Modular API
Content
- General information
- Installation and configuration
- Policies management
- Group management
- User management
- Audit service
- Modules installation
- First run
- Modular API schema
- Project information
1. General information
Modular API is a facade which allows to combine different services controls under one custom API/CLI service. A service is actually module. It includes a Compute part ( Lambda, EC2, EKS, AWS butch), it has an API(any), and this API has a CLI client. For interaction with Modular API you can use Modular CLI or any other suitable for you API-client like Postman, Insomnia, etc. Typically, a service uses the following elements:
- API: API Gateway, Lambda Function URL, Container exposed, AMQP
- Authentication: Custom JWT / Cognito
- Authorization: ABAC
- CLI: Thin client, descriptor for Modular-API
- Compute: Lambda, AWS Batch, EKS
- Runtimes: Python 3.8+, Java 11, NodeJS 18.16.0
- Persistence: AWS DynamoDB, MongoDB Atlas, AWS DocumentDB, AWS RDS, S3
The Modular-API includes interface descriptors(CLI Clients). A descriptor is a file
which specifies an entry point to the module. The Click Python library is used to
describe the interface. This information is parsed into a specific structure in the
Modular-API facade.
After that, the Modular-API puts its own features set atop of the API/module/response:
- Provides its own unified authentication mechanism.
- Provides its own unified ABAC. This allows to have multiple services managed in a unified way from a single entry point and with the same permissions settings
- Provides pre-validation of requests before the request is sent to the Module backend
- Provides centralized audit, logging and manages the temporary tokens retrieved during the client authentication on module`s backend
- Has its own database and CLI that is not available from outside.
2. Installation and Configuration
Installation
The installation of Modular-API assumed that you have Python3.9 and pip installed.
Use the following links to install the tools in case they are not installed.
NOTE: Due to the best Python practices, it is highly recommended to use virtual environment to protect project against dependency breakage.
Creating Virtual Environments Guide
- Create:
python -m venv modular_api_venv - Activate (Linux):
source modular_api_venv/bin/activate
Activate (Windows):source modular_api_venv/Scripts/activate - Installation:
pip install setup.py
Configuration
The API wrapper requires some configurations. Configuration file is modular_api\startup_config.json
The content template is placed below:
{
"swagger-ui": {
"path": '$string',
"enable": '$boolean'
},
"host": '$string',
"port": '$integer',
"secret_passphrase": '$string',
"mode": '$string',
"url_prefix": '$string',
"minimal_allowed_cli_version": '$string'
}- Key: Value
- "swagger-ui"
- "path": path where Swagger is available, for example: "/swagger"
- "enable": "true/false", if "true" allows to run Swagger
- "host": host to run the server, for example - "127.0.0.1"
- "port": port to run the server, for example - 8085
- "secret_passphrase": secret passphrase used to secure JWT, password. Also used in policy, group, user items for hash sum calculation
- "mode": mode in which the tool will be run. Allowed values: "saas", "onprem" or "private". If "onprem/private" mode enabled - local file-like database will be used. If "saas" mode enabled - AWS DynamoDB will be used
- "url_prefix": modifying the URL pointing to Swagger-API definition - $url_prefix/$path. Can be an empty string
- "minimal_allowed_cli_version": check Modular-CLI version, for example - "1.1". If Modular-CLI version lower than specified in property - warning message will be shown to the user
- "swagger-ui"
3. Policies management
Available commands:
- Add new policy
modular policy add --policy $POLICY_NAME --policy_path $PATH_TO_POLICY_FILE.JSON - Update existing policy
modular policy update --policy $POLICY_NAME --policy_path $PATH_TO_POLICY_FILE.JSON - Delete existing policy
modular policy delete --policy $POLICY_NAME - Describe all policies
modular policy describe- if flag
--expandspecified, then full description for all policies will be shown. Has no effect and always 'True' if '--policy' parameter passed - if parameter
--policyspecified, then full policy content will be shown
- if flag
Policy template
[
{
"Effect": <string>'...',
"Module": <string>'...',
"Resources": <list> [
<string>'statement_1',
<string>'statement_2',
'...',
<string>'statement_N'
]
}
]Policy rules
- Deny effect has more priority than Allow.
