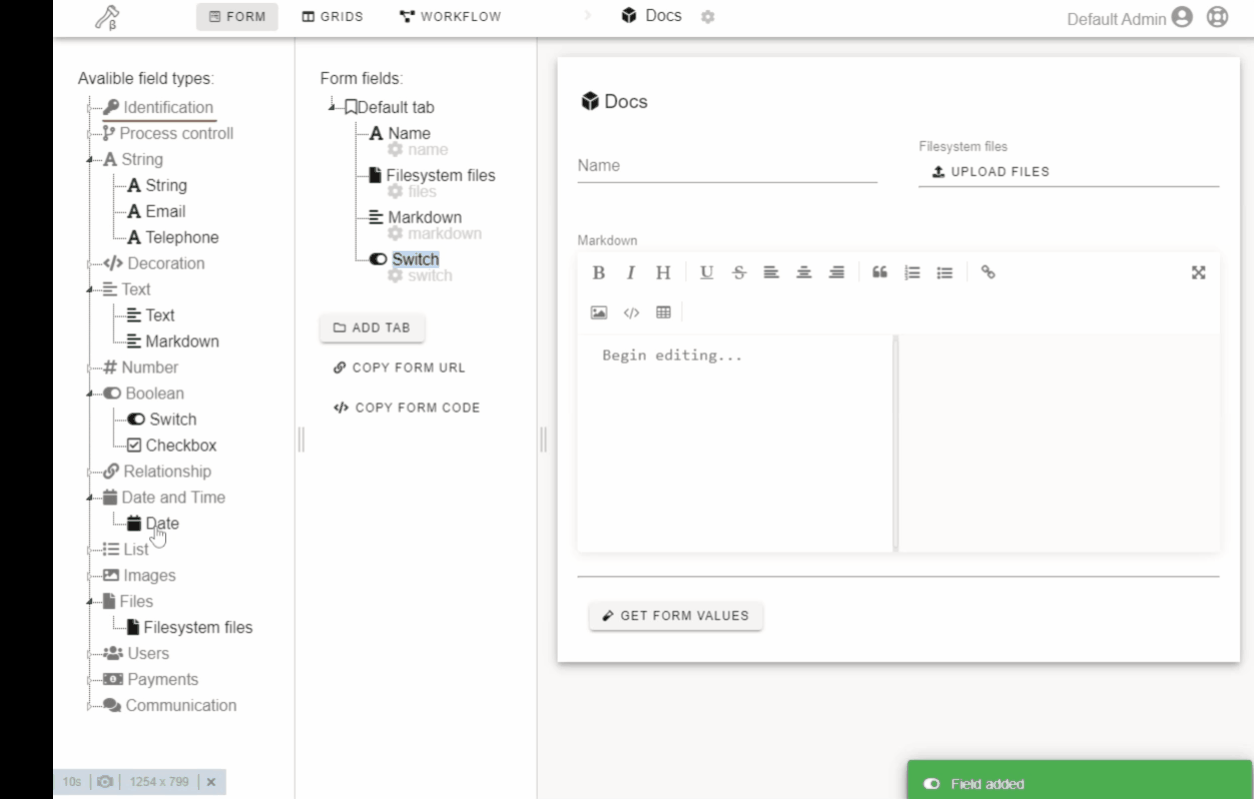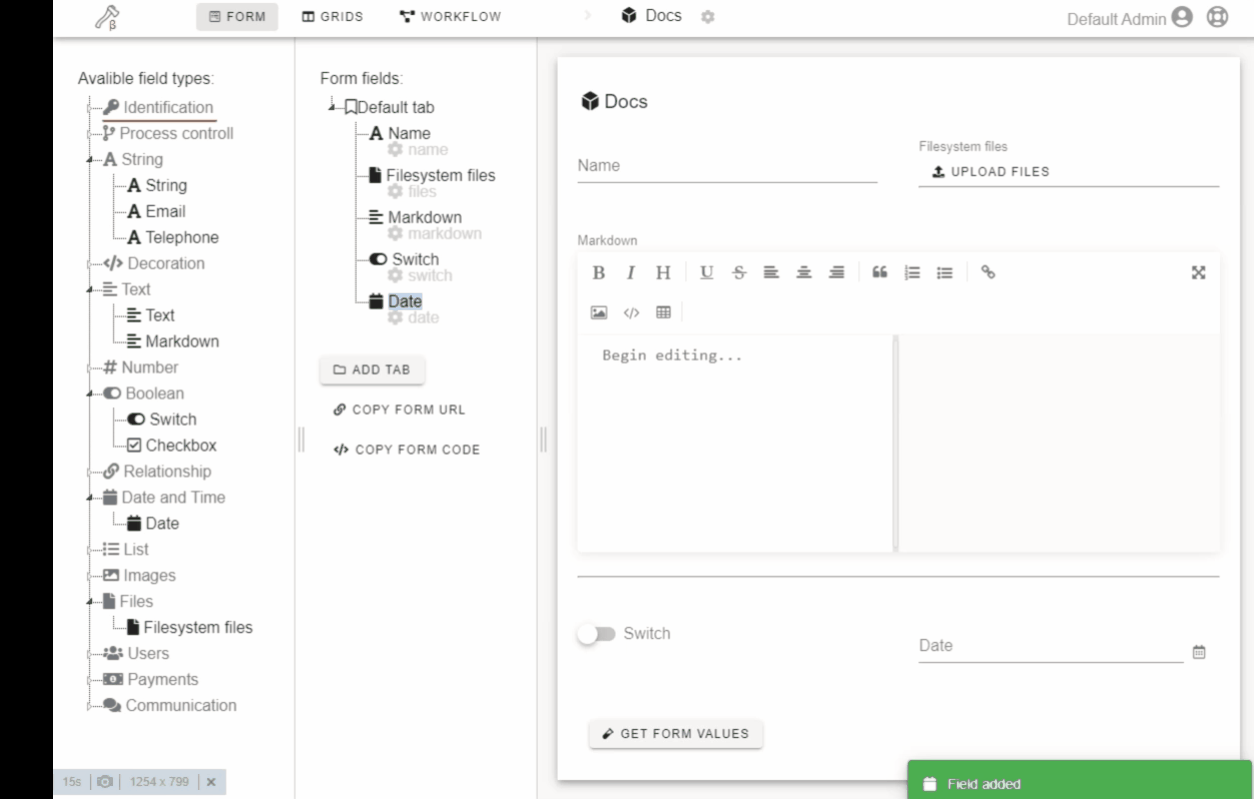
- Create a form with a constructor.
- Form records have a lifecycle that is defined by a set of states.
- States are connected with each other with "Actions" forming a Finite State Machine.
- Users can have different field permissions for each state.
- When "Action" is performed and record state is changed an arbitrary python code is executed.
- This can be used to send emails, call APIs, move robots, launch rockets, etc.
Use cases
-
Workflow automation
- Example - Facility Access Request, RFC request, Estimation queries, Asset Purchase, New Hire Request, Time Off Request, Purchase Request, Job Offer, etc
- Content management [Headless CMS]
- CRM
- ECM
- HelpDesk
- Expert systems
- Educational courses
Ax is currently in BETA
Ax team offers FREE consulting services for users with paid support plan.
If you want to automate any workflow - please contact the team describing the task. We will configure a VPS with Ax workflow, build a workflow app you need and teach you how to use it.
Ax workflow documentation is separated into four levels of complexity:
| Getting started | Beginner | Advanced | Hacker |
|
|
|
|
The Ax is a python application available as a pypi package. You can install and run Ax in 1 minute. No configuration is required. All you need is to run this simple command to install Ax:
pip3 install ax
Python 3.6 and PyPI packet manager are required.
Complete installation guide with videos:
To start Ax server on localhost (127.0.0.1:80) simply run the command:
ax
Or specify host and port:
ax --host=192.168.0.16 --port=8080
You will see this message:
Follow the URL and Use default administrator credentials to enter the Admin console:
- email: default@ax-workflow.com
- password: deleteme
With no configuration, the Ax uses built-in Sanic webserver, SQLite as database and RAM for storing cache.
If you expect a heavy load, you can configure Ax to use Gunicorn web-server, Postgre SQL and Redis.
The Ax is built on top of Sanic , the super-fast python framework.
The tour is available for each page of the Admin console. Press the life-ring icon at the right of the toolbar to start a tour.
The basic usage of Ax consists of these steps:
- Create a form
- Create a grid
- Set permissions
- Send links to users
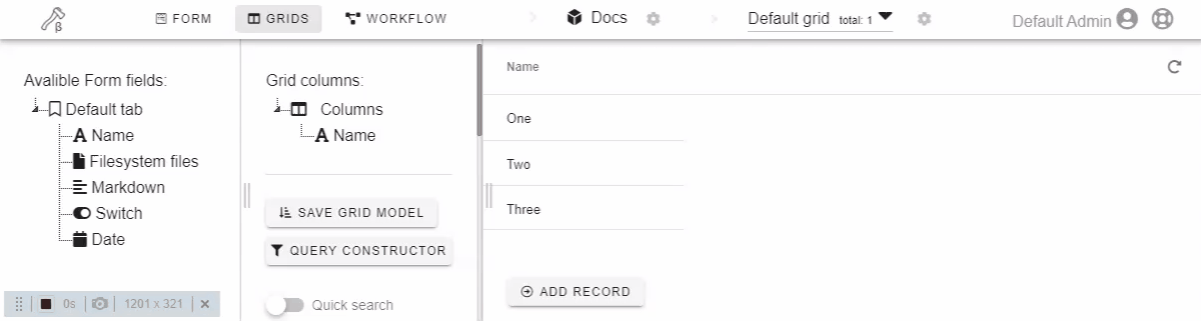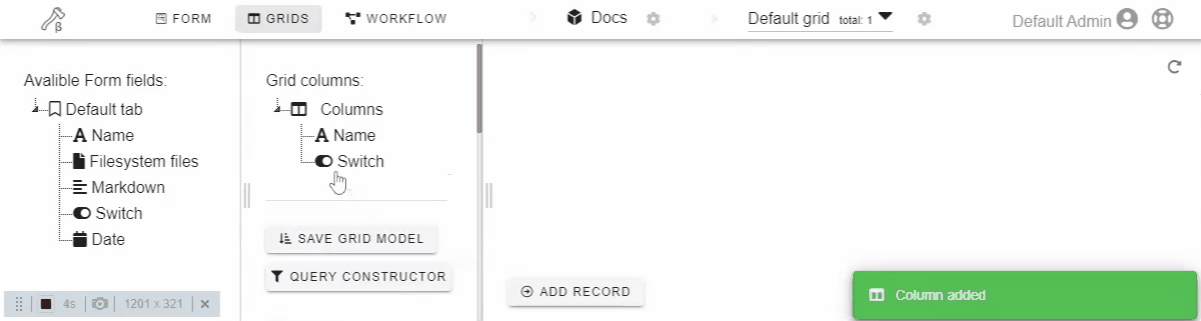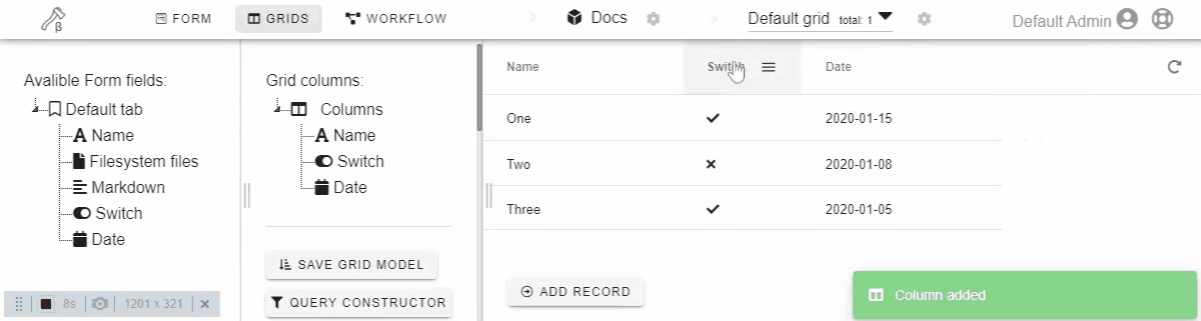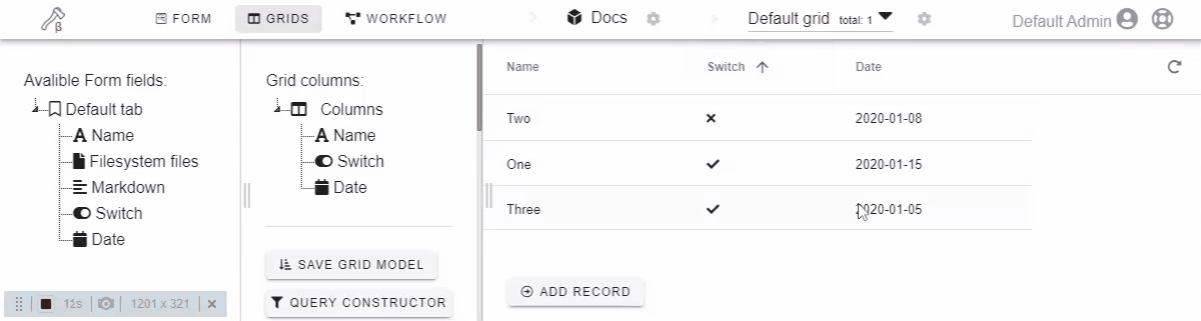
Click or drag-n-drop field on the left drawer to add it to the form.