- If some command/groups/subgroups/modules are not in user policy(ies) then they will not be available to use
Property "Effect"
- Required. Possible values: "Allow" or "Deny"
Property "Module" syntax
- Required.
- For m3admin root(src) module use "m3admin" name instead of "/"
- You can use
*symbol in "Module" property. This will mean that "Effect" is being applied for all current modules installed in Modular-API - Module name is equal to property "mount_point" in "api_module.json" file in each
Modular-API module, but use it without first symbol
/
Property "Resources", syntax for statements
- Required and property can not be empty
- "*" -> apply "Effect" for entire module
- "$command" -> apply "Effect" for a single command in module
- "$group:*" -> apply "Effect" for group and it`s commands/subgroups
- "$group:$command" -> apply "Effect" for a single command in group
- "$group/$subgroup:*" -> apply "Effect" for subgroup and it`s commands
- "$group/$subgroup:command" -> apply "Effect" for a single command in subgroup
4. Group management
Available commands:
- Add new group with policy
modular group add --group $GROUP_NAME --policy $POLICY_NAME
Assuming that policy already created - Add new policy to existing group
modular group add_policy --group $GROUP_NAME --policy $POLICY_NAME
Assuming that policy and group already exist - Delete policy from group
modular group delete_policy --group $GROUP_NAME --policy $POLICY_NAME - Describe group and attached policy(ies)
modular group describe --group $GROUP_NAME - Delete group
modular group delete --group $GROUP_NAME
5. User management
Available commands:
- Add new user
Assuming that group already created