Click or drag-n-drop form field on the left drawer to add it to the grid.
Configuring workflow is optional. If you are building something like a simple survey, you can stick with the default workflow.
It consists of a single state - "Created" and three actions - "Add record", "Update", "Delete record".
The default workflow does not contain any user roles. So initially only administrators can create and view records.
In order to give your users the ability to use form and grid, you have to:
- Create a new role
- Assign a role to States and actions by drag-n-drop
- Add users to the role
- Set field permissions for each state
Note: Two technical user groups are available - All Users and Everyone
Now you can send users a link to form or grid.
There is "Copy form URL" and "Copy grid URL" buttons available at the form and grid constructors.
There are more advanced options for representing workflow applications to end-users. Please read Pages Designer, Using web-components, Using GraphQL API
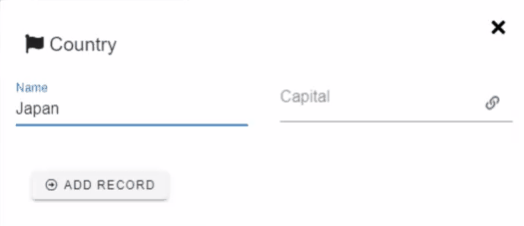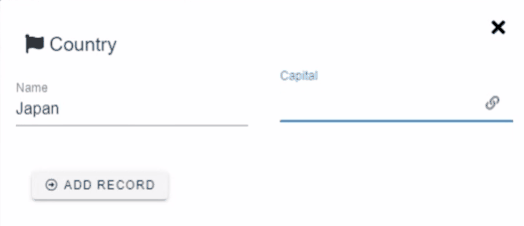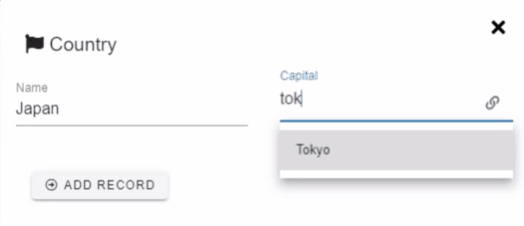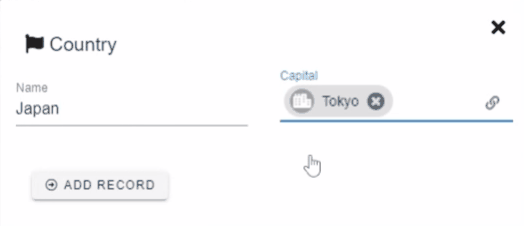
Ax starts to shine when you are dealing with complex applications with dozens of interconnected forms. The forms can be connected with reference fields. Currently, there are 3 types of reference field types available:
1to1 - Simplest relationship. One record is connected to one record of another form.
Example: Country → Capital city. The country can have only one capital.
The text and icon of reference chips can be configured in form settings.
Set form reference label to {{name}} in order to user "name" fields value for chips. By default, the row GUID is used for chips.
1toM - One record is referencing multiple records.
Example: Country → Cities. The country can have many cities.
1toM Table view - Same as 1toM but looks like a table and allows the creation of new records.
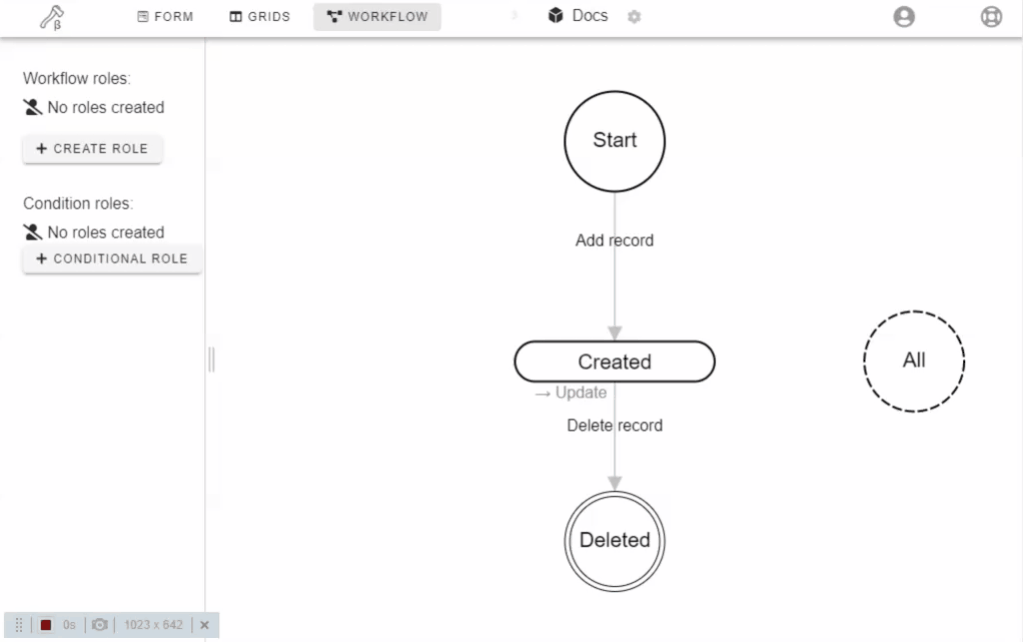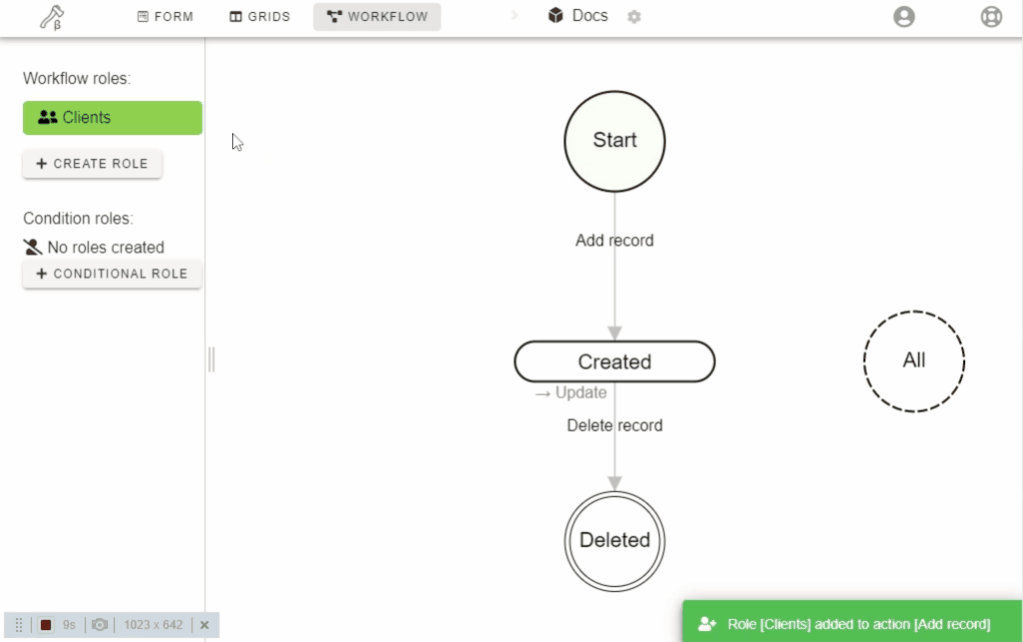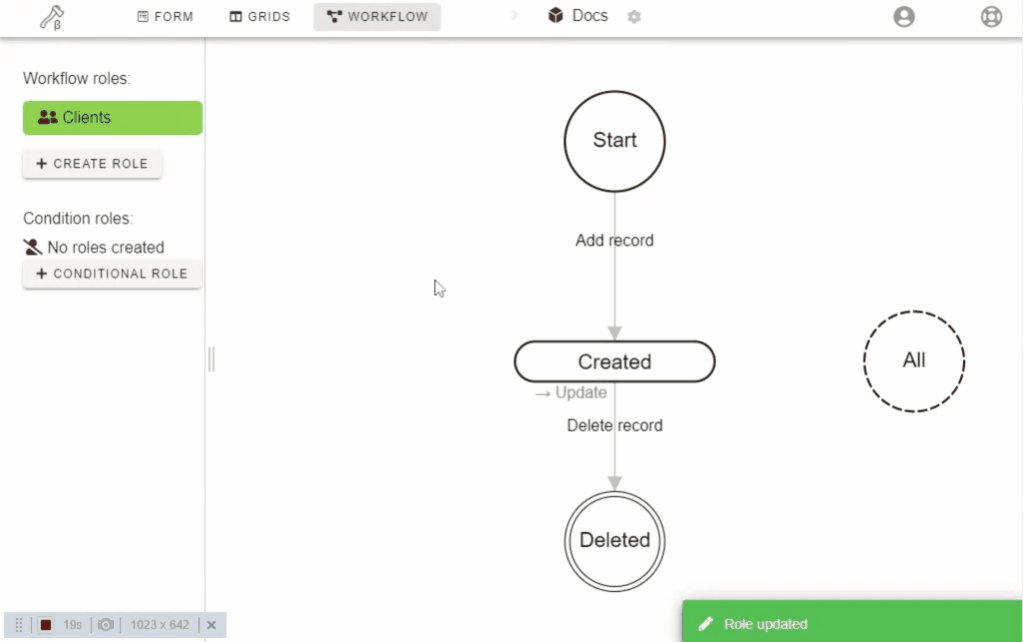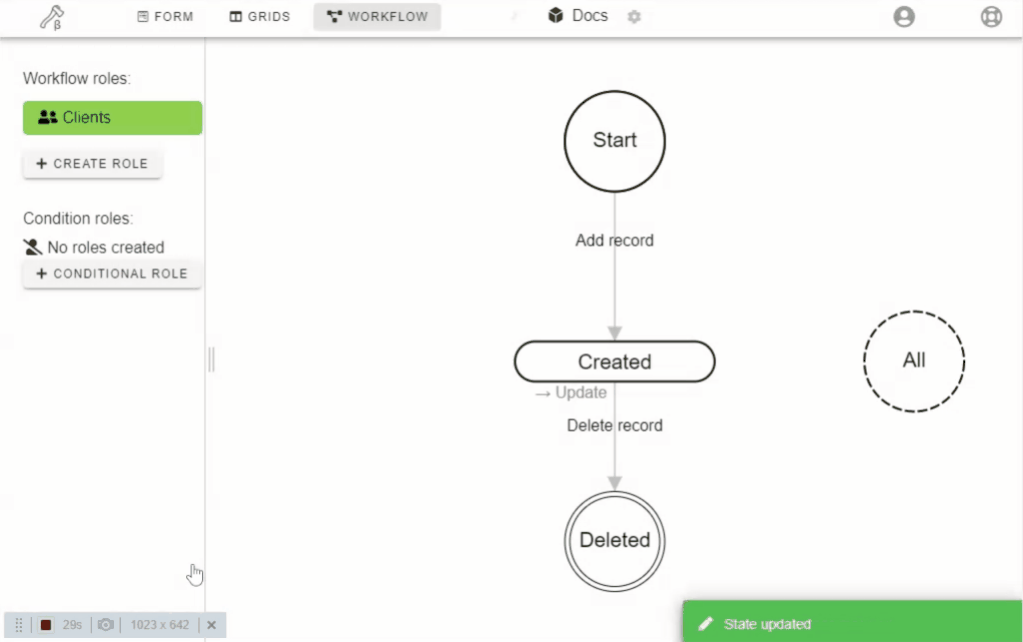