modular user add --username $USER_NAME --group $GROUP_NAME- if
--passwordpassed, then your custom password will be saved for user item.
If--passwordparameter not specified then autogenerated password will be provided.
Please NOTE: there is no mechanism to retrieve it again if it lost, just reset and set a new password.
- if
- Delete existing user:
modular user delete --username $USER_NAME - Block existing user access without deletion
modular user block --username $USER_NAME --reason $INFO_WHY_USER_IN_BLACK_LIST - Restore blocked user access
modular user unblock --username $USER_NAME --reason $INFO_WHY_USER_BACK_TO_WHITE_LIST - Restore lost password for user
modular user change_password --username $USER_NAME --password $NEW_PASSWORD - Attach group(s) to user
modular user add_to_group --username $USER_NAME --group $GROUP_1 --group $GROUP_2 ... --group $GROUP_N - Remove group(s) from user
modular user remove_from_group --username $USER_NAME --group $GROUP_1 --group $GROUP_2 ... --group $GROUP_N - Describe users information
modular user describe- if
--usernameparameter passed, then particular user will be described
- if
Commands to restrict some parameters values in allowed for user commands:
- Set parameter name and its value(s)
modular user set_meta_attribute --username $USER_NAME --key $PARAMETER_FULL_NAME --value $VALUE_1 --value $VALUE_2 ... --value $VALUE_N
For example: modular user set_meta_attribute --username user --key key1 --value value1 So,userallowed to execute$module_name $command_name --key1 value2, but$module_name $command_name --key1 value1command is not allowed - Update parameter value(s)
modular user update_meta_attribute --username $USER_NAME --key $PARAMETER_FULL_NAME --value $VALUE_1 --value $VALUE_2 ... --value $VALUE_N - Delete parameter name(s)
modular user delete_meta_attribute --username $USER_NAME --key $PARAMETER_FULL_NAME_1 --key $PARAMETER_FULL_NAME_2 ... --key $PARAMETER_FULL_NAME_N - Erase all restricted parameters from user
modular user reset_meta --username $USER_NAME - Describe restricted parameters for user
modular user get_meta --username $USER_NAME
6. Audit service
All successful results of modular commands execution will be saved to ModularAudit collection. For
describing audit content use command:
modular audit - describes all audit records for the last 7 days from the current date. Also, you can
use some filters to expand time range or filter records by group/commands:
--from_date: Filter by date from which records are displayed. Format yyyy-mm-dd--to_date: Filter by date until which records are displayed. Format yyyy-mm-dd--group: Filter by group name--command: Filter by command name--limit: Number of records that will be shown. Default value is 10--invalid: Flag to show only invalid audit events
Please NOTE: "describe" like commands are not recorded into ModularAudit
7. Modules installation
To install new module into Modular-API check the next steps:
- Ensure that component installation directory has file
api_module.jsonwith the next content:
{
"module_name": "$MODULE_NAME",
"cli_path": "$PATH_TO_CLI_MAIN_GROUP",
"mount_point": "/$MODULE_NAME" // "/entry point for module"
}-
Ensure that component's
setup.pyfile is in the same directory asapi_module.jsonfile -
Component files that contain commands have the next naming:
groupname.pyfor group with commandsgroupname_subgroupname.pyfor subgroup commands in group