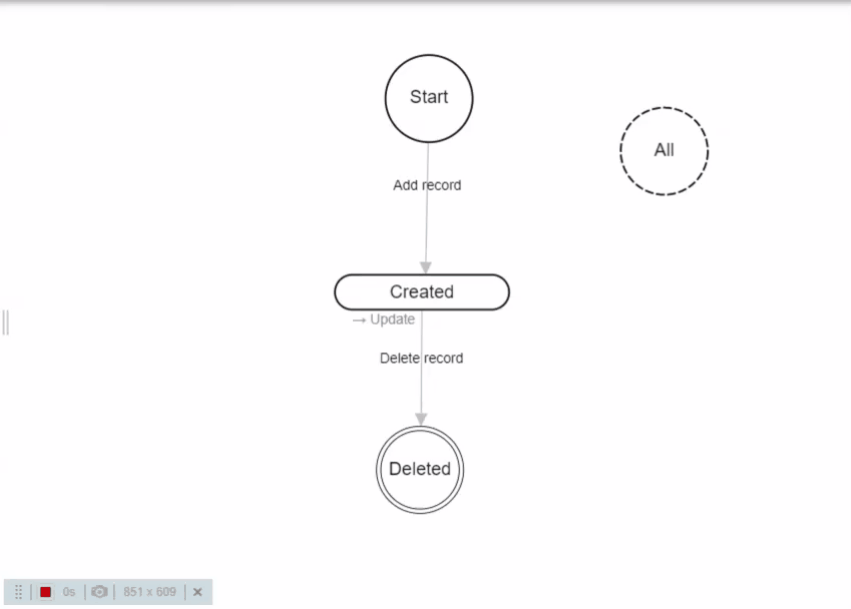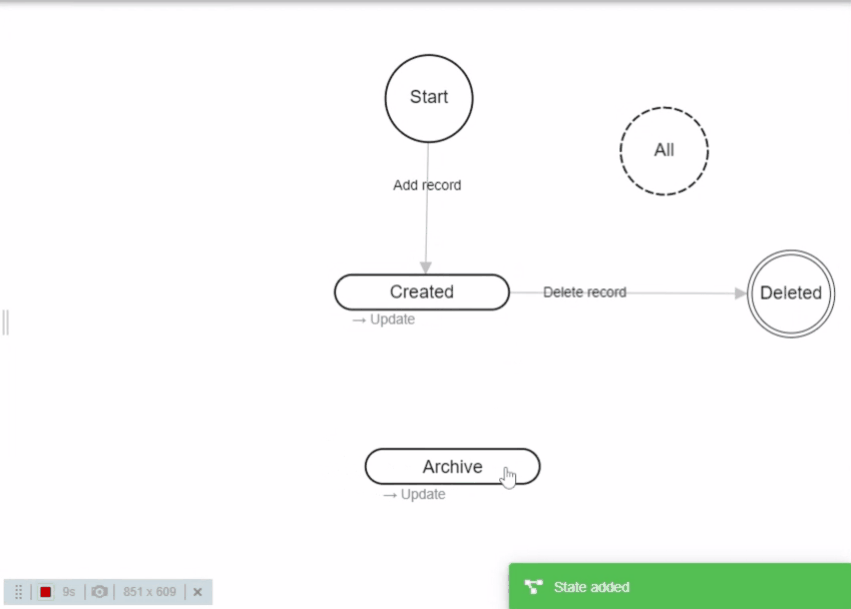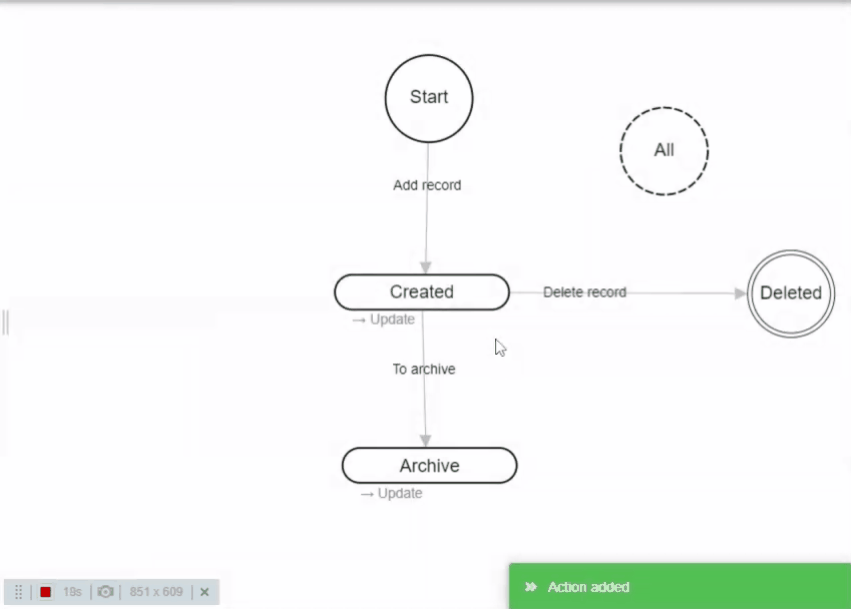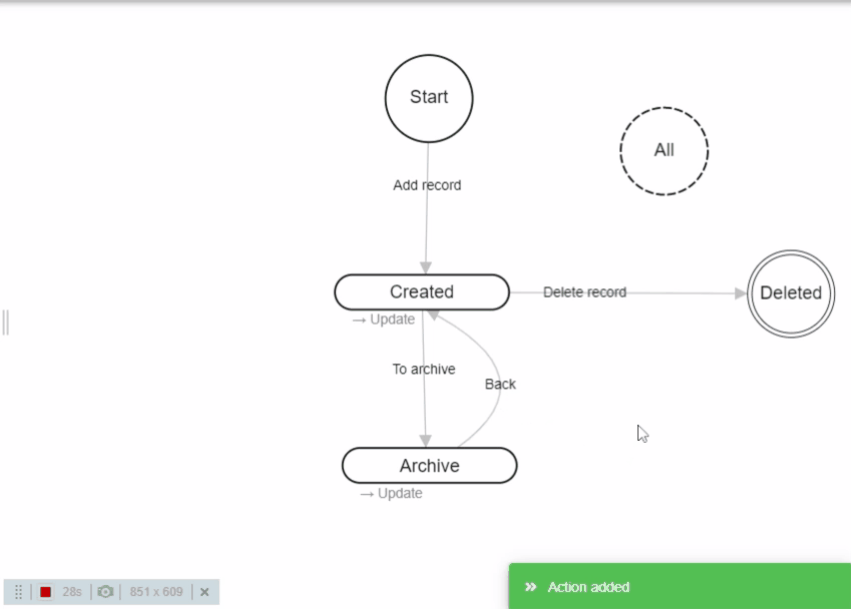
Every form record in Ax has a "State" attribute. Form states are shown as rounded rectangles.
Users change state of a record by performing "Actions". Actions are shown as arrows from one state to another.
Example: Action "Create record" of default workflow creates record and changes state to "Created"
Steps needed for creating a workflow:
- Create states
- Creates actions between states
- Create workflow roles
- Assign roles to states and actions by drag-n-drop
- Assign users to roles
- Set fields permissions for each state
By default, the workflow has only one state "Created" and three actions - "Create record", "Update" and "Delete"
There are three technical states:
- Start - Actions from the Start state are creating new records. The Start state means that the record does not yet exist. Start actions are available in grids. You can modify field permissions for Start state.
- Deleted - Actions to the Deleted state are deleting records from the database.