"_" symbol in filename means that first part of name is group name, second one - subgroup name
-
Execute command
modular install --module_path $PATH_TO_SETUP.PYPlease note: if module to be installed has dependency from other module(s)api_module.jsonfile can be extended with the optional property "dependencies"":
{
"dependencies": [
{
"module_name": "$MODULE_NAME_DEPENDENT_FROM",
"min_version": "$MIN_ALLOWED_VERSION_OF_DEPENDED_MODULE"
},
...
]
}During installation/uninstallation process all mentioned dependencies will be checked automatically
8. First run
Check list before start:
startup_config.jsonfile properly configuredstartup_config.jsonmodes:- if "mode" property is "saas" then AWS DynamoDB will be used as DB. You
should set the following environment variables:
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
- AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
- AWS_REGION
- if "mode" property is "onprem" then local file-based DB will be in usage. By
default, all IO operations with DB use the next storage path:
~user-home-dir\.modular_api\databases. You can change this path by setting environment variable, key -MODULAR_LOCAL_DB_PATHand value is the path to the custom directory
- if "mode" property is "saas" then AWS DynamoDB will be used as DB. You
should set the following environment variables:
- at least one policy created and attached to the group
- user created and group with policy attached to the user
- at least one component installed in Modular-API
Go to directory modular_api/ and run command python index.py
Bottle v0.12.19 server starting up (using WSGIRefServer())...
Listening on http://127.0.0.1:8085/