- All - Actions from the All state are available on all states.
- To create a new State you must double-click on an empty spot in workflow constructor.
- Drag states to change there location.
- Hold mouse over State and press "Del" on the keyboard to delete it.
- Click on the State to change field permissions, rename it or to delete it.
- To create new action you need to click on a state, hold the mouse button for 0,5 sec, then drag to another state to create an Action.
- While creating new action you can drag it to the same state to create "Self-action" (like the default "Update" action). Self actions do not change state, but form values are updated.
- Hold and drag the name of created action to make the line curved. Useful for visually organizing actions in the workflow.
- Hold mouse over action name and press the "Del" button on the keyboard to delete it.
- Click on the action name to open settings.
Available settings are:
- Action name - Label of a button that displayed to users
- Action code name - Ax allows you to call form Actions from enother form actions using python code. In order to do so, you must specify a code-name. Additionally, actions can be called as GraphQL mutations. The name of the mutation is the same as code-name.
- Roles that can perform the action - A list of workflow roles that can perform this action.
- Actions python code - Custom python code to be executed when action is performed. More info in advanced docs.
- Confirmation text - If this field is not empty the user will be prompted the confirmation when he clicks the action button. Default "Delete" action has confirmation text.
- Close modal on action - If enabled the form will be closed after an action is performed. (Only works if the form was opened from the grid)
There are several way to present grids and forms to your users. The simplest is to send link to a specific form. But if you are building a complex app with dozen inter-connected forms, then you need a custom interface. Ax pages can help you out.
Ax Pages is a stand-alone web-application for end-users of Ax workflow apps. Basically it is a collection of HTML pages with tree-like navigation. Ax Pages comforts progressive web application requirements, so it can be installed as an application on android and ios phones.
- You create page using Markdown or HTML
- Insert
<ax-grid form='SomeFormDbName' grid='SomeGridDbName' />tag in page to display a ax grid. SomeFormDbName and SomeGridDbName are database names of form and grid. You can skip the grid attribute if you want a default grid. - Insert
<ax-form db_name='SomeFormDbName' row_guid='someGuid' />tag in page to display form of certain record. Skip row_guid attribute if you want to create new records. You can use AxNum field values as a row_guid. Check the AxNum field type hint for more info.
Pages are avalible as root of the host.
http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin/home- Admin consolehttp://127.0.0.1:8080- Ax Pages
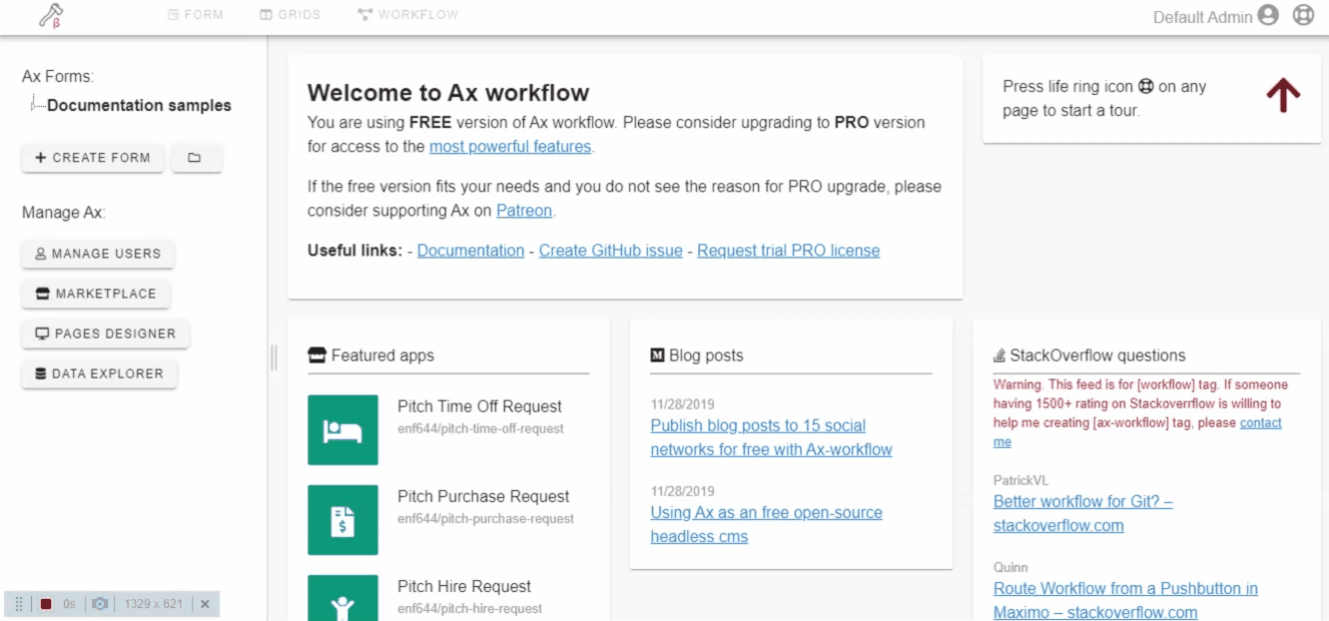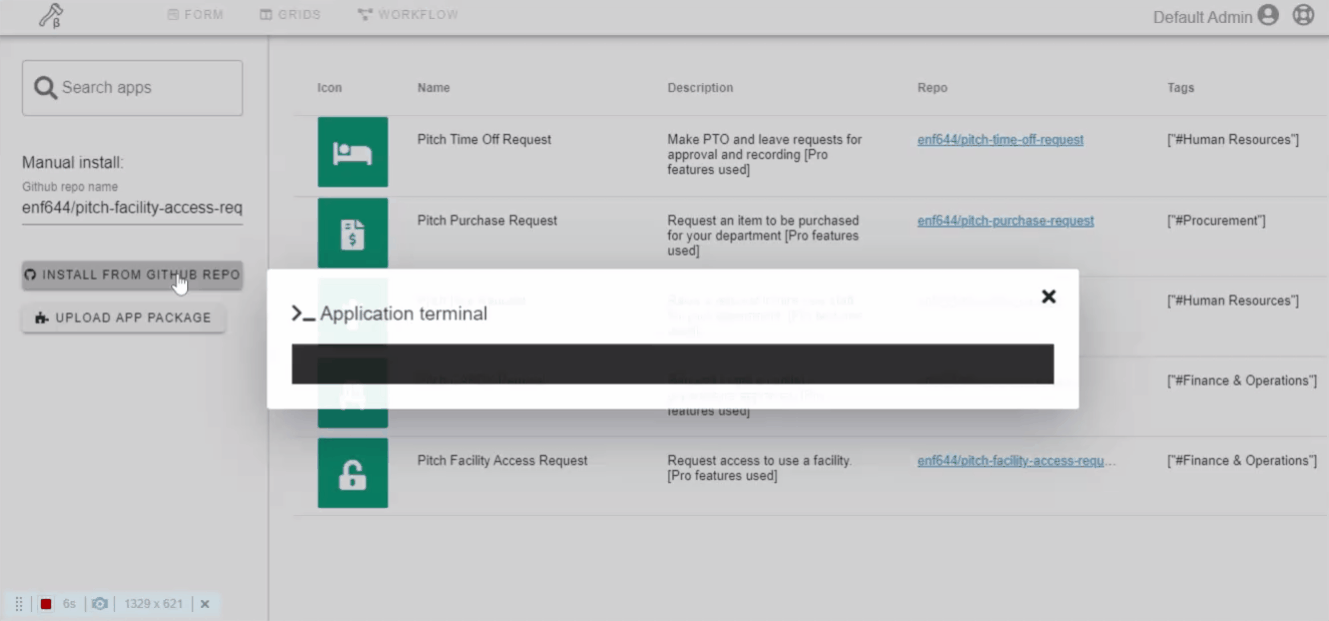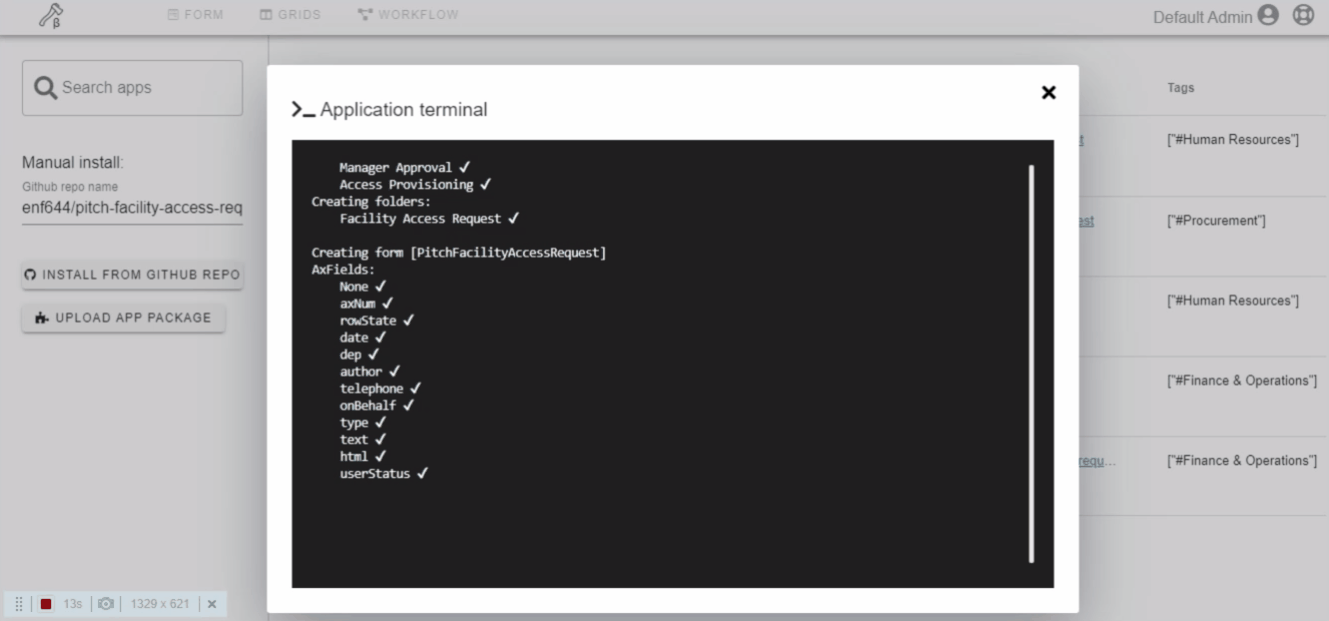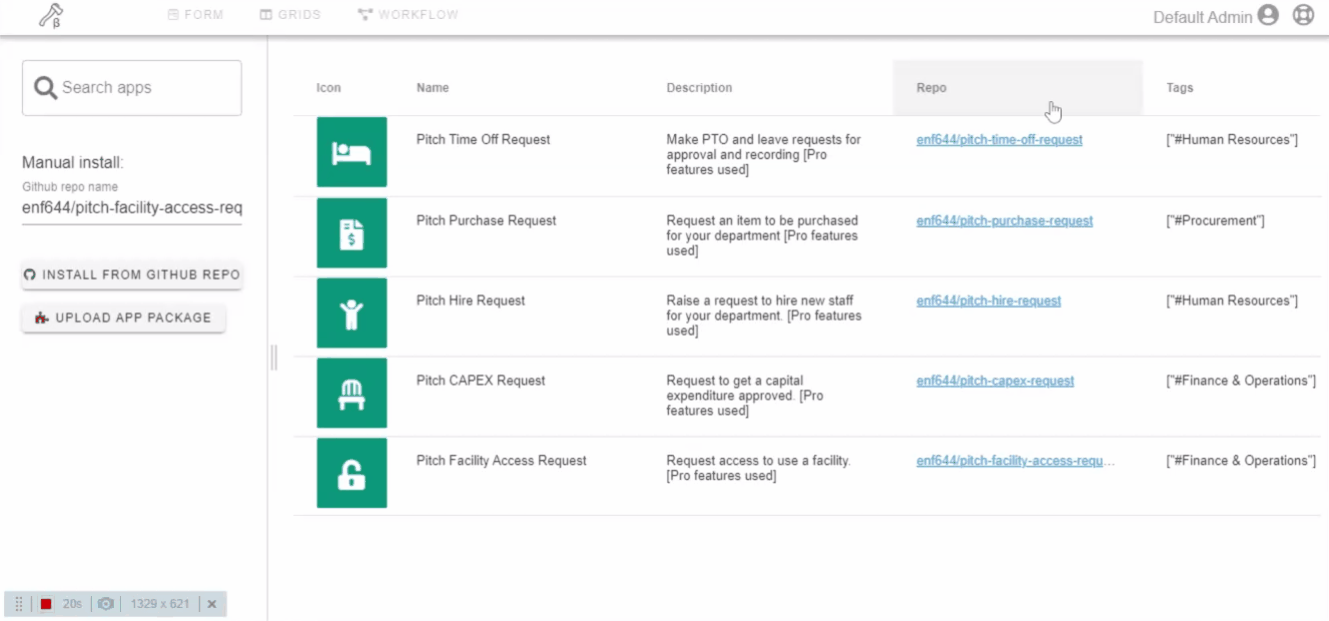
Applications can be installed either from GitHub repo or by uploading a package file. Also, the marketplace has a curated list of workflow applications that you can search and install.
Click on the application repo link to know more about workflow application. Read the description of forms and workflows. Check Github starts and issues. Check source code.
Beta Note: Reload page if the app folder does not appear after the install is complete.
"Manage users" page allows you to create and modify Ax users and groups.
The Ax user is defined only by email and a short name.
If you need more data about users (full name, department, etc), please create Ax Form for that and link it to the user.
Ax allows to run a custom python code while performing workflow actions. Form and user data is available inside the python code.
Here are some examples of how code can be used:
- Send emails with form data
- Check form values and abort actions if certain conditions are not met
- Calculate field values
- Perform actions on other records or even other forms
- Generate documents - pdf, word, excel
- Scrap information from external web-sites
- Execute custom SQL query on data
- Call external APIs
While performing the action code, you can use these predefined properties:
- ax.row.guid - GUID of the current record
- ax.row.<field_name> - For data on any field of the current record. Note that changing this property value will change value of the field.
- ax.arguments - Dict of arguments. Used if action is called from another action
- ax.stripe - See AxPaymentStripe documentation for more info
- ax.user_email - email of current user
- ax.user_guid - GUID of the current user
- ax.tom_label - Reference label of the current record
- ax.host - Host of Ax server. Taken from app.yaml
- ax.form_url - Url of the current record
- ax.form - Current forms data - name, database name, icon, fields list, grids list etc.
- ax.action = Data of currenlty performing action - name, code name, from state, to state etc.
- ax.paths.uploads - OS directory for file uploads
- ax.paths.tmp - OS directory for temporary file uploads
- ax.modal_guid = GUID of a modal window that was used to run action
Also, you can use these handy methods:
- ax.email - sends email (SMTP must be configured)
await ax.email(
to='info@ax-workflow.com',
text='Hello ax',
html='Hello <b>ax</b>',
subject='Sample email')- ax.sql - Execute custom SQL command
sql = 'UPDATE "Stock" SET "axState"=\'Confirmed\' WHERE "sourceCatalog"=:load_guid'
params = {"load_guid": ax.row.guid}
ax.sql(sql, params)- ax.print - Async action that opens a terminal window and shows a message to user. Useful for debugging and for long-lasting actions. If your action takes 5 minutes to execute, you can use ax.print to notify the user on progress.
ax.print('Hello world')- ax.do_action - Execute another Ax action
for idx, stock in enumerate(drafts):
ax.print(f'\n 📦 {idx}')
await ax.do_action(
form_db_name='Stock',
action_db_name='findWineAsync',
row_guid=stock['guid'],
modal_guid=ax.modal_guid,
values=None,
arguments={"aiohttp_session": session})- ax.add_action_job - Add scheduler job (Work in progress)
In addition, you can set these output properties:
- ax.message -String property. Outputs a message modal when action is finished.
- ax.error - String property. Outputs an error modal when action is finished.
- ax.abort - Boolean property. If set to true - the record will not change state after performing action. Useful when you want to check field values inside actions python code.
Ax allows you to construct custom SQL queries for grids. Press the "Query constructor" button on "Grids" page to open modal.
Here is the default value for a grid:
ax.query = f"""
SELECT {ax.db_fields}
FROM "{ax.db_table}";
"""As you can see, it is a python code that is executed before SQL query.
you can use these predefined properties:
- ax.db_fields - String that contains all grid fields. Used in the default SQL query.
- ax.db_table - Grid database name. Same as a database table.
- ax.arguments - Dict of arguments. Used if when the grid is used as web-component.
- ax.user_email - email of current user
- ax.user_guid - GUID of the current user
- ax.form - Current forms data - name, database name, icon, fields list, grids list etc.
- ax.grid - Data of the current grid.
Example usage:
If you want a grid that shows only records created by current User, you have to use an Author field and this grid query:
ax.query = f"""
SELECT {ax.db_fields}
FROM "{ax.db_table}"
WHERE "author"='{ax.user_email}';
"""Sometimes you want to give user permissions based on values of the record. (Example - only the author can modify the record) For this purpose, you can create a dynamic role.
The dynamic role is a custom python code that is executed before displaying the form.
WARNING: These roles are working only for form view. Not working for grids.
The default code for dynamic role is:
ax.result = False
if(ax.row.some_field == ax.user_email):
ax.result = True- ax.result - Is a boolean output property that is used to determine if the current user fits dynamic role.
These pre-defined properties are available:
- ax.row.guid - GUID of the current record
- ax.row.<field_name> - For data on any field of the current record. Note that changing this property value will change the value of the field.
- ax.user_email - email of current user
- ax.user_guid - GUID of the current user
- ax.host - Host of Ax server. Taken from app.yaml
You can configure Ax by editing app.yaml file at the installation folder.
To determine folder location run pip command:
pip show ax
All available settings are already present in the app.yaml file but are commented. Here are the list of what you can configure:
- Logging settings - Set log level. Set a logfile name if you want to save logs to file. Set directory if you want to save logs to specific place.
- Internalization settings - Set timezone and language (Only English is available at a time)
- Sanic server settings - Set host and port of web-server. Set number of workers. The number of workers cant be bigger than your CPU cores. Only 1 worker available for MS Windows machines
- Database settings - By default Ax uses SQLite database. The database file is ax_sqlite.db which is located in the installation folder. For better performance, Ax can use the PostgreSQL database.
- Upload settings - Set custom upload folder.
- Email settings - Set SMTP settings to be used
- SSL Settings - SSL settings for Sanic web-server
- Field types settings - Currently there are only Stripe payment field settings
We recommend running ax using Monit daemon. It will restart ax if it freezes of crashes (Ax is in Beta, remember?)
Check guid for more info:
Ax application is a collection of forms and pages that can be installed on any Ax instance using a package zip file or GitHub repo. (The zip file is actually just an archive of a repo).
Simple steps to create an app:
- Create a form folder
- Group all forms that you want to save inside created folder
- Group all pages that you want to save under one root page
- Open folder setting and click "Create app"
You will be asked:
- Code name - the name of archive
- Application root page - the code name of the page you used to group all application pages.
- Create Readme.md from root page - Set this option if your want to generate readme.md file. Useful for publishing to GitHub.
- Save form data? - Set this option if you want to save the data of your forms, not just structure.