Hit Ctrl-C to quit.
Now you can send requests to Modular-API via Modular-CLI or any other API-client like Postman, Insomnia, etc.
If you use Modular-CLI, please see README file.
If you use another API client (for example, Postman):
- Login and get API meta
Path: Modular-API server http
Resource: "login"
Authorization type: "Basic auth"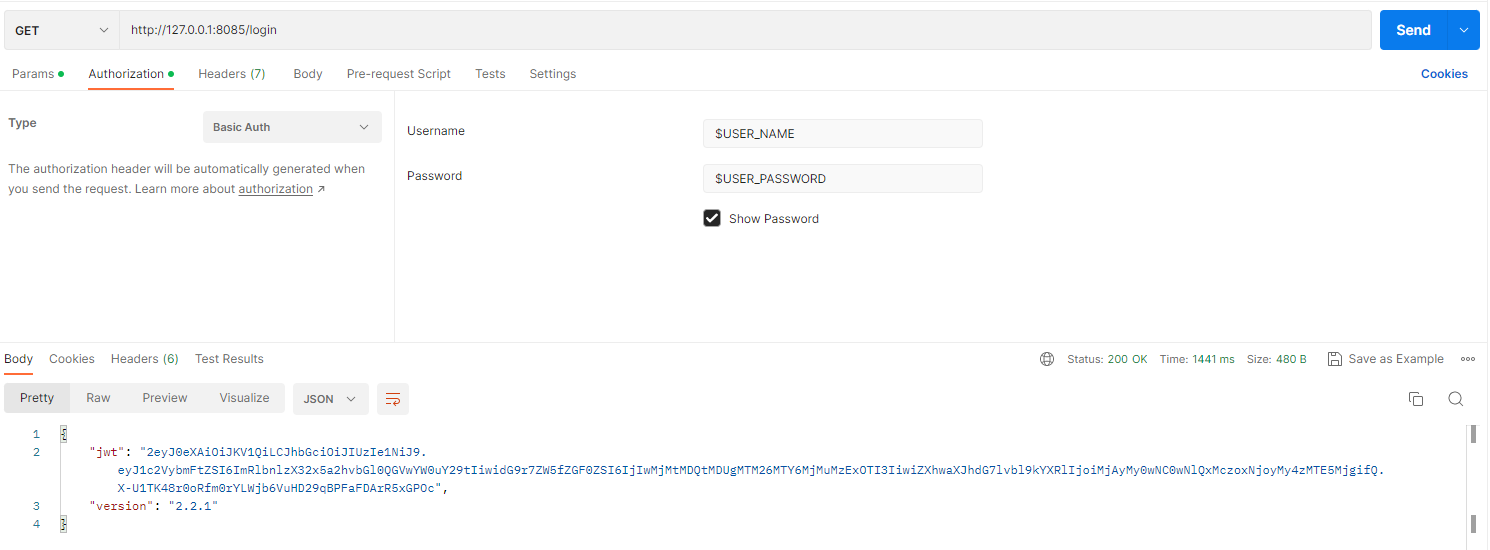
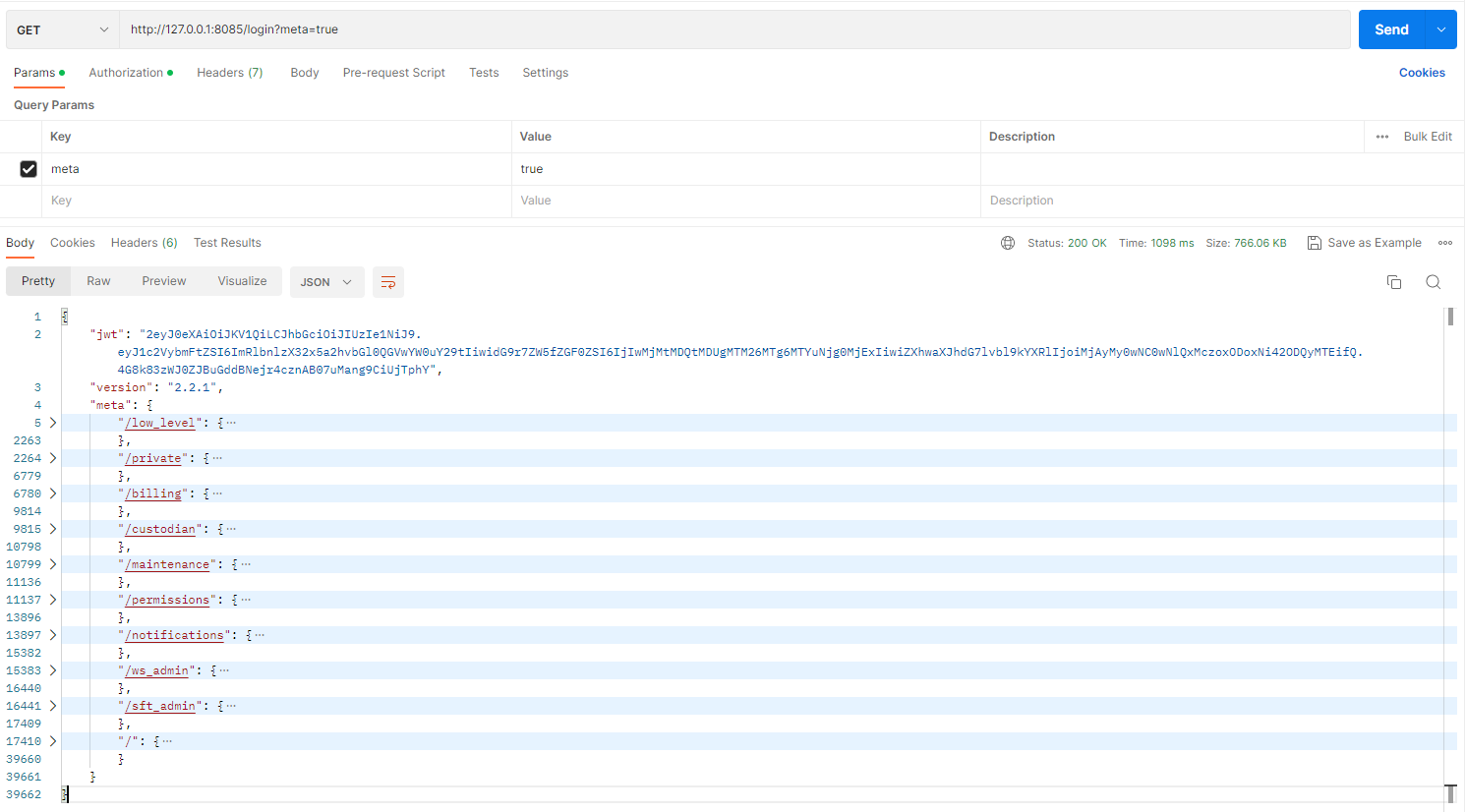
For retrieving commands meta pass parameter meta, value is true
- Use API meta to find desired command and create new request for command execution
Path :meta>$module_name>body>$command_name>body>route>path
Method :meta>$module_name>body>$command_name>body>route>methodAuthorization : "Basic auth" with the username and password or "Bearer Token" with the token fromjwtproperty in API meta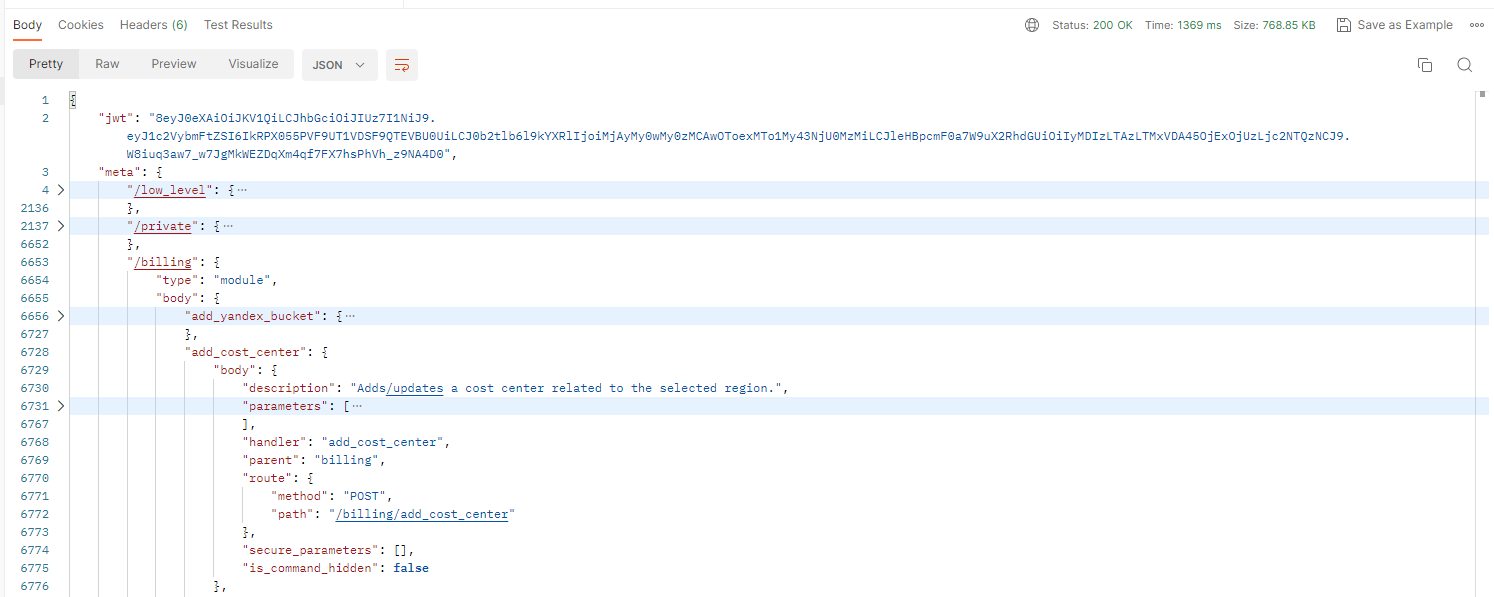
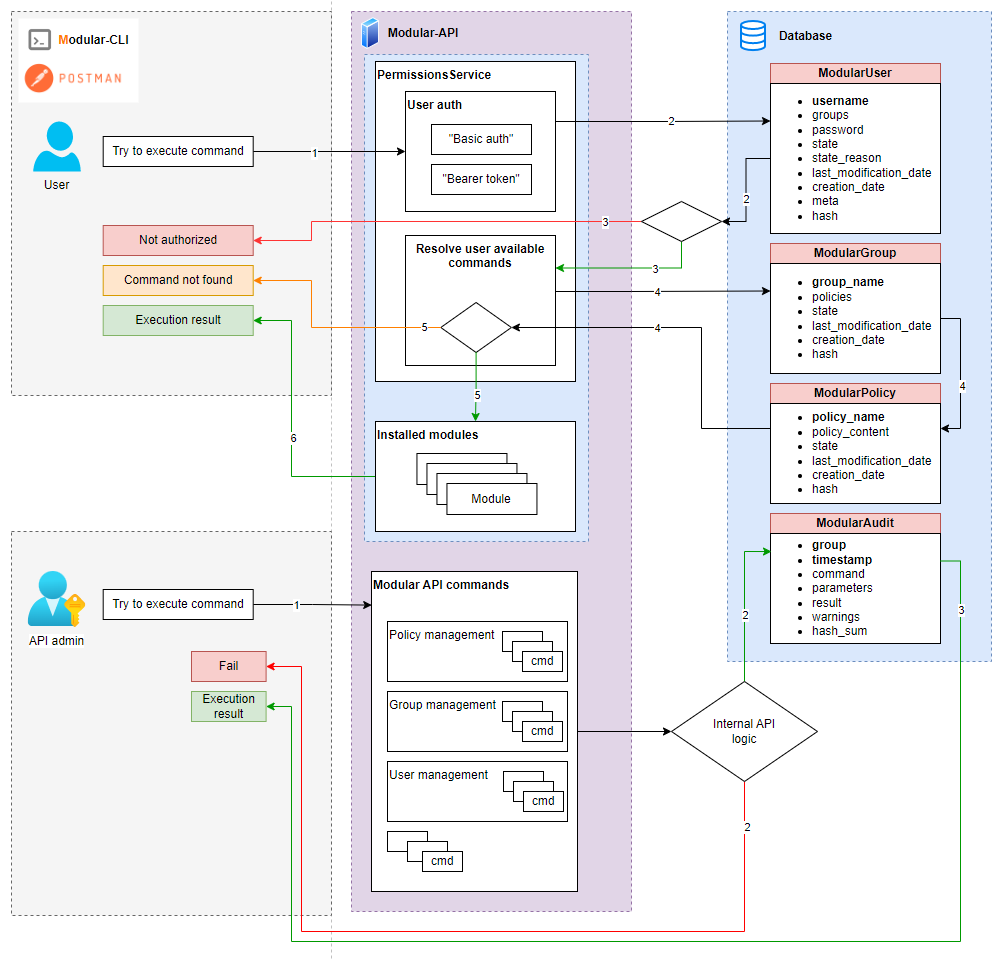
9. Modular API schema
Agenda
For "User":
- Execute command
- Check user in DB
- Resolve commands available for user or exit if user not found
- Get user's group, then get user's policy from group. Check command in policy
- Try to execute command or exit
- Execution result
For "API admin":
- Execute command
- Save execution result to ModularAudit collection if execution successful, else exit without saving
- Return execution result
10. Project Information
Source Code: https://git.epam.com/epmc-eoos/m3-modular-admin/
Documentation: https://git.epam.com/epmc-eoos/m3-modular-admin/-/blob/master/README.md
Changelog: https://git.epam.com/epmc-eoos/m3-modular-admin/-/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md
Supported Python Version: 3.9
Support: Oleksandr_Onsha@epam.com